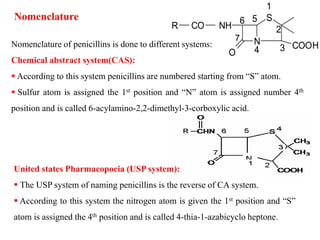
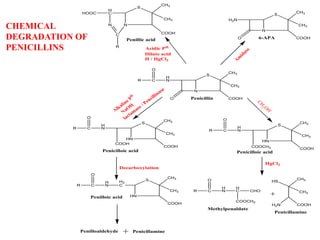
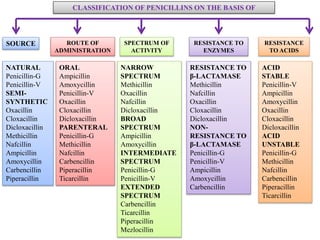
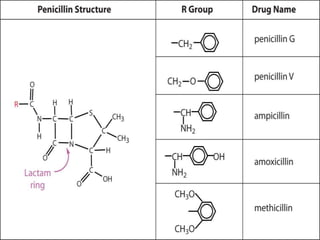
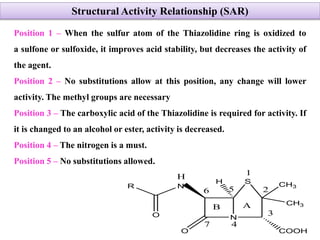
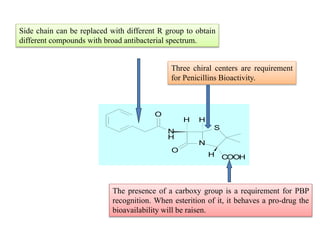
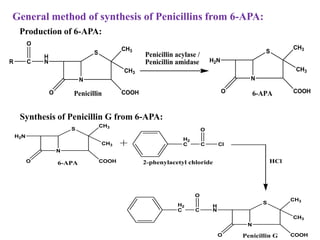
Penicillins are a group of antibiotics derived from the Penicillium mold. Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1928 after noticing bacteria-killing properties of the mold. Penicillins work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis through binding to penicillin-binding proteins. They are classified based on source, administration route, and spectrum of activity. Common side effects include diarrhea and rash. Therapeutic uses include pneumonia, meningitis, and other bacterial infections.