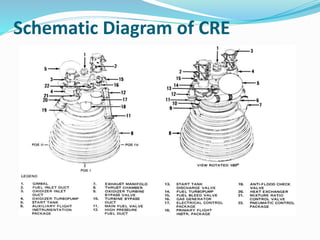
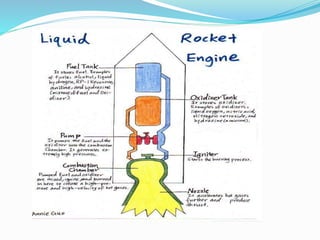
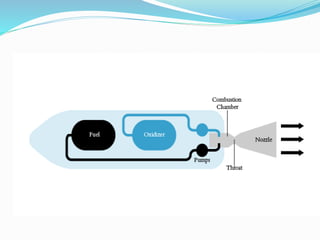
Cryogenic rocket engines use liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants that are stored at extremely low cryogenic temperatures. They provide several advantages like high energy density and clean, non-toxic exhaust but also have challenges like boil off rates and leakage of the reactive cryogenic fuels. The document traces the history of cryogenic engines from early US and Soviet designs to current engines used by various countries. It describes the key components and working of cryogenic engines and concludes by discussing future engine technologies still under development.





![Cont…….
(AMERICAN) - ATLAS V
(Russian) - N 1 [1969]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryogenicrocketengine-150222063740-conversion-gate01/85/Cryogenic-rocket-engine-7-320.jpg)