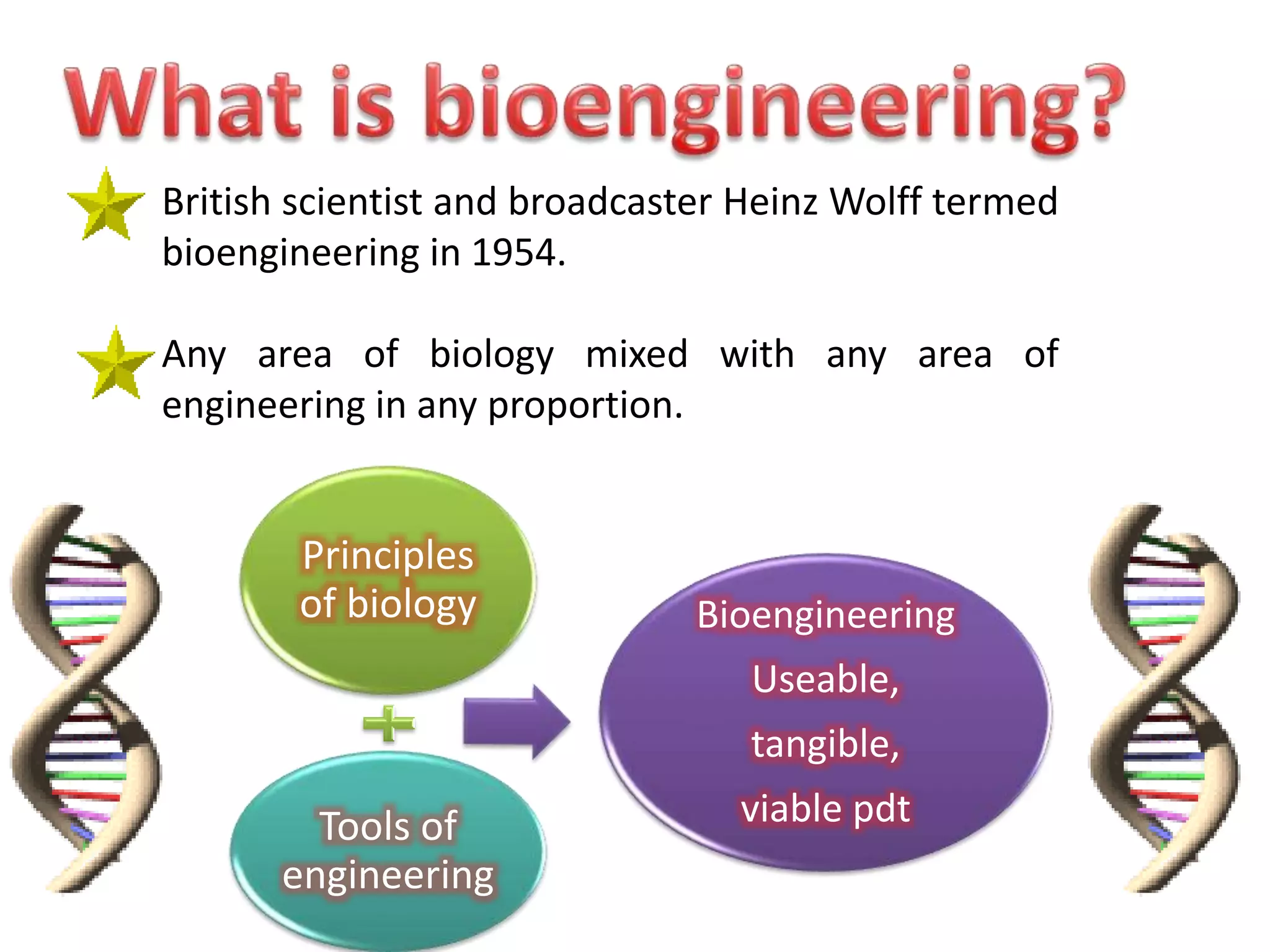
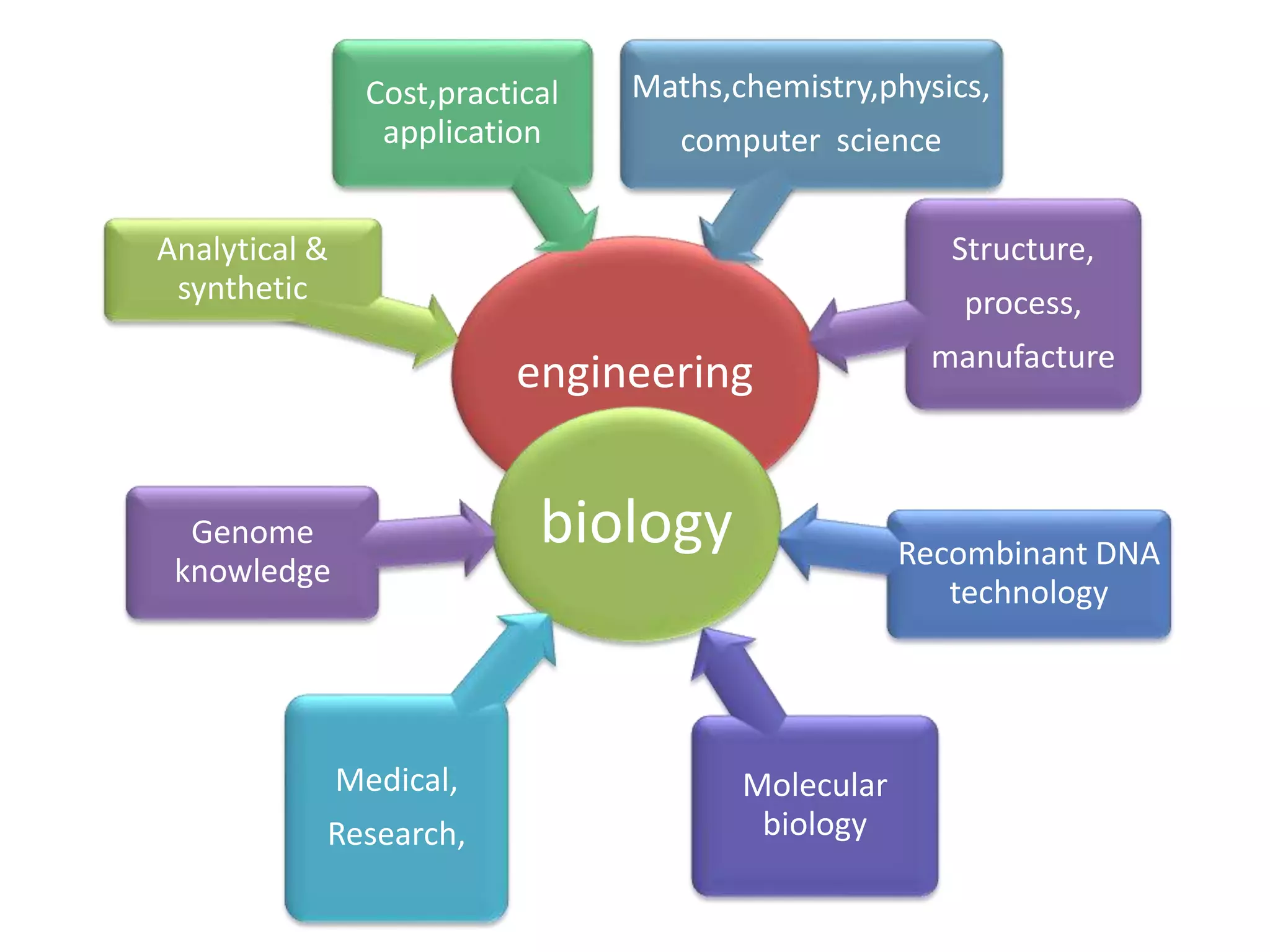
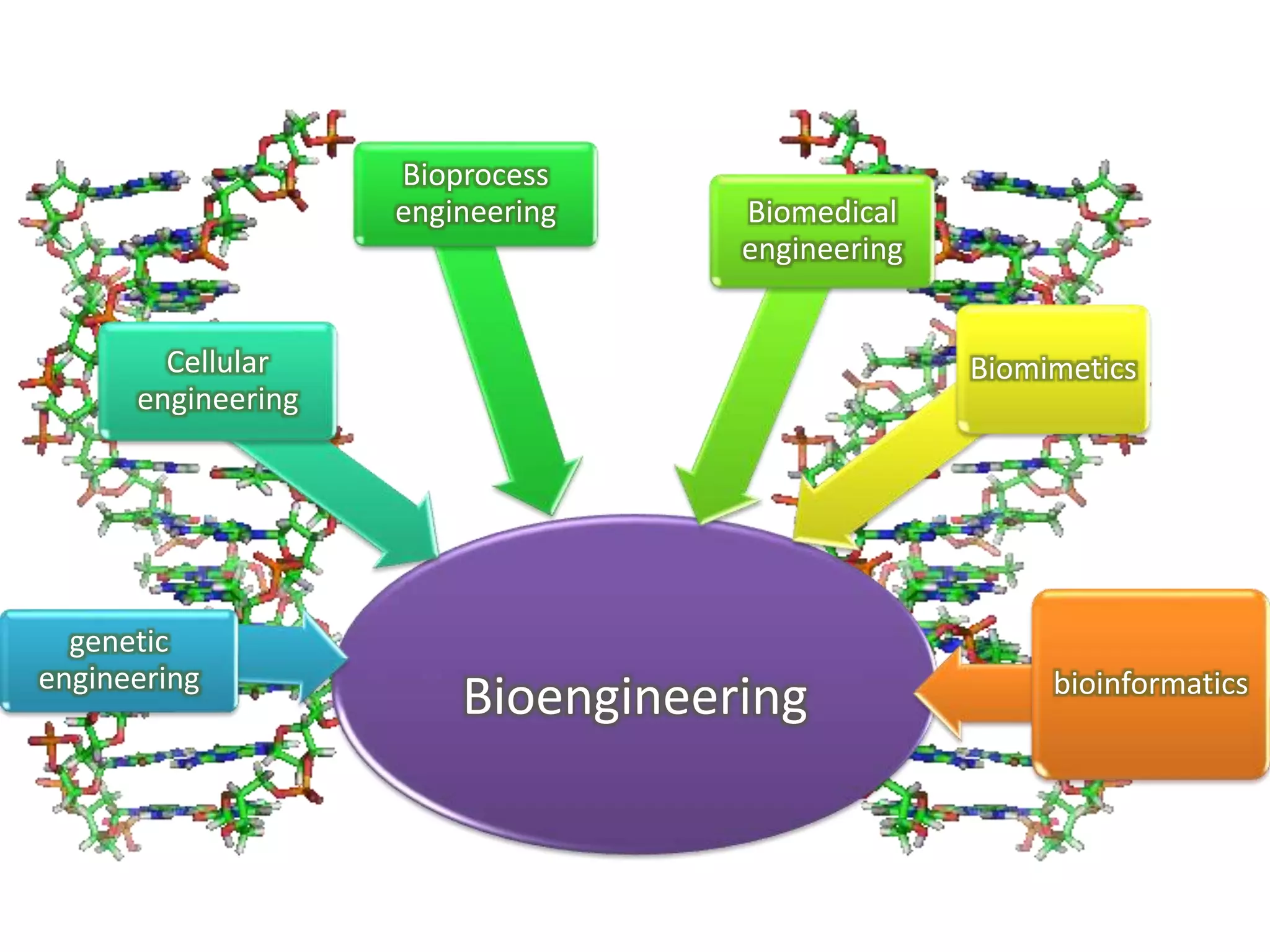
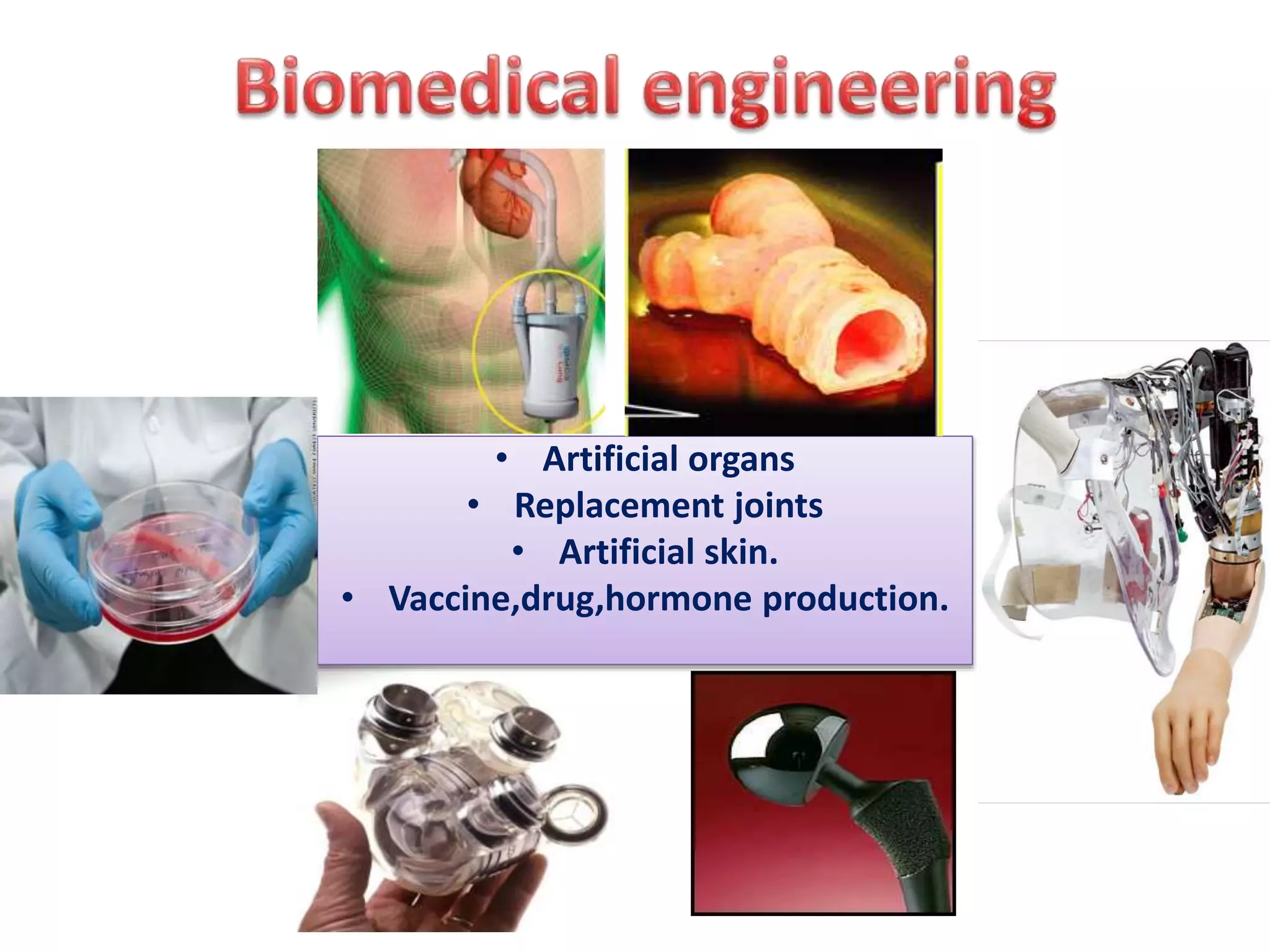
