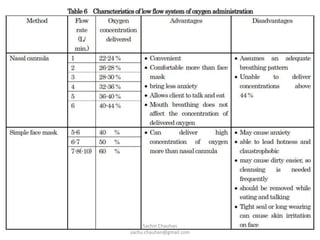
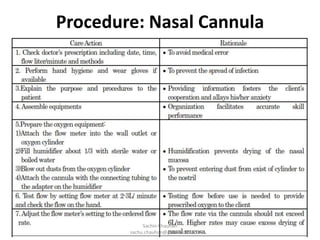
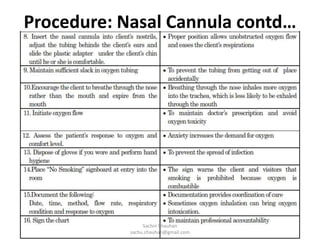
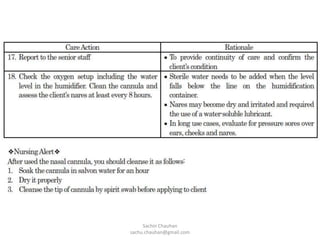
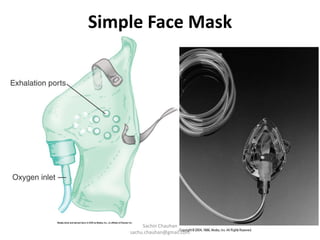
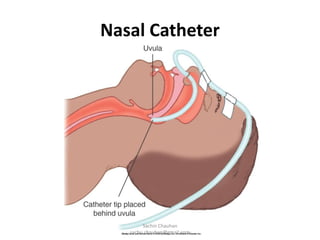
Oxygen administration is used to treat conditions causing hypoxia by delivering higher than normal levels of oxygen. It aims to relieve shortness of breath, reduce low blood oxygen levels, and alleviate struggling to breathe. Oxygen can be provided from wall outlets or oxygen cylinders through nasal cannulas, simple face masks, or nasal catheters. When administering oxygen, nurses must carefully follow the prescribed flow rate and concentration and educate patients on safety issues like avoiding smoking around oxygen.