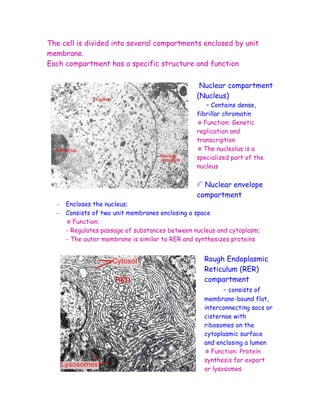
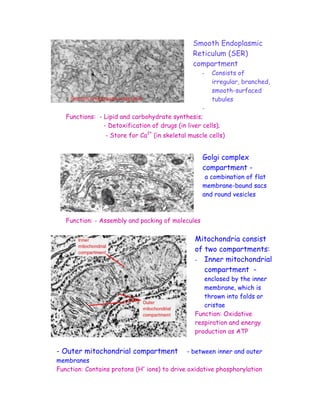
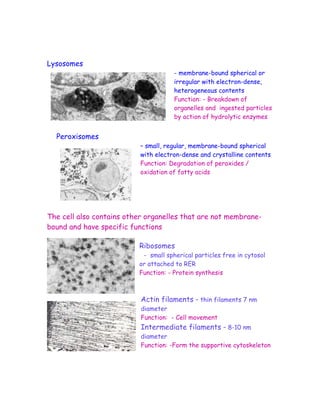
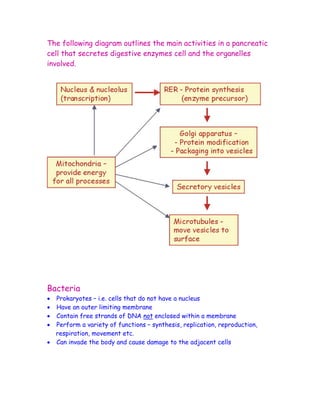
The document discusses the compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells. It explains that eukaryotic cells are divided into membrane-bound compartments, each with a specific structure and function. It provides examples of key organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Compartmentalization allows cells to perform specialized functions and accommodate larger sizes. While prokaryotes like bacteria are not compartmentalized, eukaryotes compartmentalize to increase surface area and efficiency.