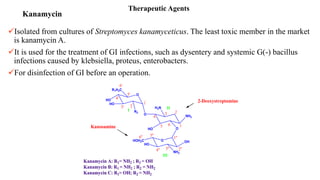
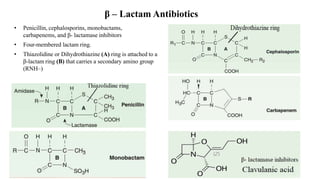
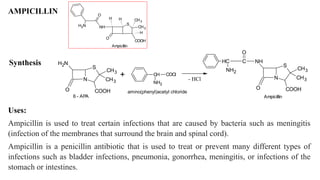
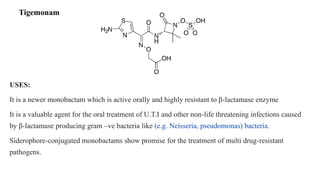
Antibiotics are chemical compounds produced by microorganisms that kill or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms at low concentrations. They are classified based on their chemical structure and include beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephalosporins, and monobactams. Penicillins work by inhibiting the bacterial enzyme transpeptidase which is involved in cell wall synthesis, becoming covalently linked to the enzyme's active site and causing irreversible inhibition. Common penicillins include penicillin G, penicillin V, ampicillin, amoxicillin, and methicillin.












































































































![CHLORAMPHENICOL
MOA:
It inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by interfering with transfer of the elongating peptide chain
to the newly attached aminoacyl-tRNA at the ribosomal mRNA complex.
It is specifically attaches to the 50S ribosome and thus may hinder the access of aminoacyl-
tRNA to the acceptor site for amino acid incorporation.
It also prevent peptide bond formation.
Oesophageal ulceration, dizziness, loss of hearing, Nausea, Vomiting etc.
ADR:
Aplastic anemia, Bone marrow suppression, Leukemia, Gray baby syndrome, Hypersensitivity
reactions, Neurotoxic reactions etc.
USES:
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.
This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a
vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, and typhoid fever.
O2N CH CH NH C CHCl 2
CH2OH
OH
O
2,2-dichloro-N-[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)ethyl]acetamide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-220410052354/85/Antibiotics-pptx-112-320.jpg)