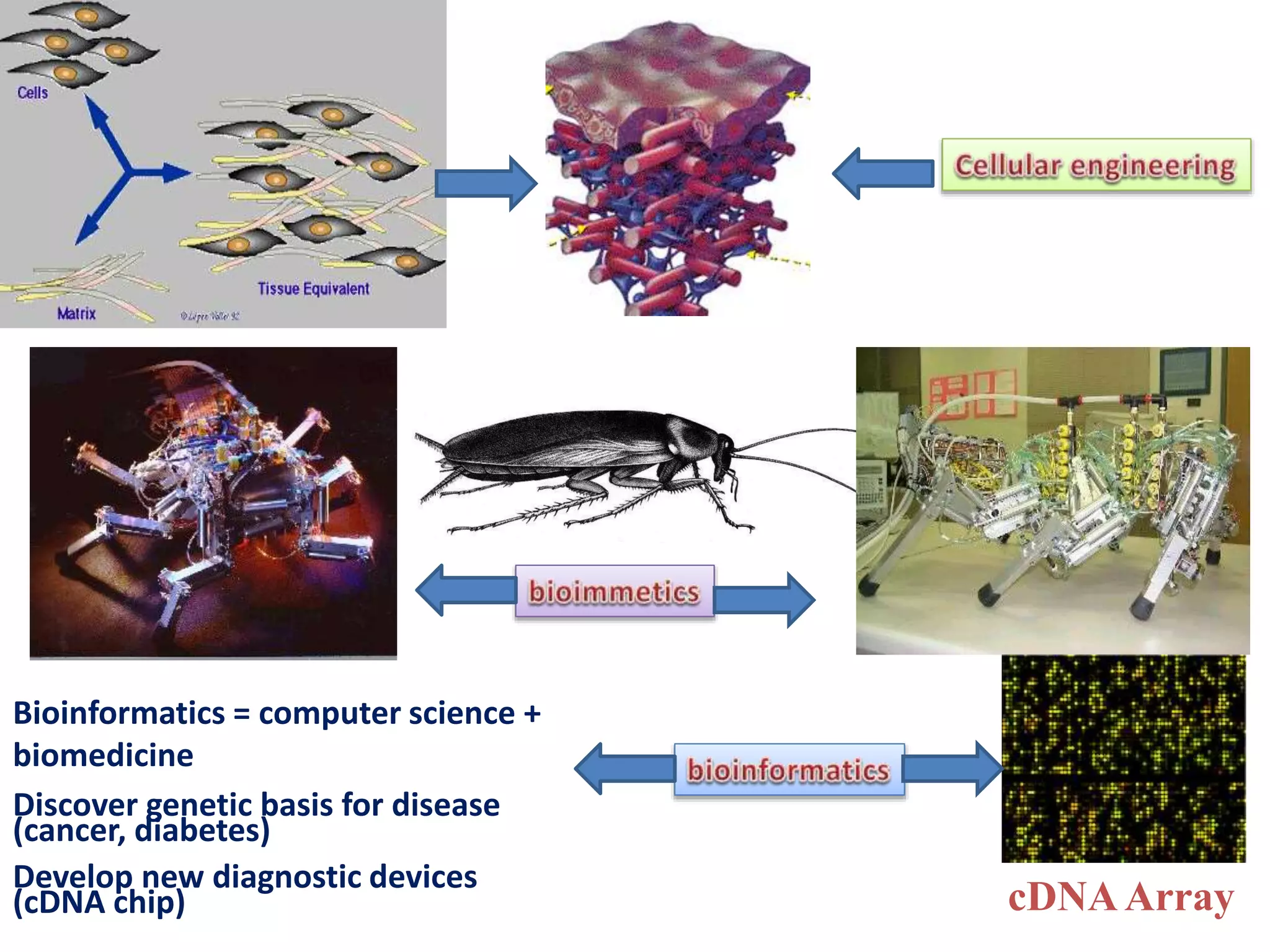
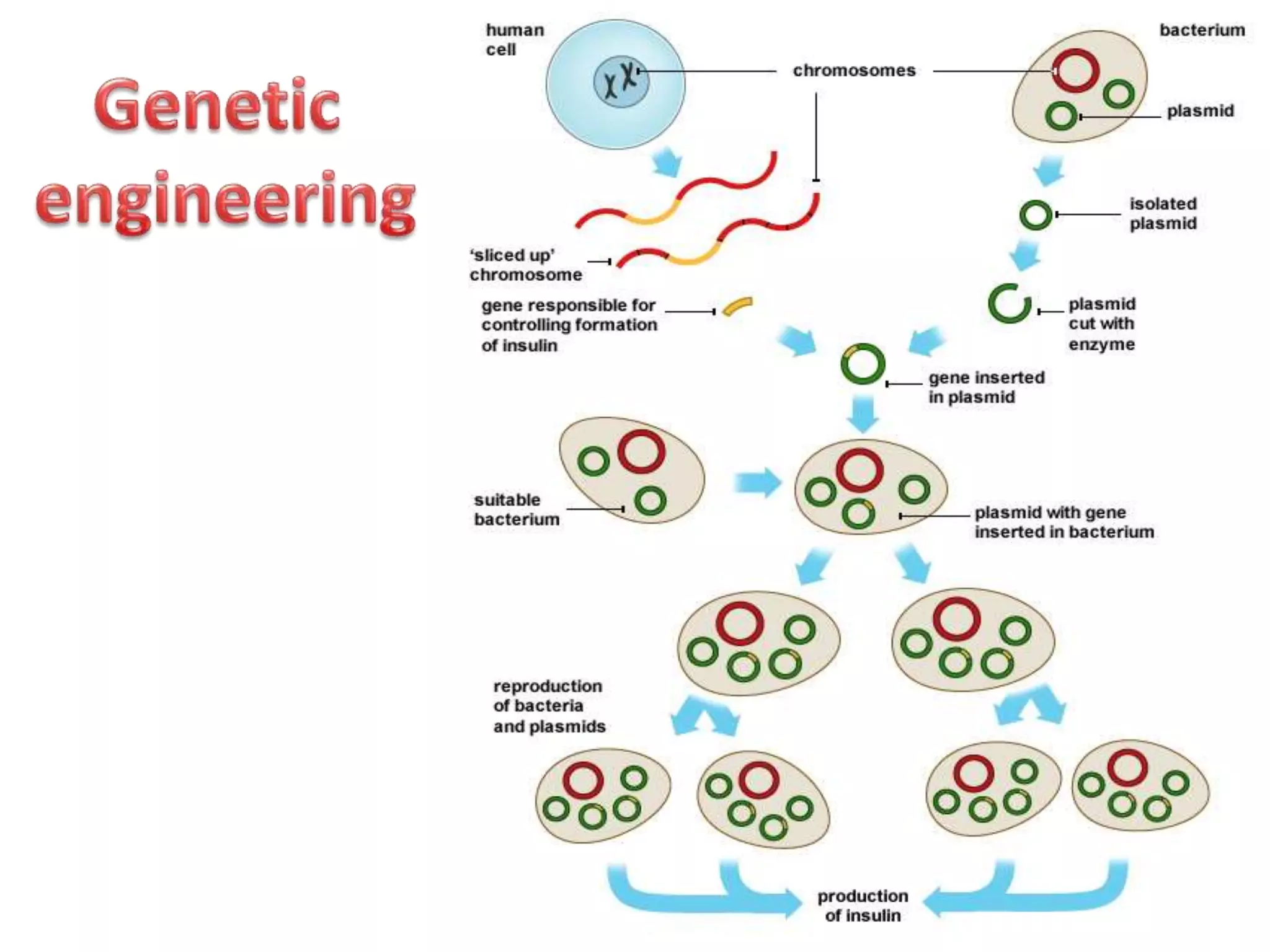
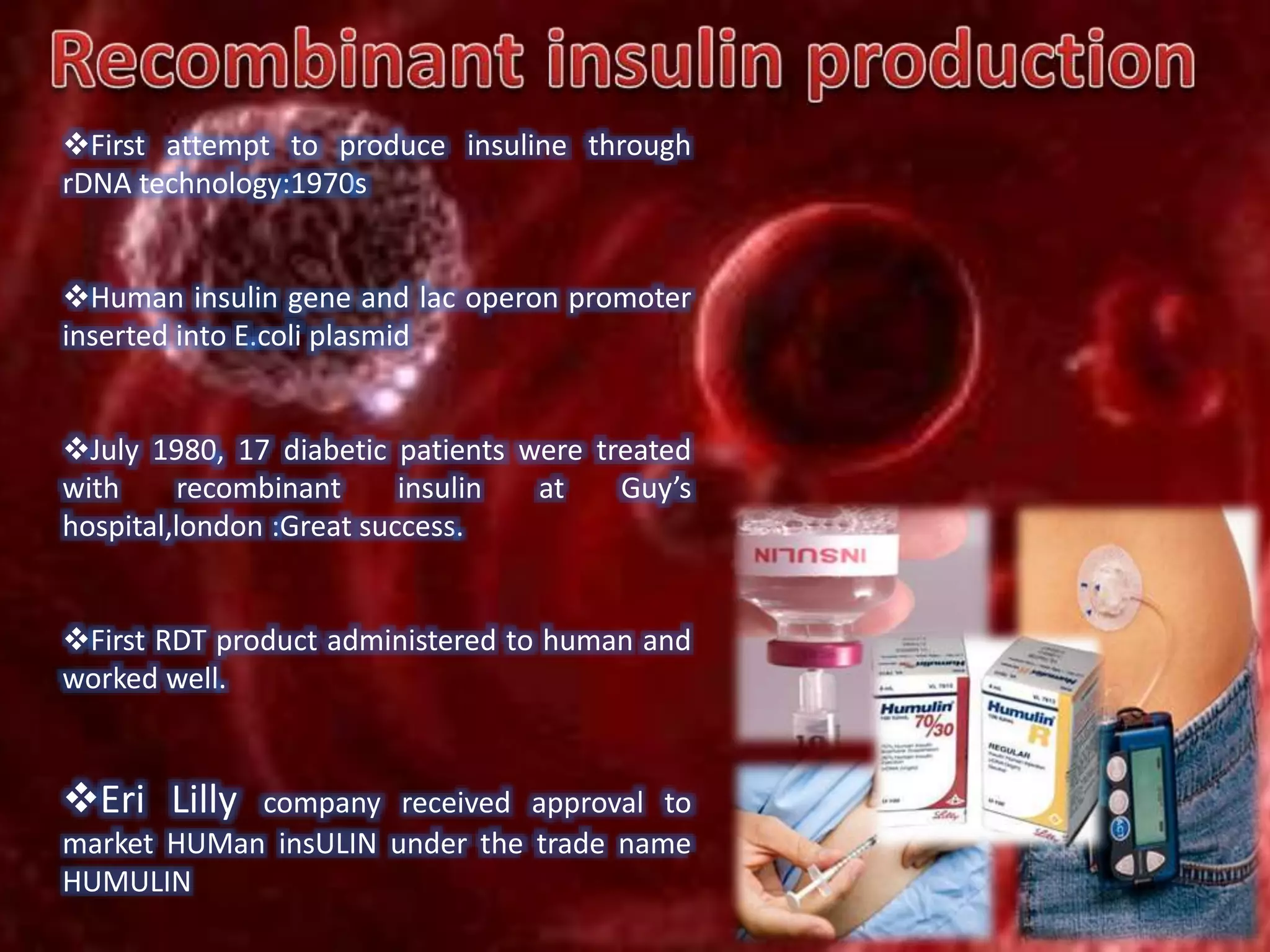
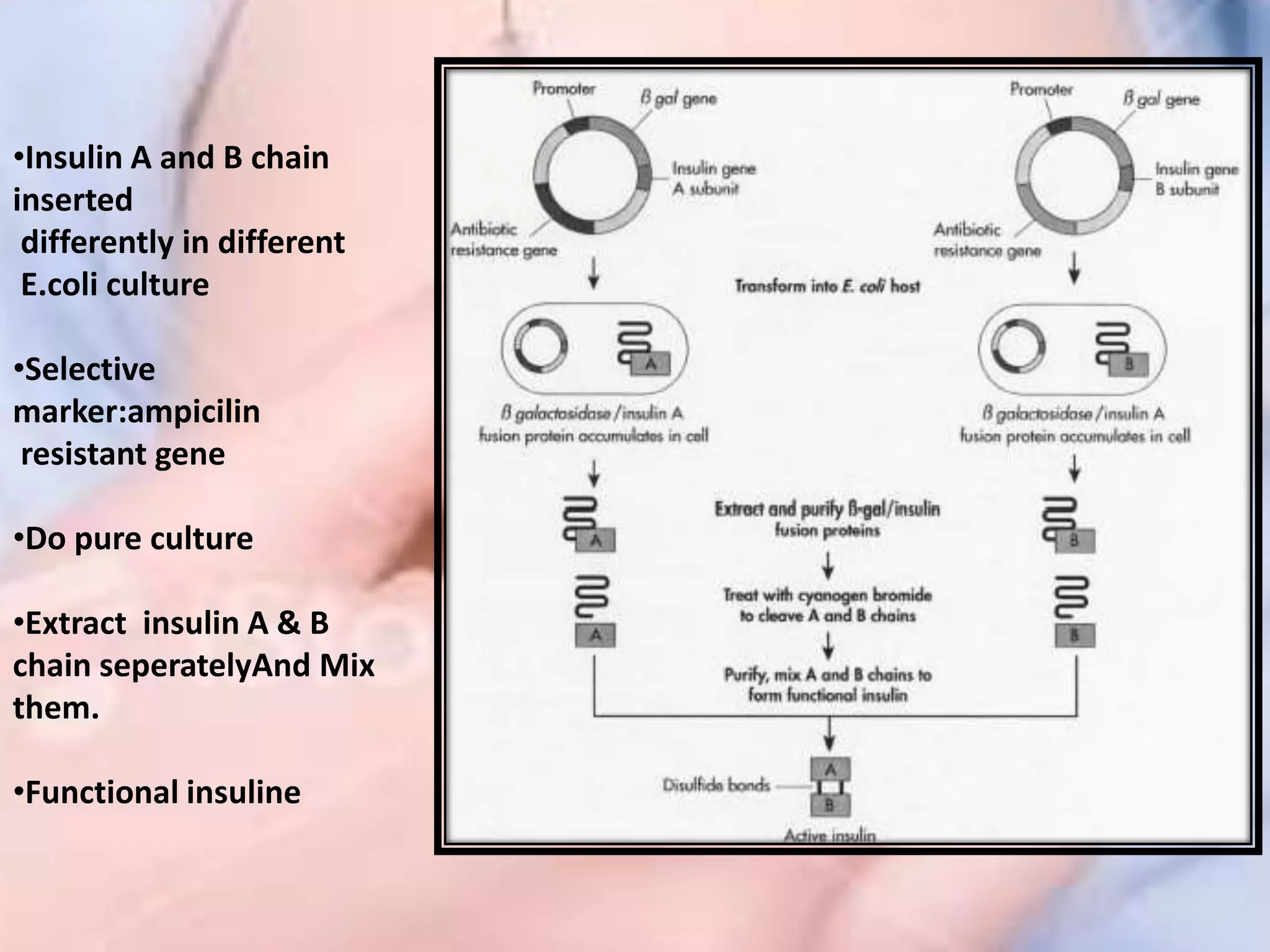
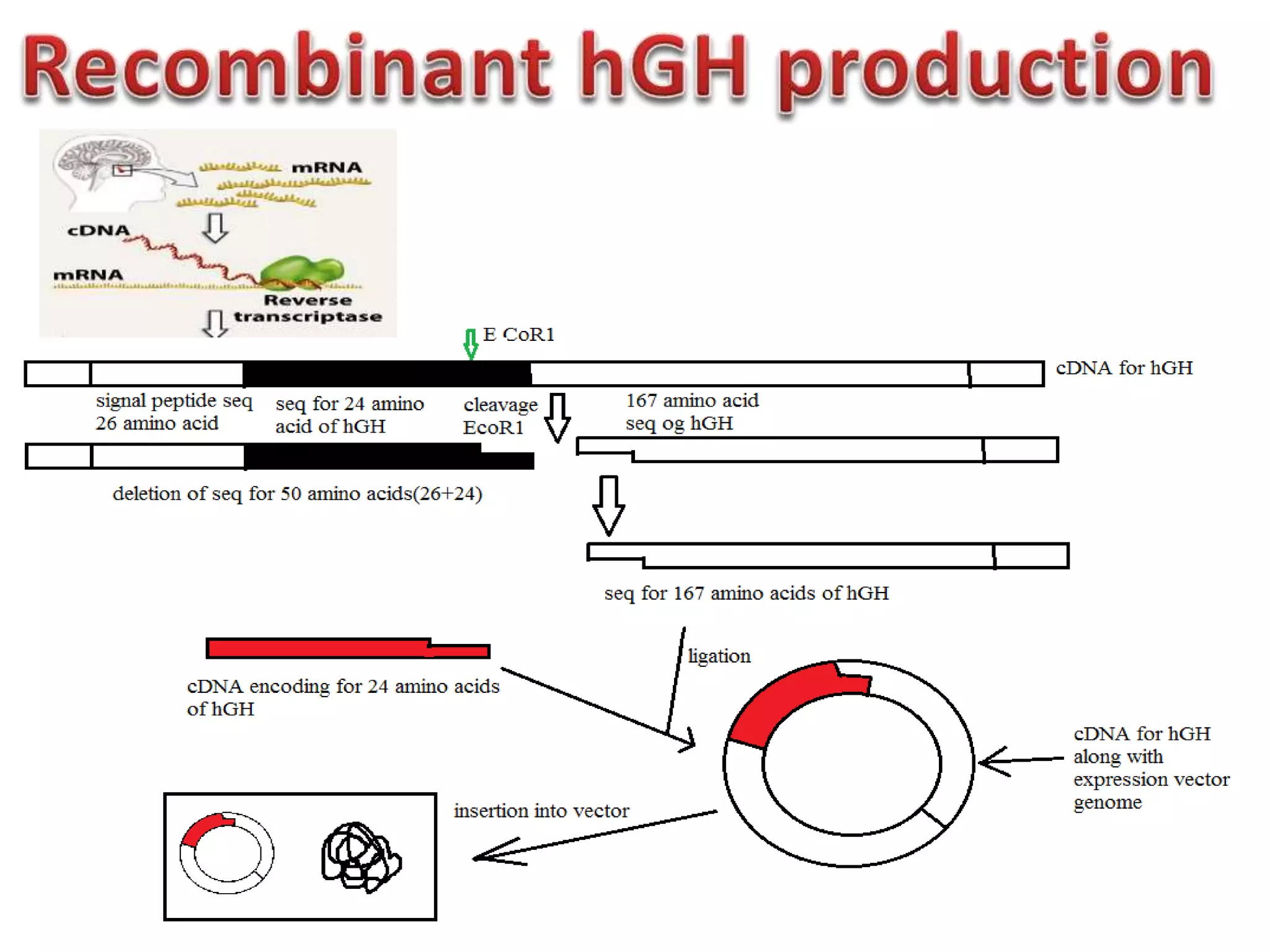
