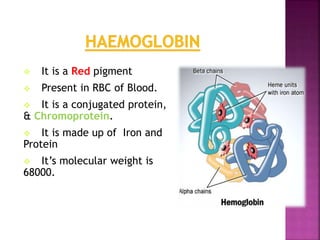
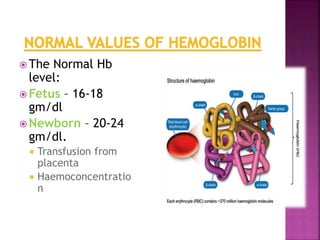
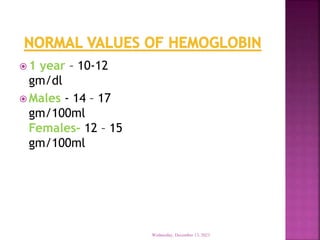
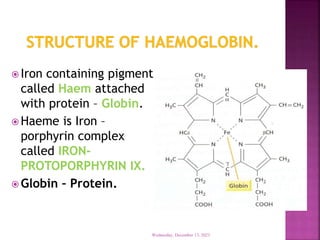
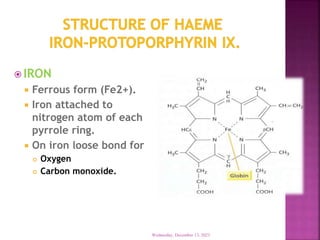
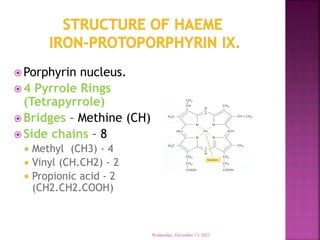
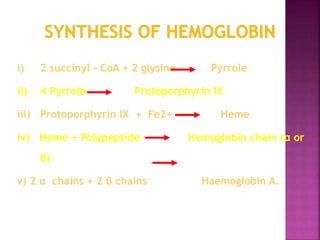
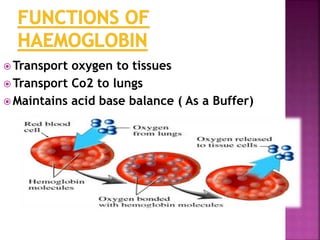
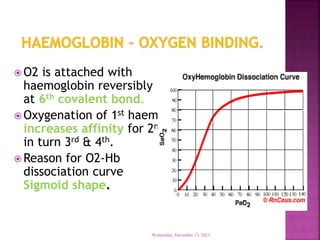
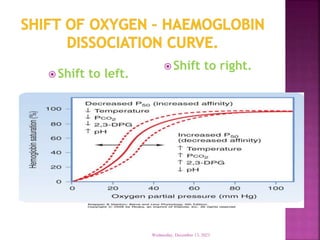
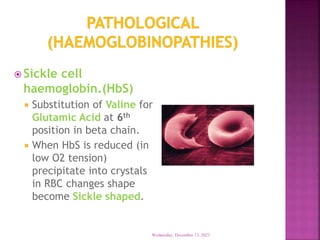
This document discusses hemoglobin, including its structure, function, variations, synthesis, and degradation. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen throughout the body. It is composed of four polypeptide chains and an iron-containing heme group that reversibly binds oxygen. Variations include fetal hemoglobin, sickle cell hemoglobin, and thalassemias. Hemoglobin levels can be affected by many factors and diseases can result from genetic variations in hemoglobin structure.