This document provides information about administering oxygen therapy, including:
1. It defines oxygen therapy and discusses its indications for treating hypoxemia. Conditions that can cause hypoxemia include cyanosis, breathlessness, anemia, and lung diseases.
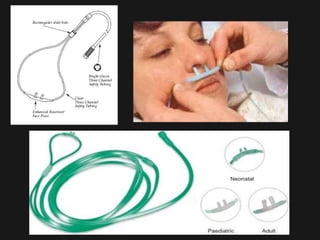
2. It describes different methods of oxygen administration including nasal catheters, oxygen masks, nasal cannulas, oxygen tents, and transtracheal oxygen.
3. It discusses the nurse's responsibilities in setting up oxygen therapy, assessing the patient, and monitoring for complications like infection or oxygen toxicity.






![INTRODUCTION
Patients with respiratory dysfunction
are treated with oxygen inhalation to relieve
Anoxemia or hypoxemia. The normal amount of
oxygen in the arterial blood should be in the
range of 80 to 100 mm of Hg. Tissues vary in
their oxygen requirements.
the cerebral cells receives 20% of the body’s
oxygen supply, and if oxygen is not supplied to
brain, the can live only few minute[5-7 min] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oxygenation-170715044737/85/Oxygenation-7-320.jpg)