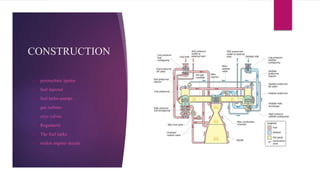
Cryogenic rocket engines use cryogenic fuels like liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen that must be stored at extremely low temperatures to remain liquid. They have several advantages like high thrust and specific impulse but also disadvantages like complexity and cost. Common cryogenic engines include the RL-10, CE 7.5, and CE-20 which use liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen and have specifications like thrust levels and specific impulse. Cryogenic engines require specialized construction elements to handle the extreme cold like fuel injectors, turbo-pumps, valves and tanks.