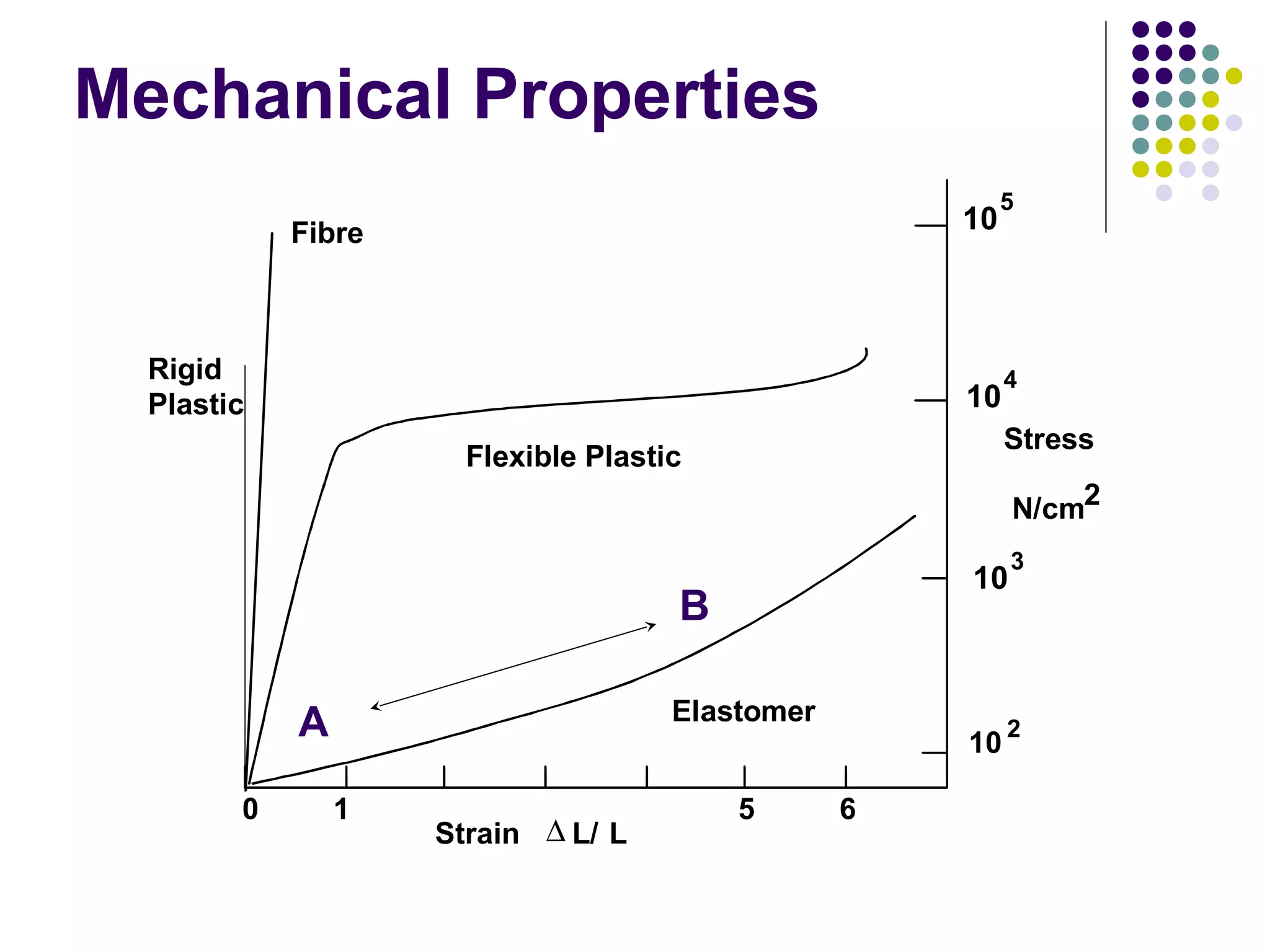
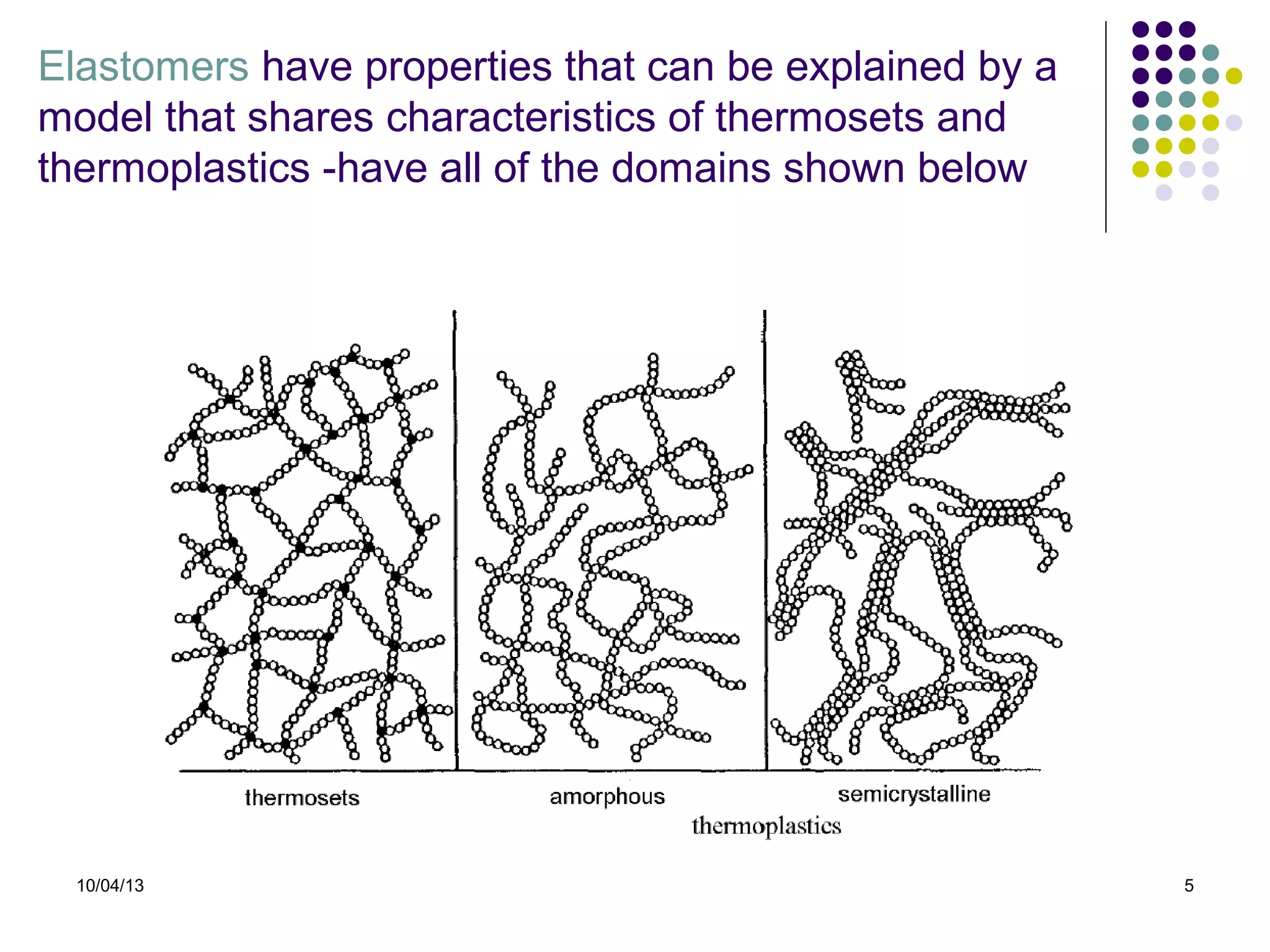
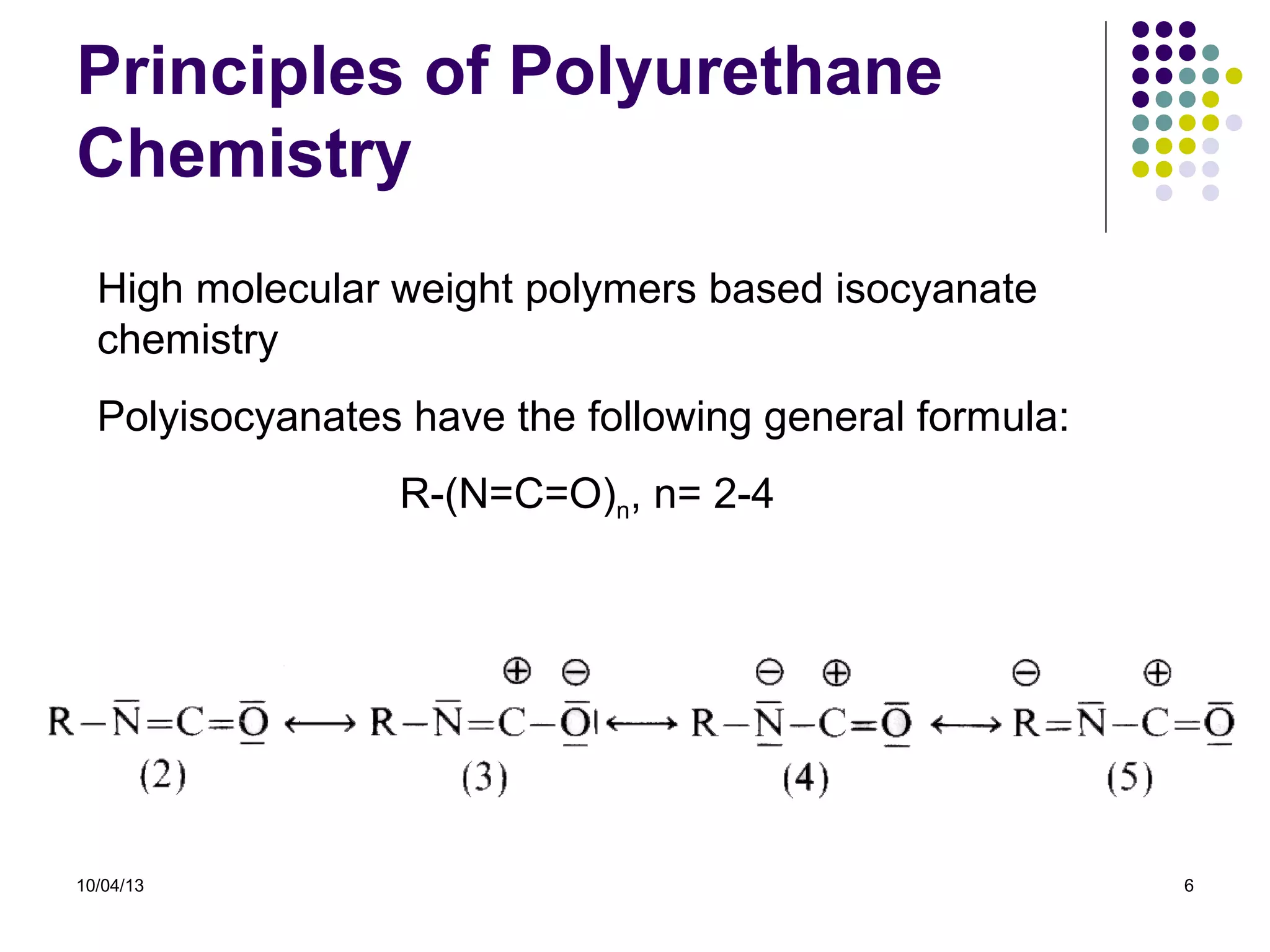
