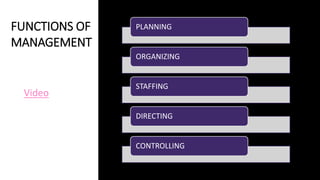
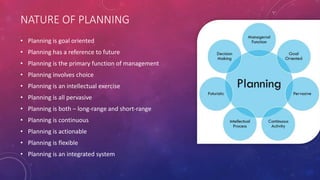
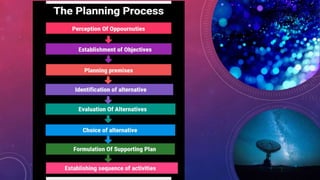
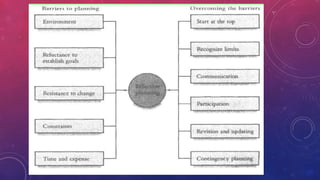
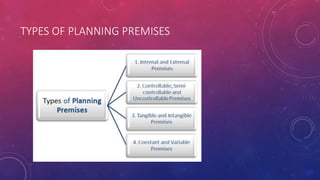
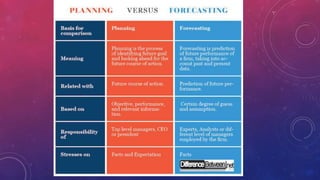
This document discusses the key aspects of planning as a management function. It defines planning as determining objectives and methods to achieve goals. The document outlines the nature, scope, objectives and significance of planning. It discusses the types of plans including operational, tactical, and strategic plans. The document also covers planning principles, premises, forecasting, barriers to planning, and how to overcome those barriers. Planning is presented as the primary management function that sets goals and bridges gaps between current and desired future states.