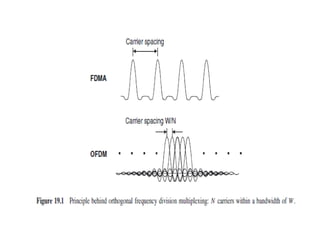
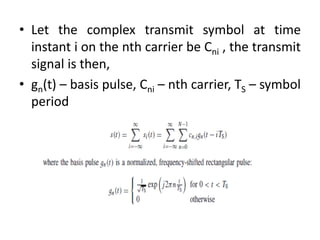
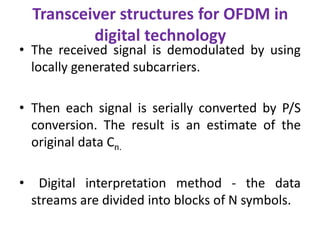
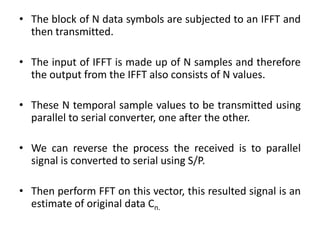
OFDM is a digital multi-carrier modulation scheme that divides the available bandwidth into multiple orthogonal subcarriers. It converts a high-rate data stream into multiple lower-rate streams that are transmitted in parallel over narrowband channels. OFDM has advantages for high data rate transmission in delay dispersive environments and is used in technologies like DAB, DVB, wireless LANs, and 4G cellular systems. It works by splitting information into parallel streams that modulate distinct subcarriers. The subcarriers are chosen to be orthogonal to avoid interference between signals. OFDM can be implemented digitally using the IDFT/DFT, which makes it simpler and more efficient than analog implementations.