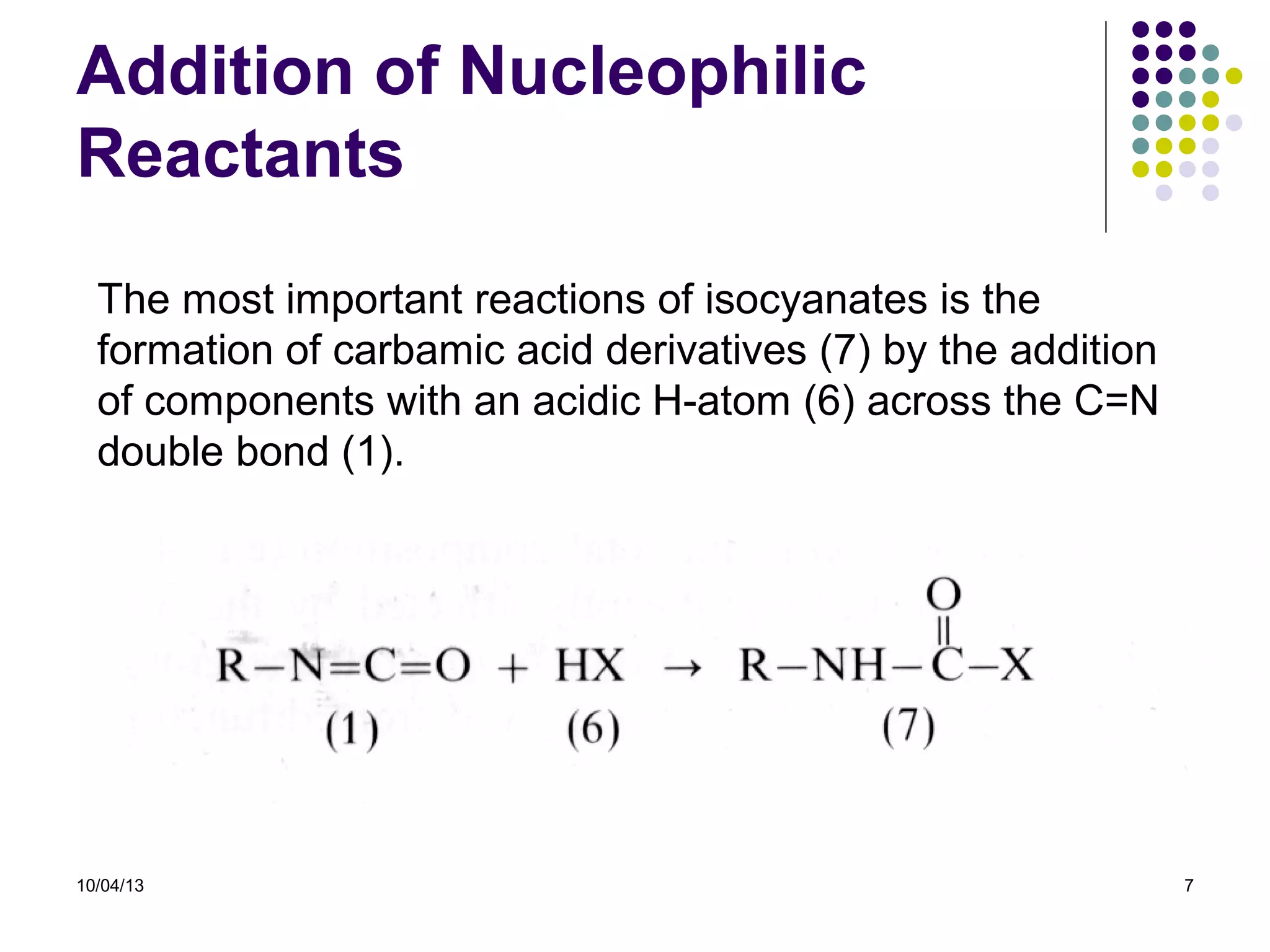
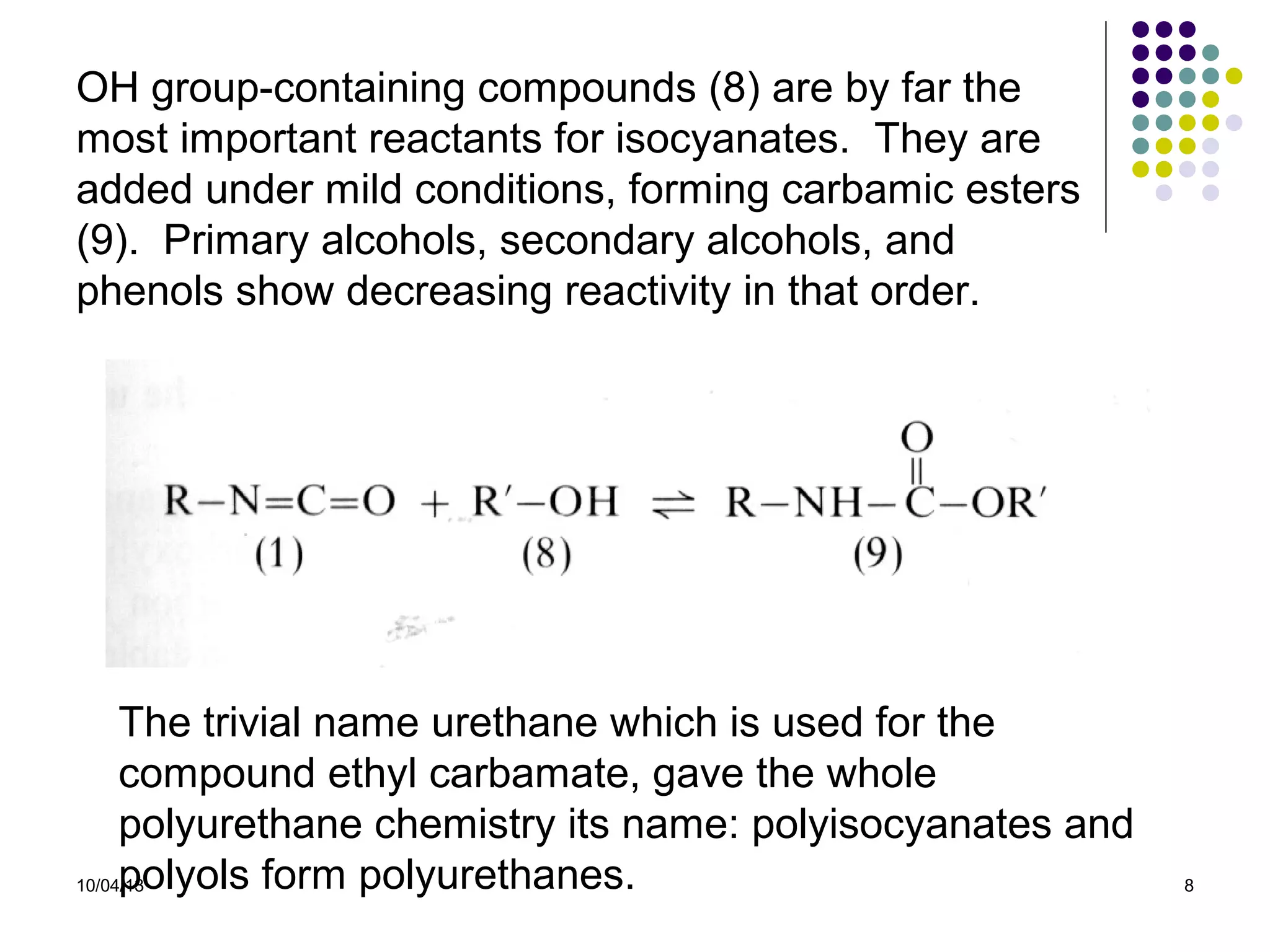
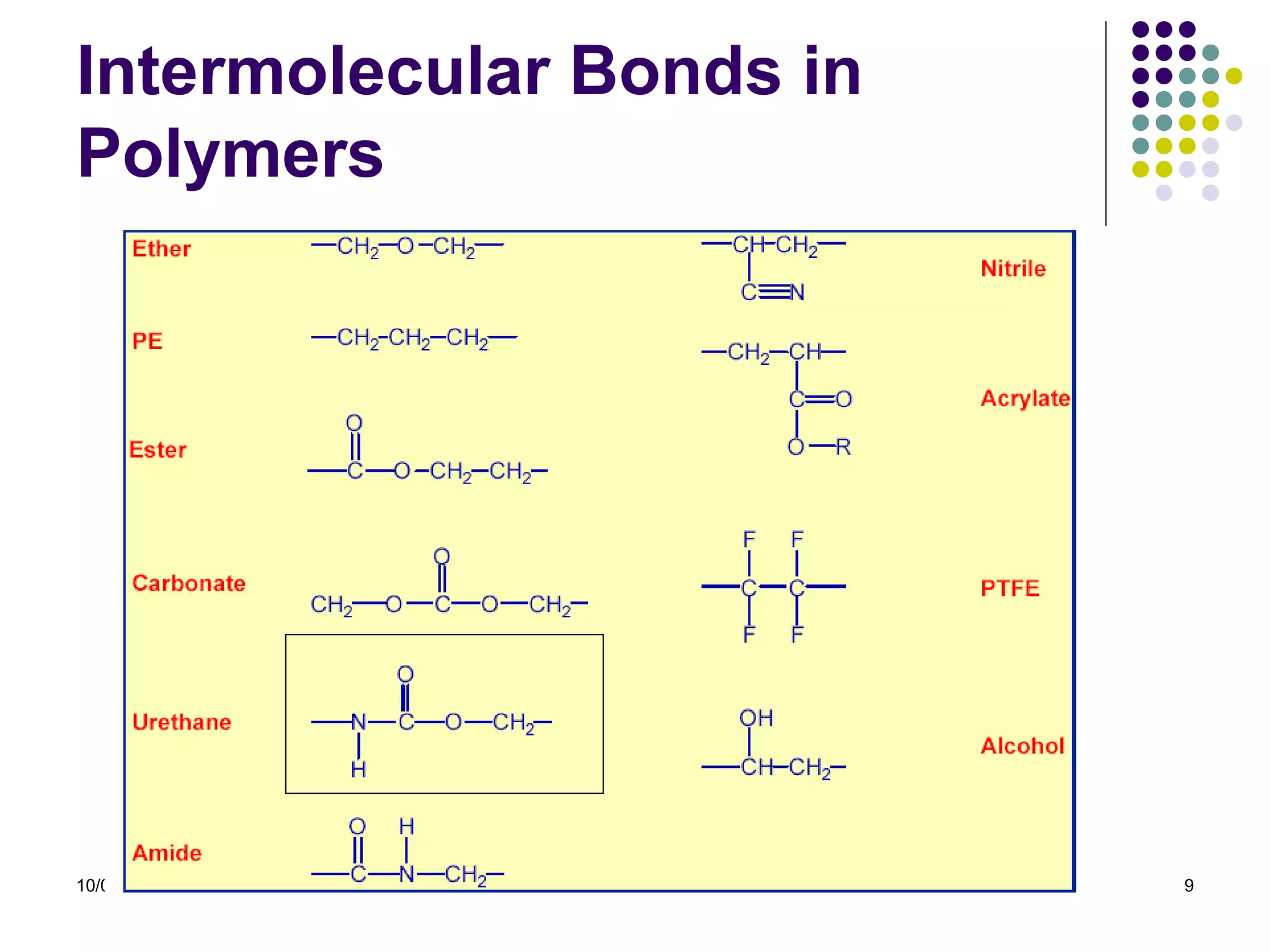
