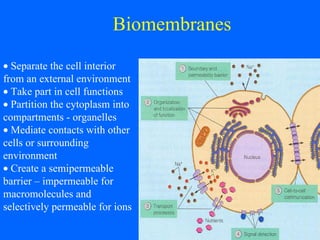
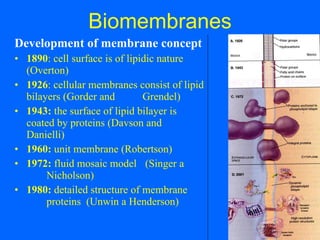
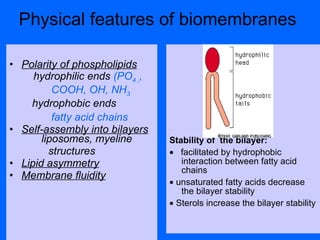
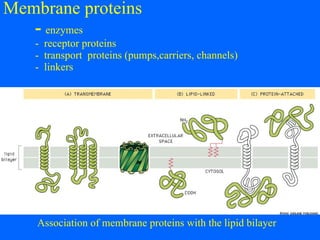
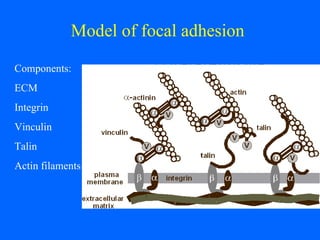
Biomembranes separate cell interiors from the external environment, participate in cell functions, and mediate cell-cell and cell-environment interactions. Biomembranes are composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded and peripheral proteins. The phospholipid bilayer forms a semipermeable barrier through self-assembly of phospholipid molecules with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads. Membrane proteins have hydrophobic regions that extend through the bilayer and hydrophilic regions exposed to the aqueous environment on either side. Additional structures like the glycocalyx, extracellular matrix, basal lamina, and focal adhesions further facilitate cellular interactions and processes like migration.