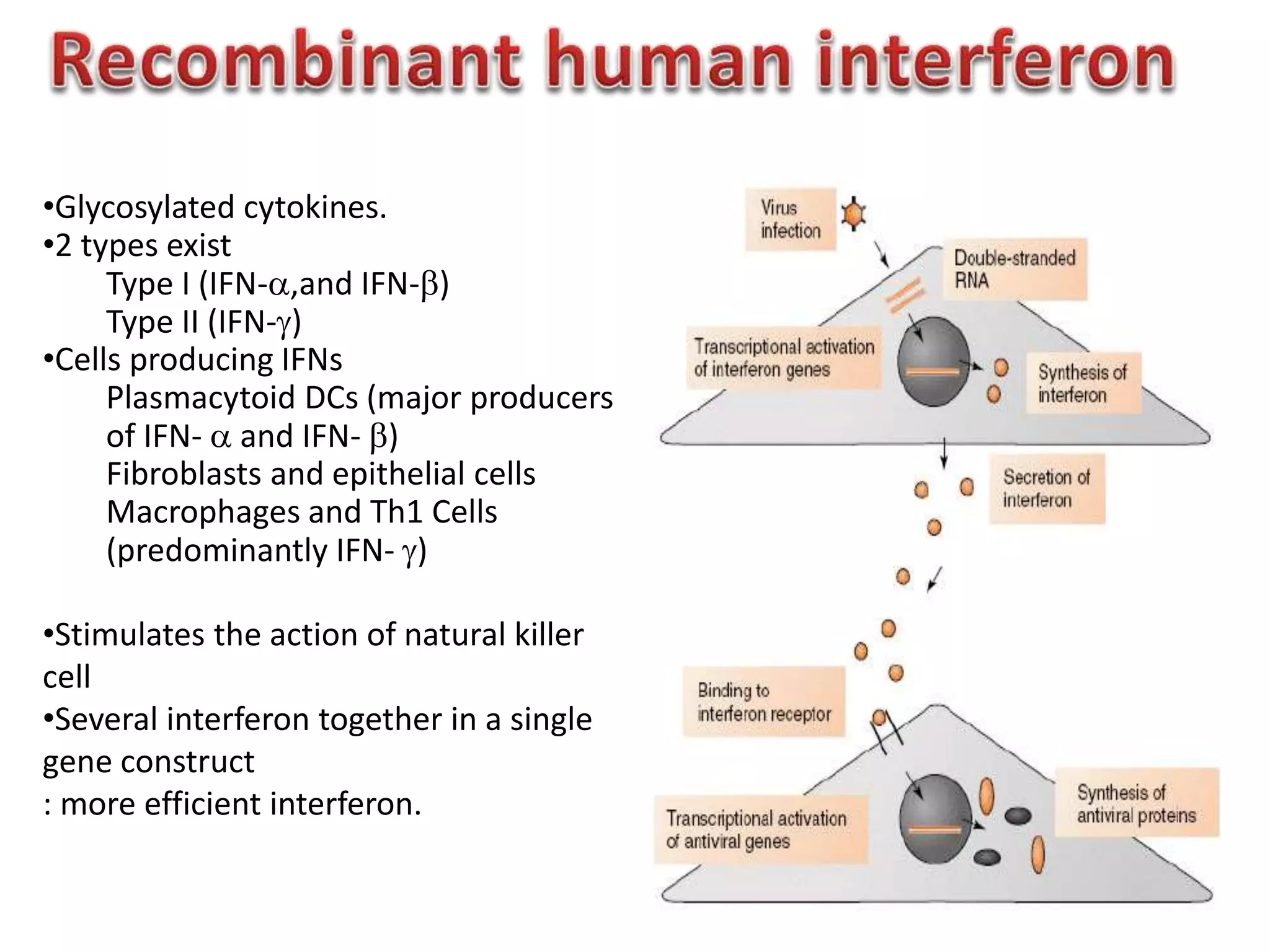
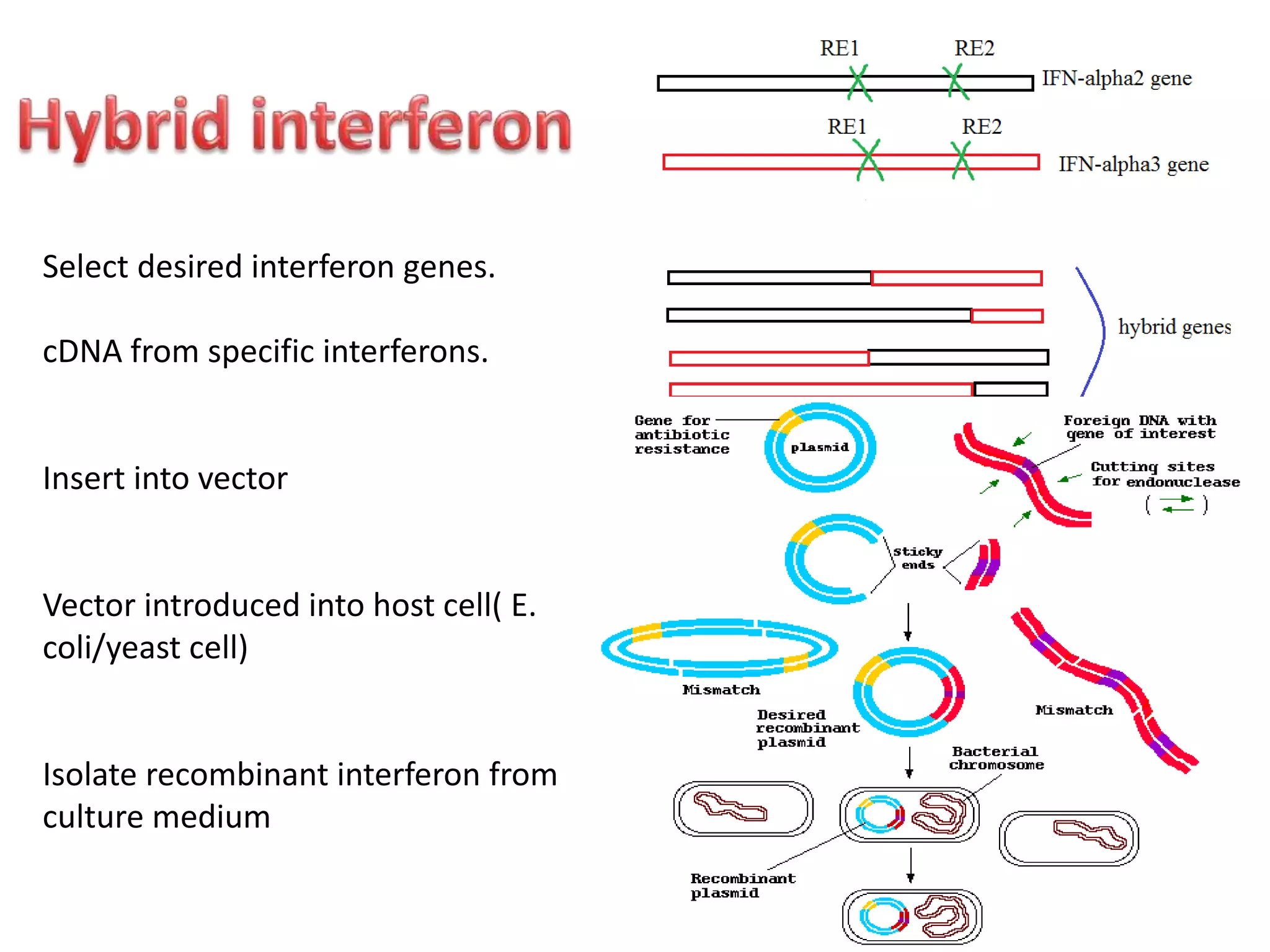
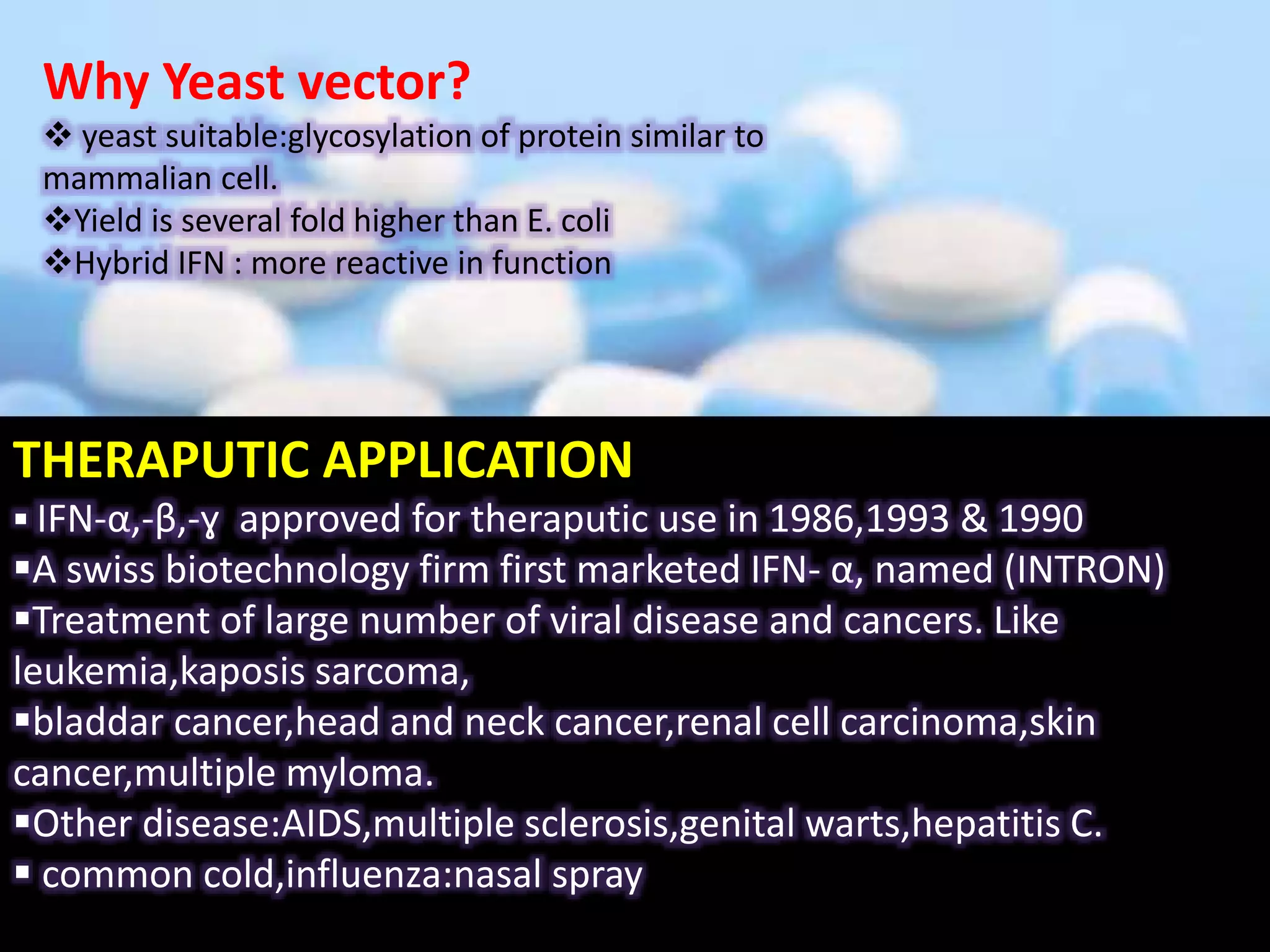
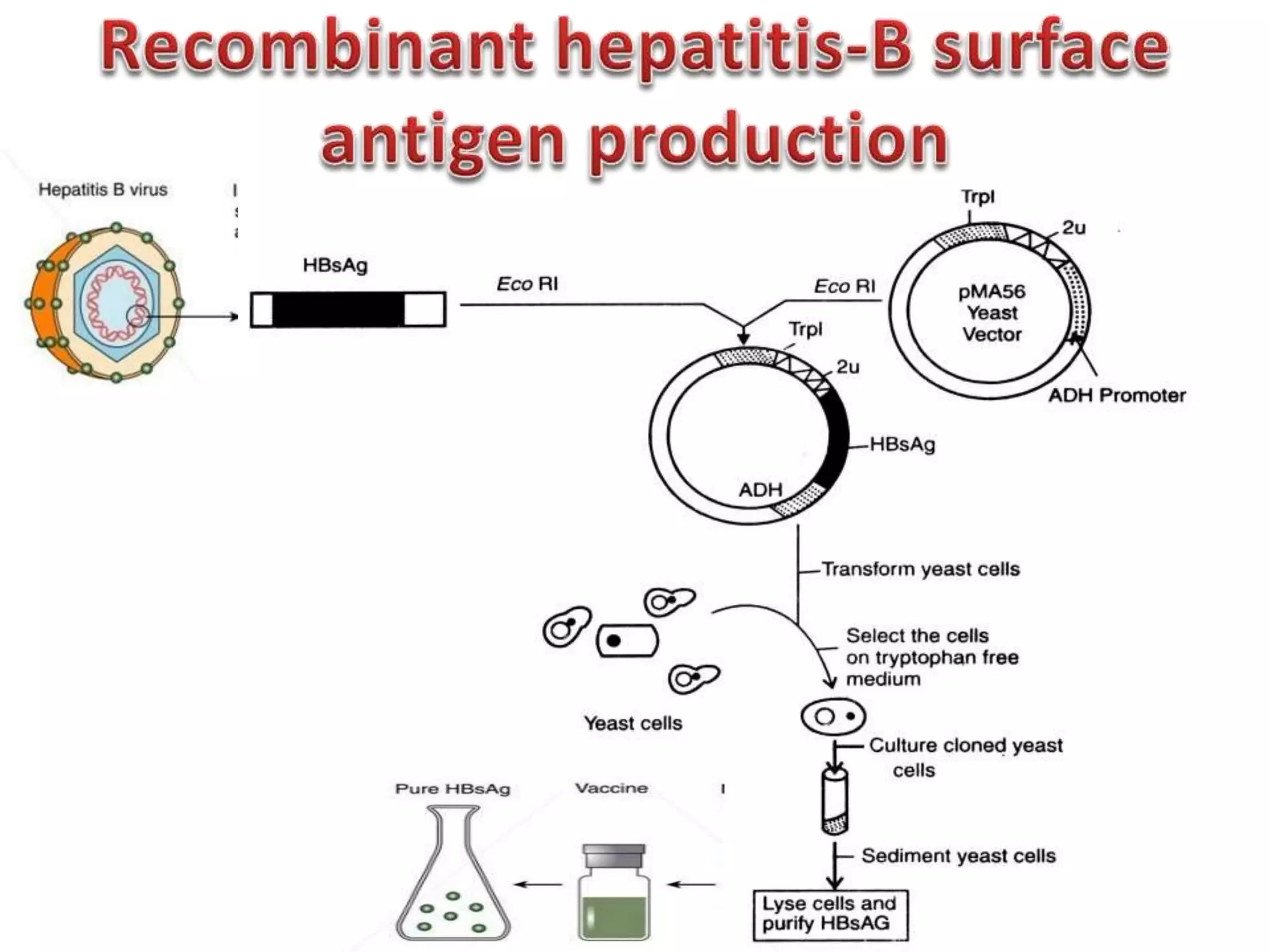