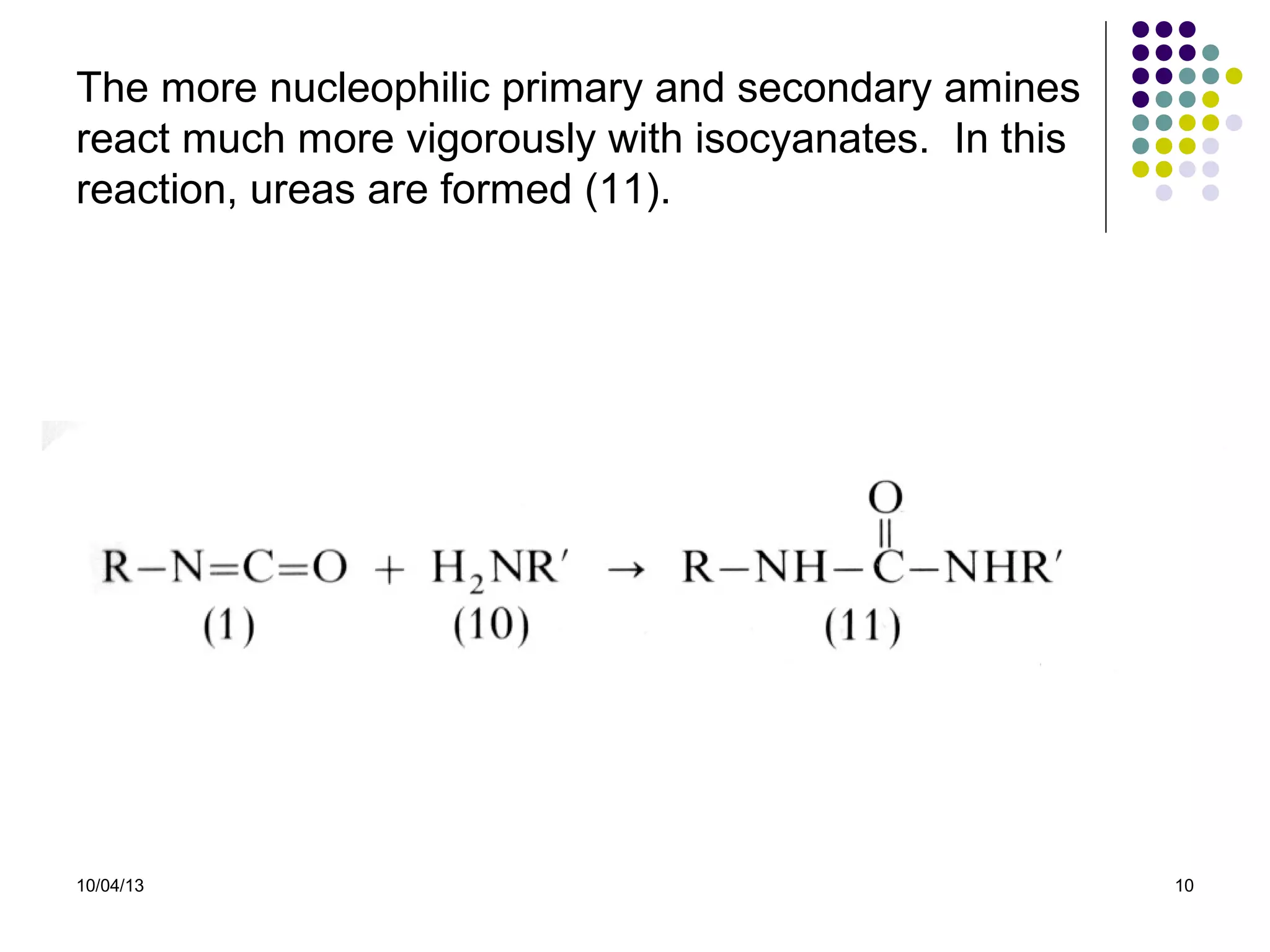
Elastomers are materials that can reversibly change length when a load is applied and return to their original dimensions once the load is removed. They include both natural and synthetic rubbers. Elastomers have properties that can be explained by a model sharing aspects of thermosets and thermoplastics, with reversible domains. Polyurethanes are high molecular weight polymers formed from reactions of polyisocyanates with polyols and chain extenders, producing urethane and urea bonds in the polymer structure. The interactions between hard and soft domains in the polyurethane structure influence the resulting mechanical properties.