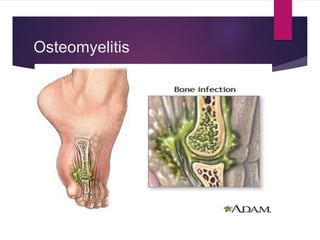
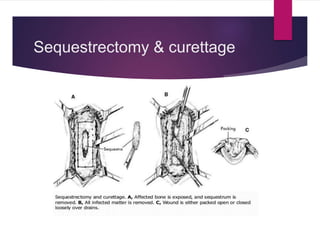
Osteomyelitis is an infection of bone tissue that is commonly caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. It can be classified based on duration of symptoms, mechanism of infection such as hematogenous or contiguous spread, or type of host response. Common symptoms in children include swelling, tenderness, and irritability on movement. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging like MRI or bone scan, and tests like bloodwork. Treatment involves antibiotics to treat the infection as well as possible surgical debridement or bone grafting. Nursing care focuses on pain management, preventing infection recurrence, and educating on treatment compliance.