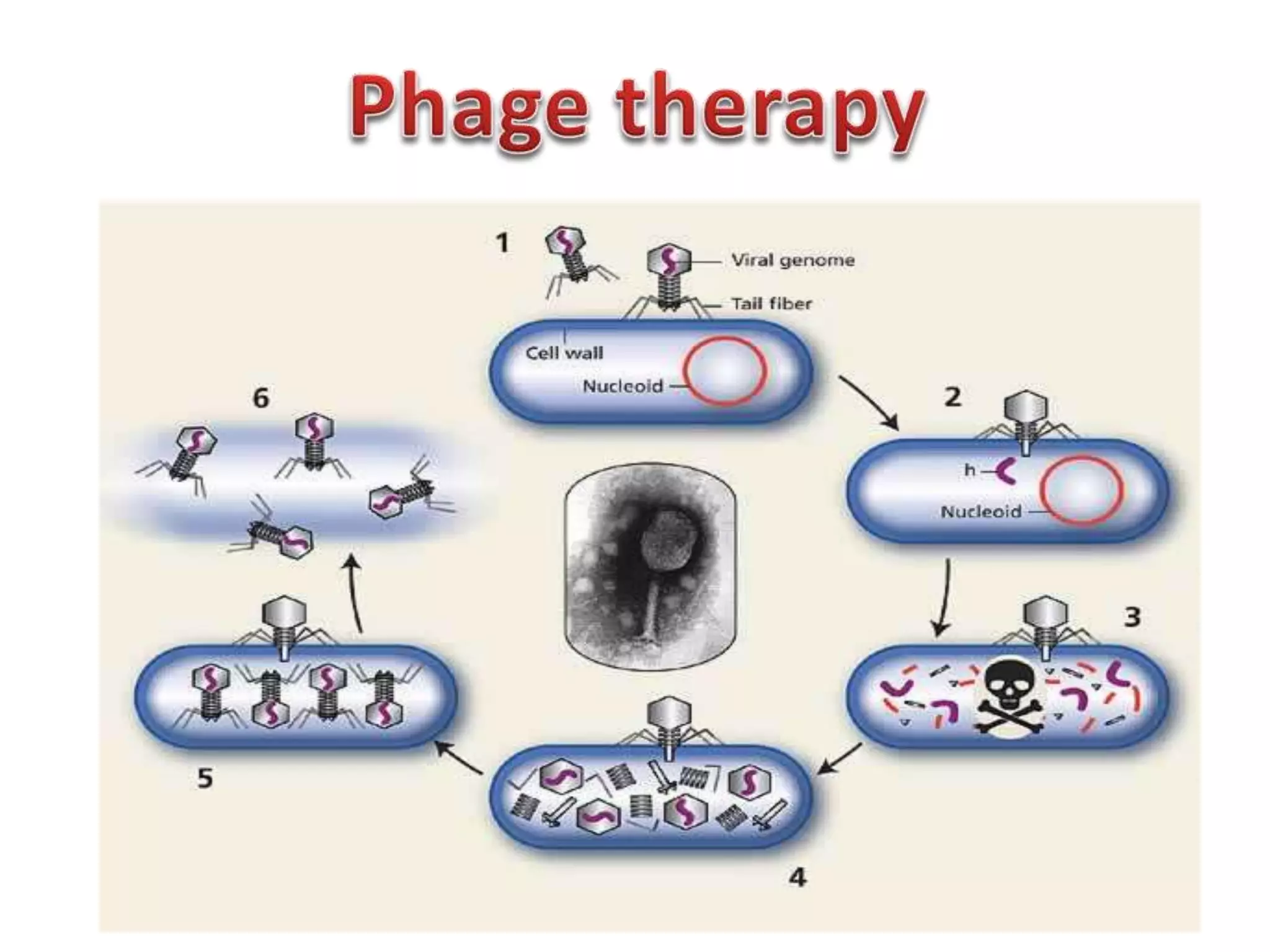
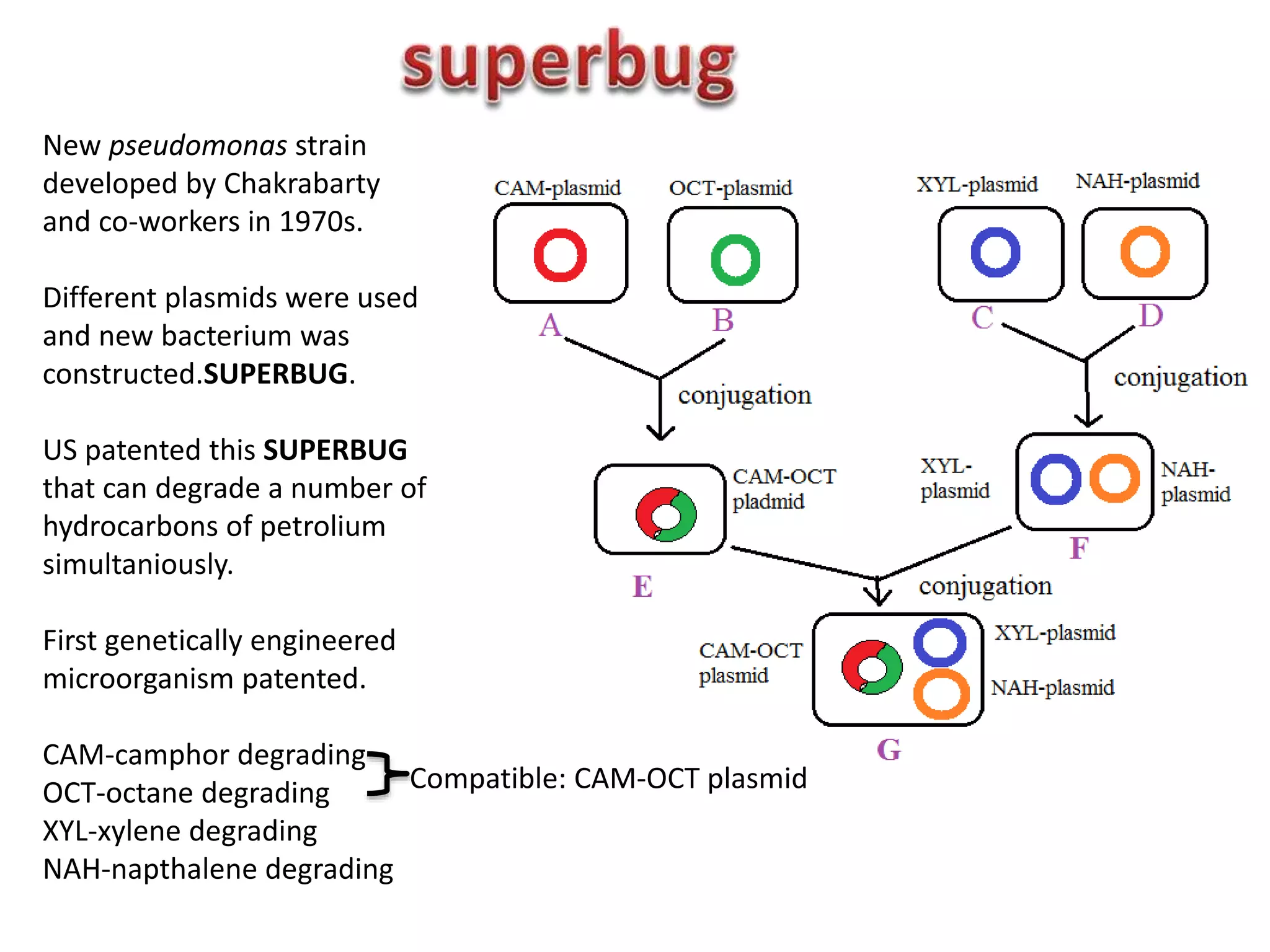
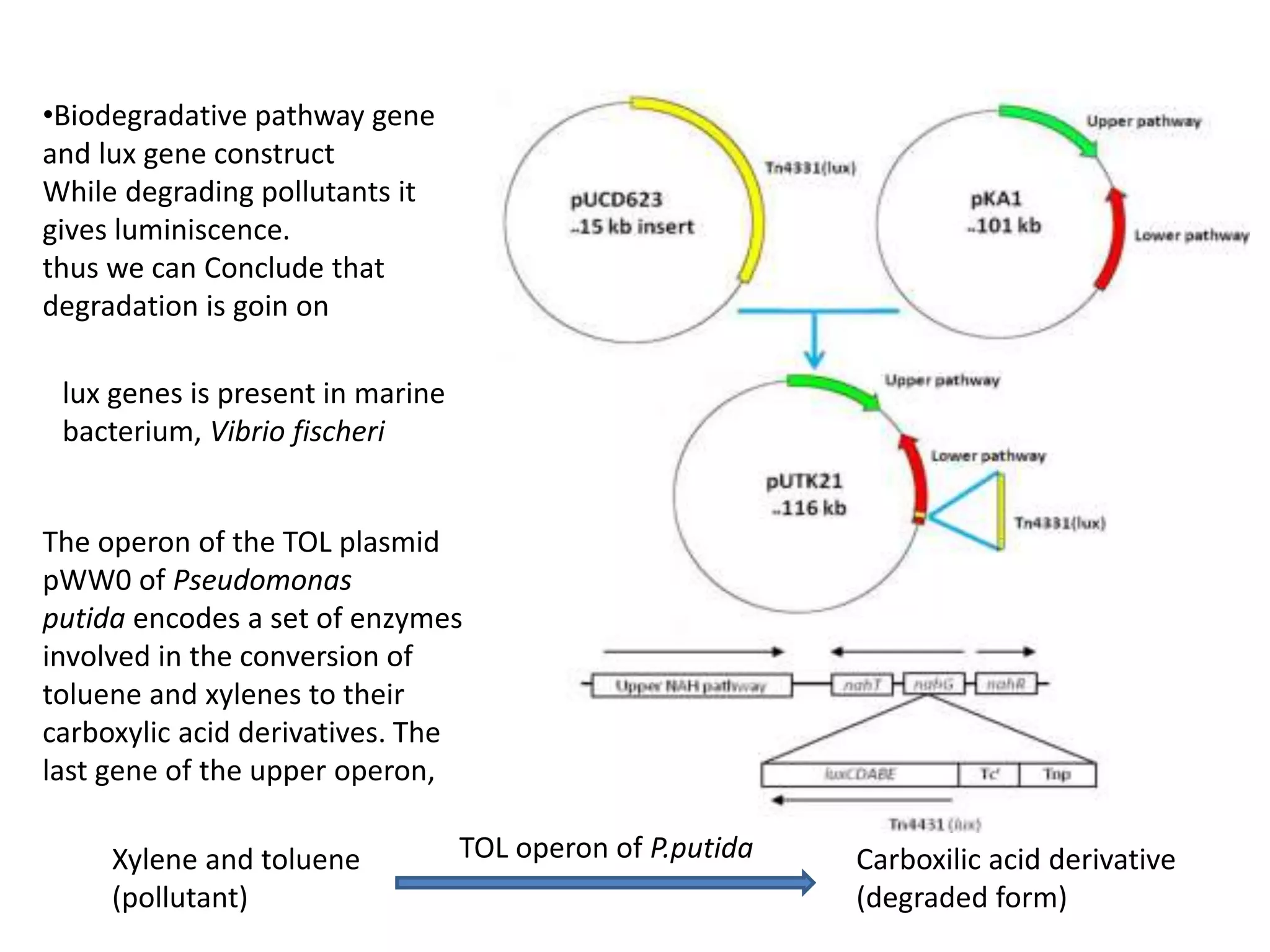
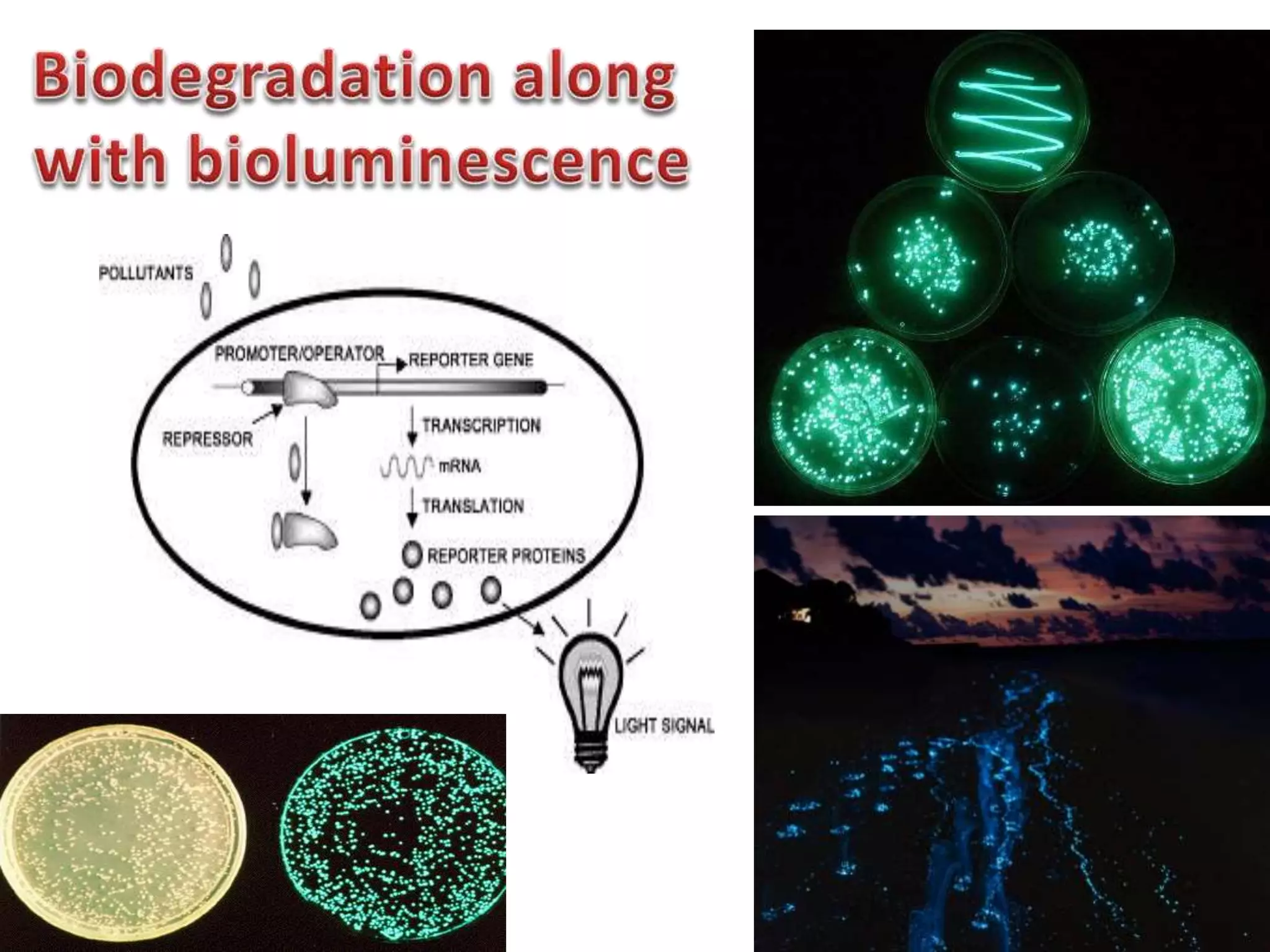
