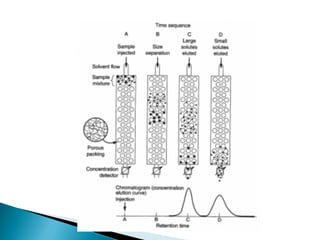
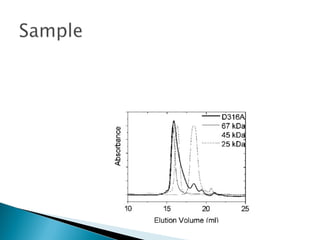
This document discusses gel filtration chromatography, also known as size exclusion chromatography. It separates biomolecules based on hydrodynamic size. Larger molecules pass through the pores of the stationary phase more slowly than smaller molecules. Applications include estimating molecular weight, purifying protein mixtures, and changing solution conditions like pH or salt concentration. Common stationary phases include cross-linked agarose or dextran beads packed into a glass column.