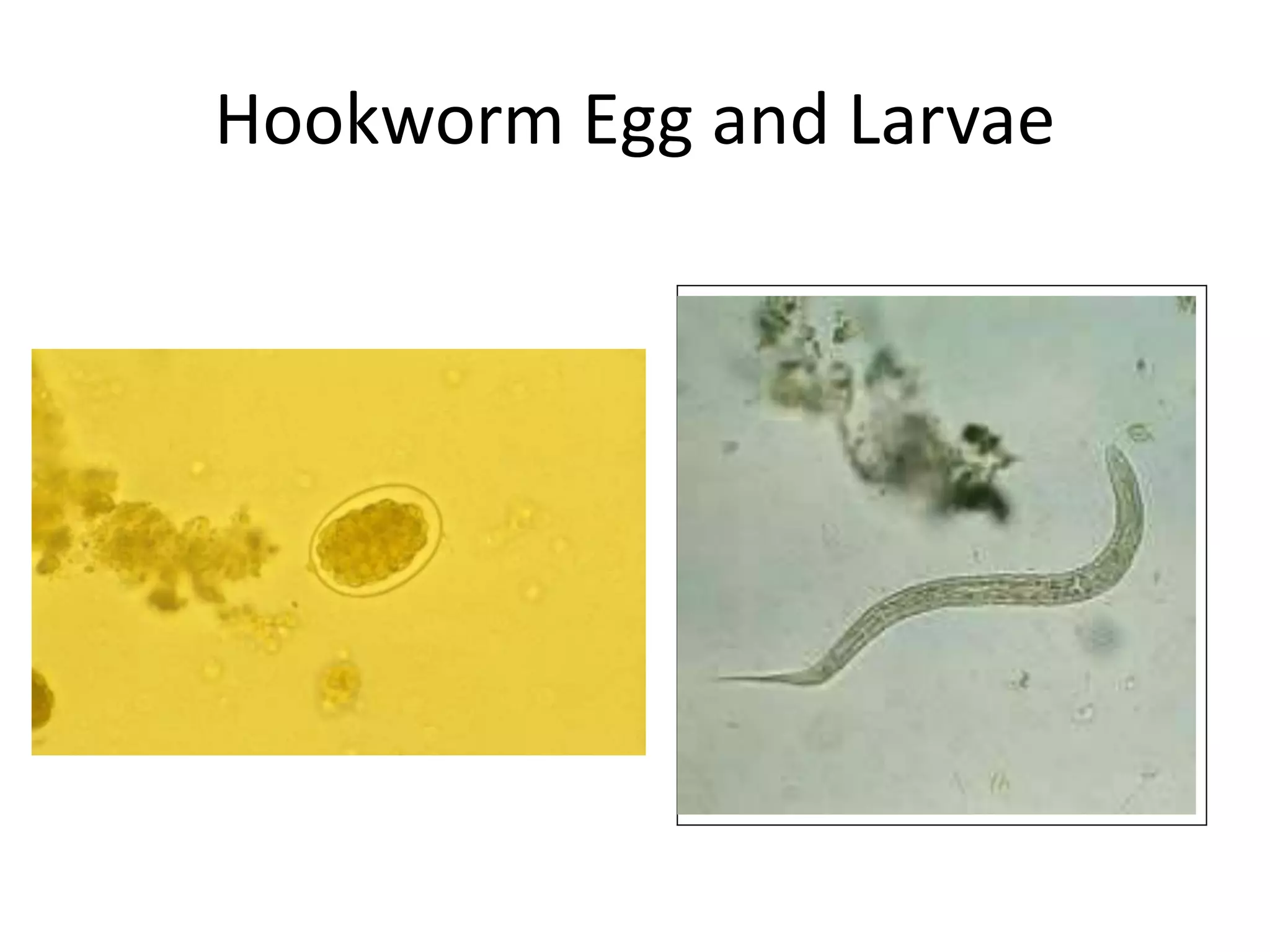
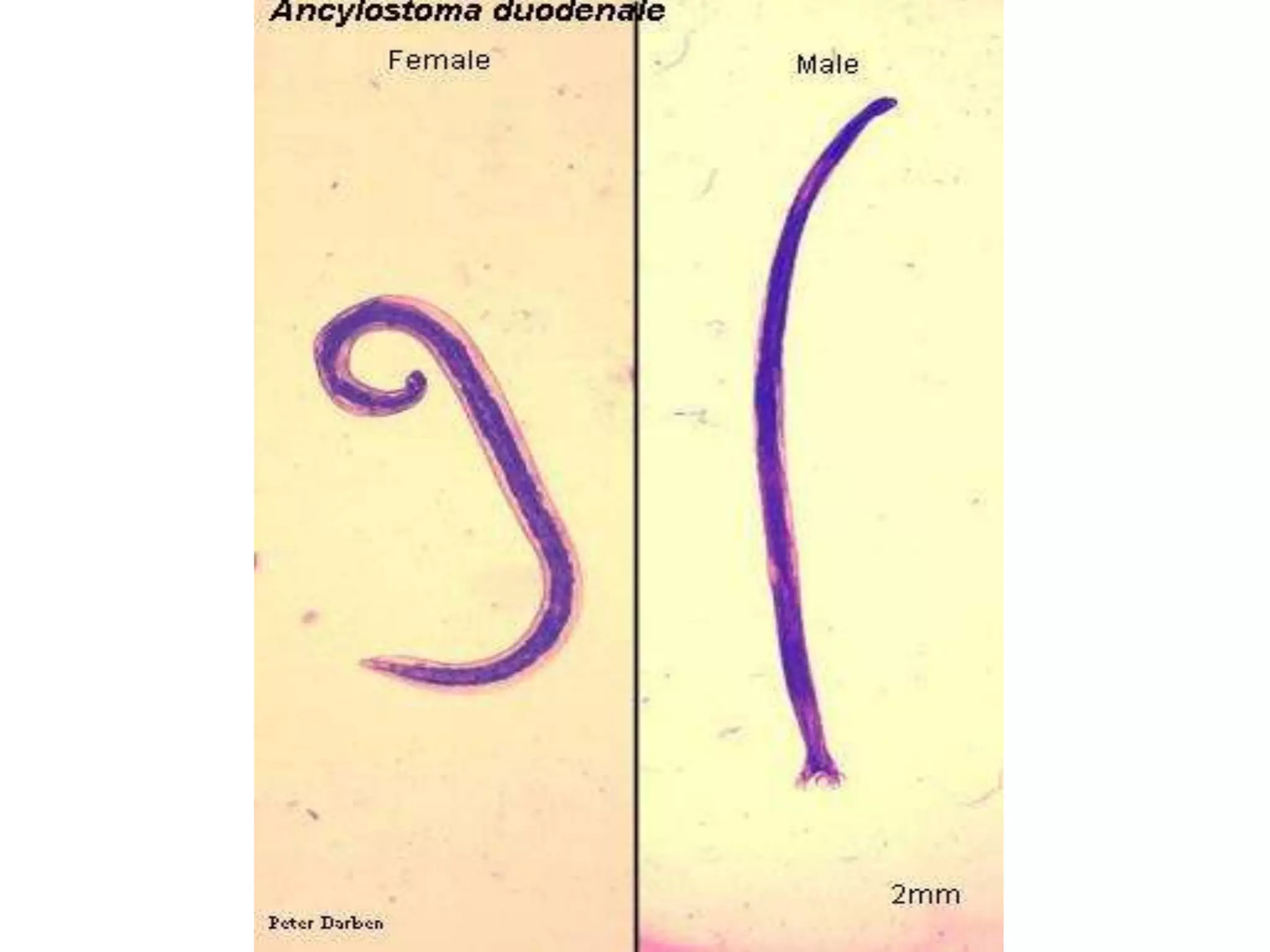
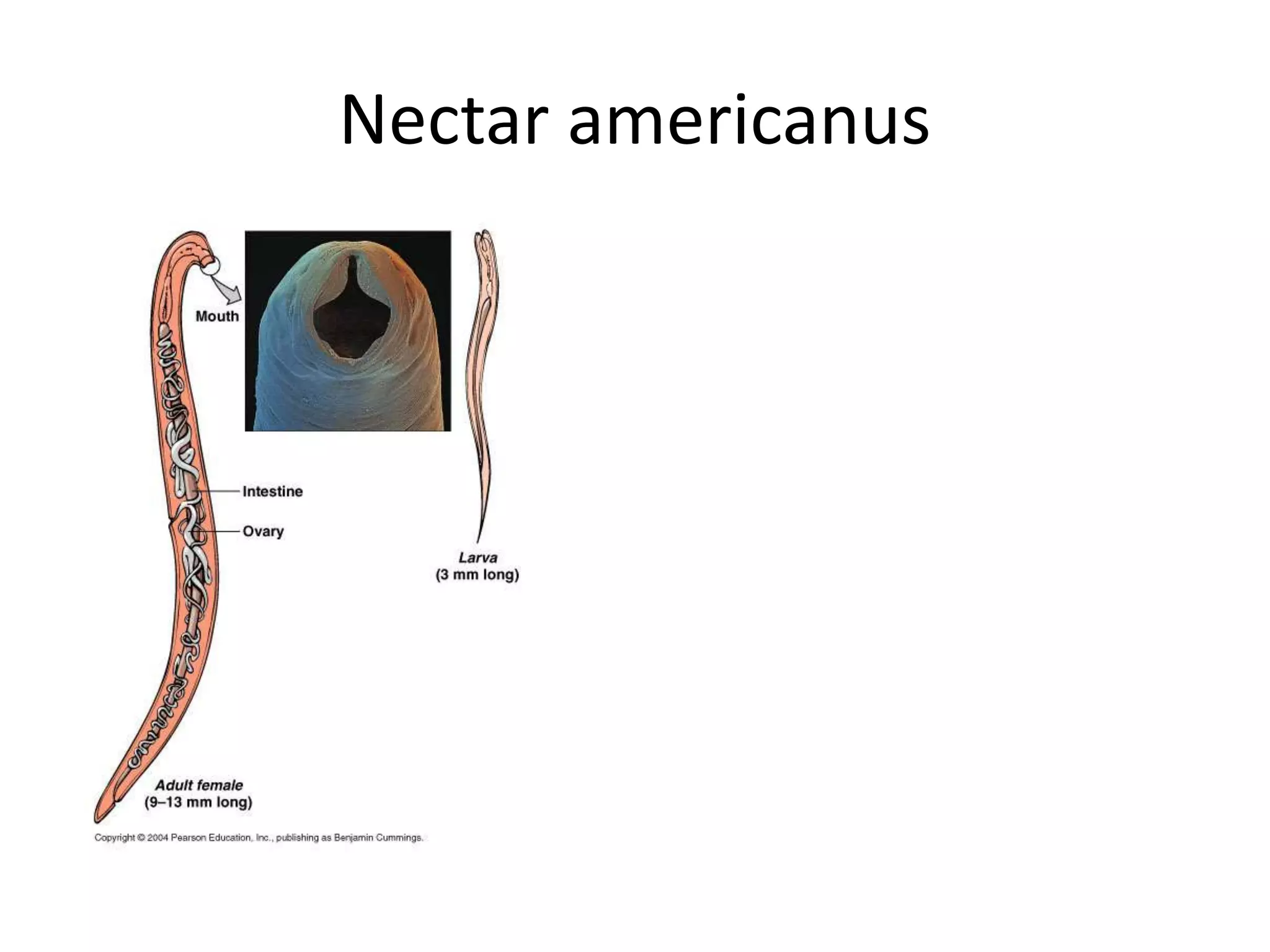
Hookworm affects about 576 million people globally, predominating in tropical and subtropical regions. The two major pathogens that cause hookworm infections are Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. Symptoms of hookworm infection include skin irritation, coughing and pneumonia during larval migration through the lungs, anemia and abdominal pain once the worms reach the intestines. Diagnosis involves examining stool samples microscopically for eggs. Treatment consists of anthelmintic drugs like albendazole or mebendazole. Prevention relies on sanitation measures, wearing shoes, health education, and treatment of infected individuals.