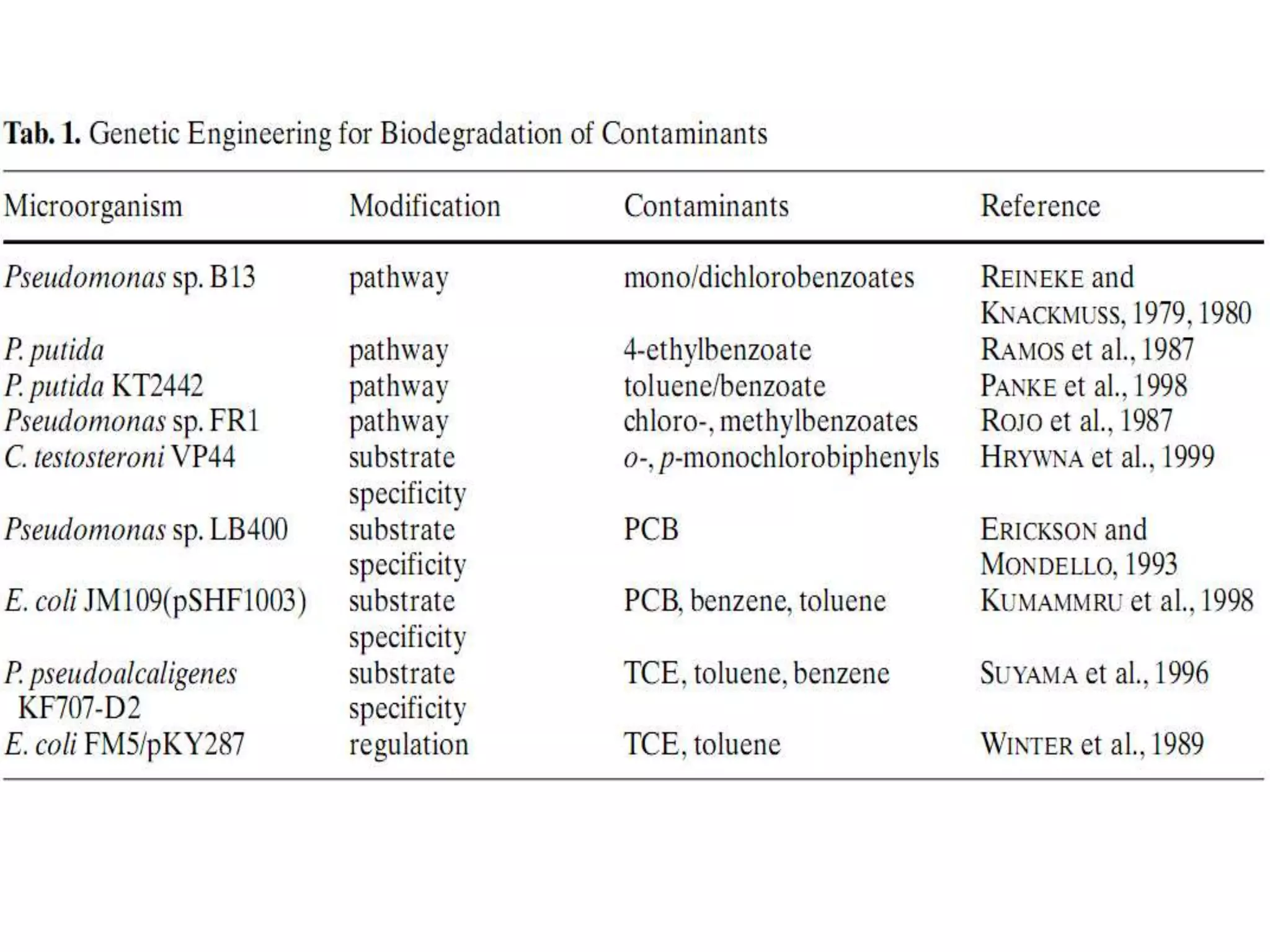
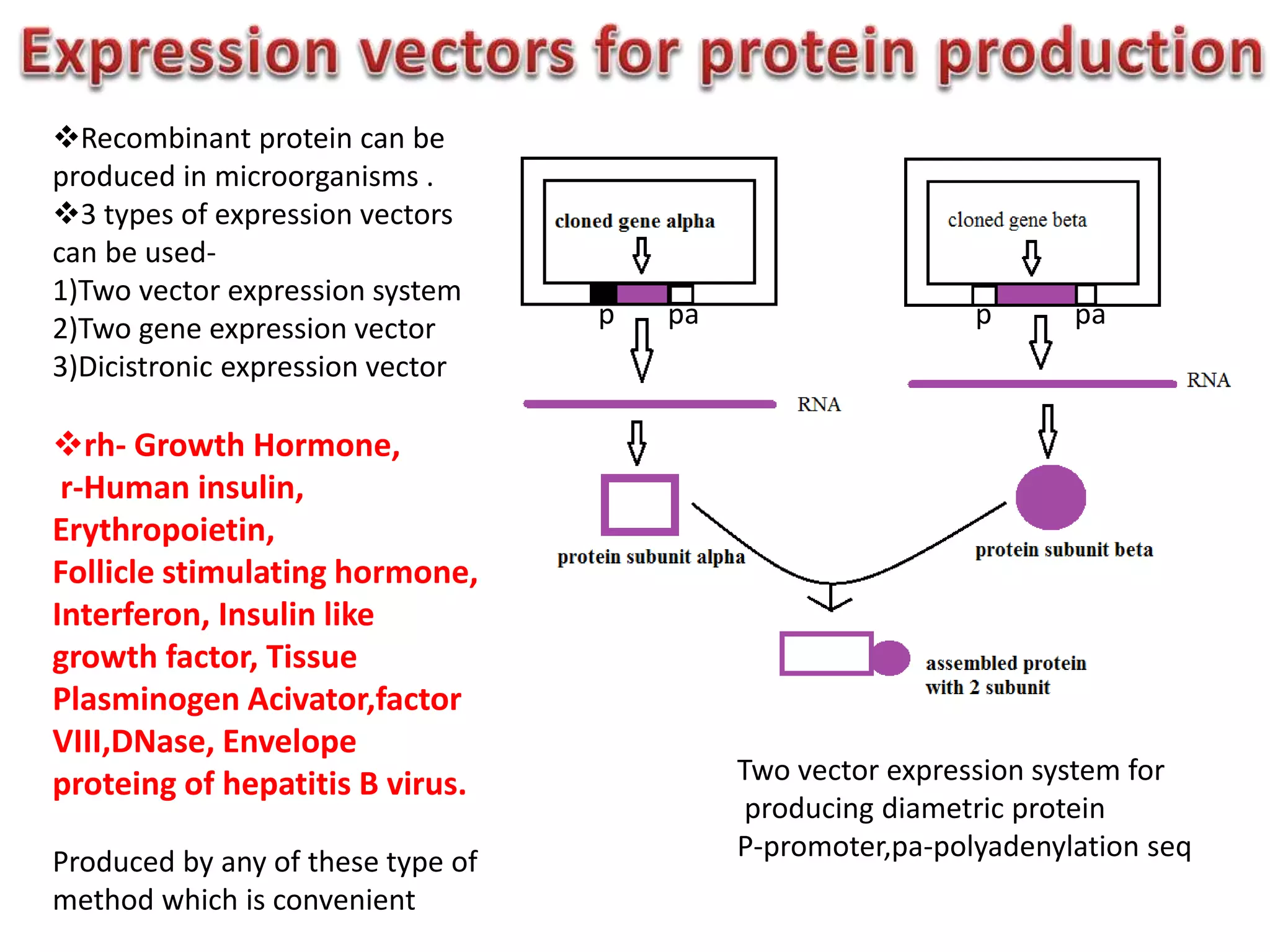
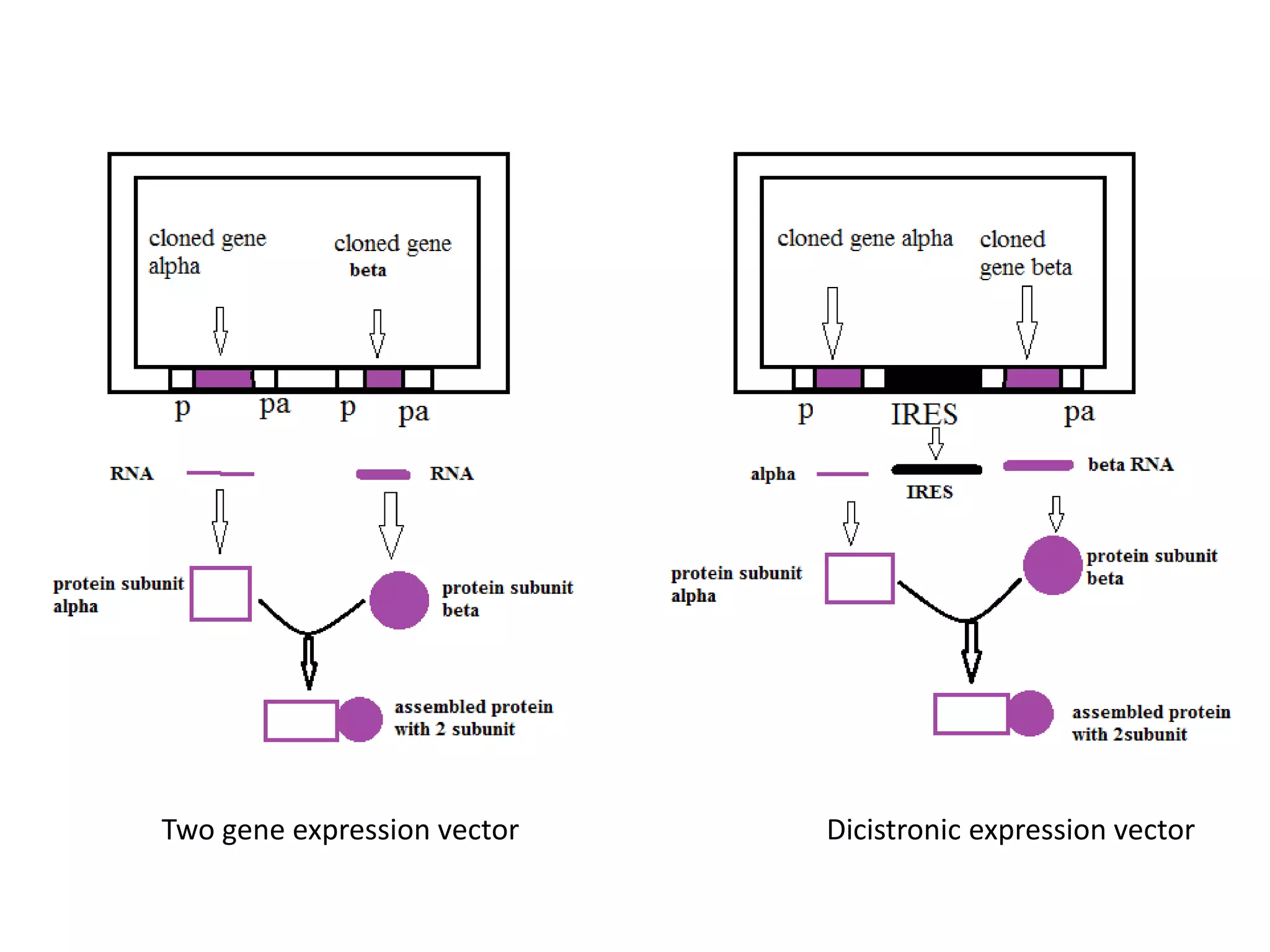
Bioengineering is an interdisciplinary field that applies engineering principles to biology. It involves using tools and principles of engineering to analyze and synthesize biological systems. Some key areas of bioengineering include genetic engineering, biomedical engineering, bioprocess engineering, and bioinformatics. Genetic engineering has led to the production of important recombinant proteins and vaccines through the use of recombinant DNA technology. This document provides examples of insulin, growth hormone, interferon, and vaccines being produced through genetic engineering techniques.