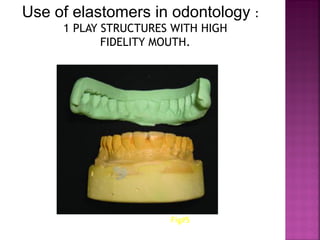
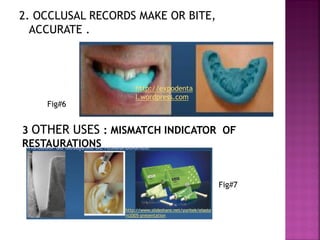
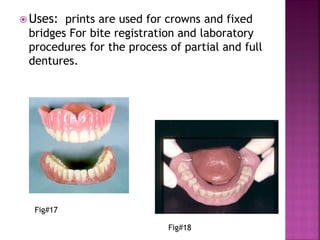
Elastomers (polysiloxanes) are organic polymer materials that have the ability to stretch, deform, and ultimately bear tension. There are four main types of elastomeric impression materials: 1) poly sulfide, 2) silicone condensation polymerization, 3) addition polymerization silicone, and 4) polyether. Condensation silicones are composed of polydimethylsiloxane, ethyl orthosilicate, silica filler, and a tin octoate catalyst. They polymerize through a condensation reaction between the siloxane and silicate. Condensation silicones are widely used for dental impressions and bite registrations due to their elastic recovery, fluency, and stability over