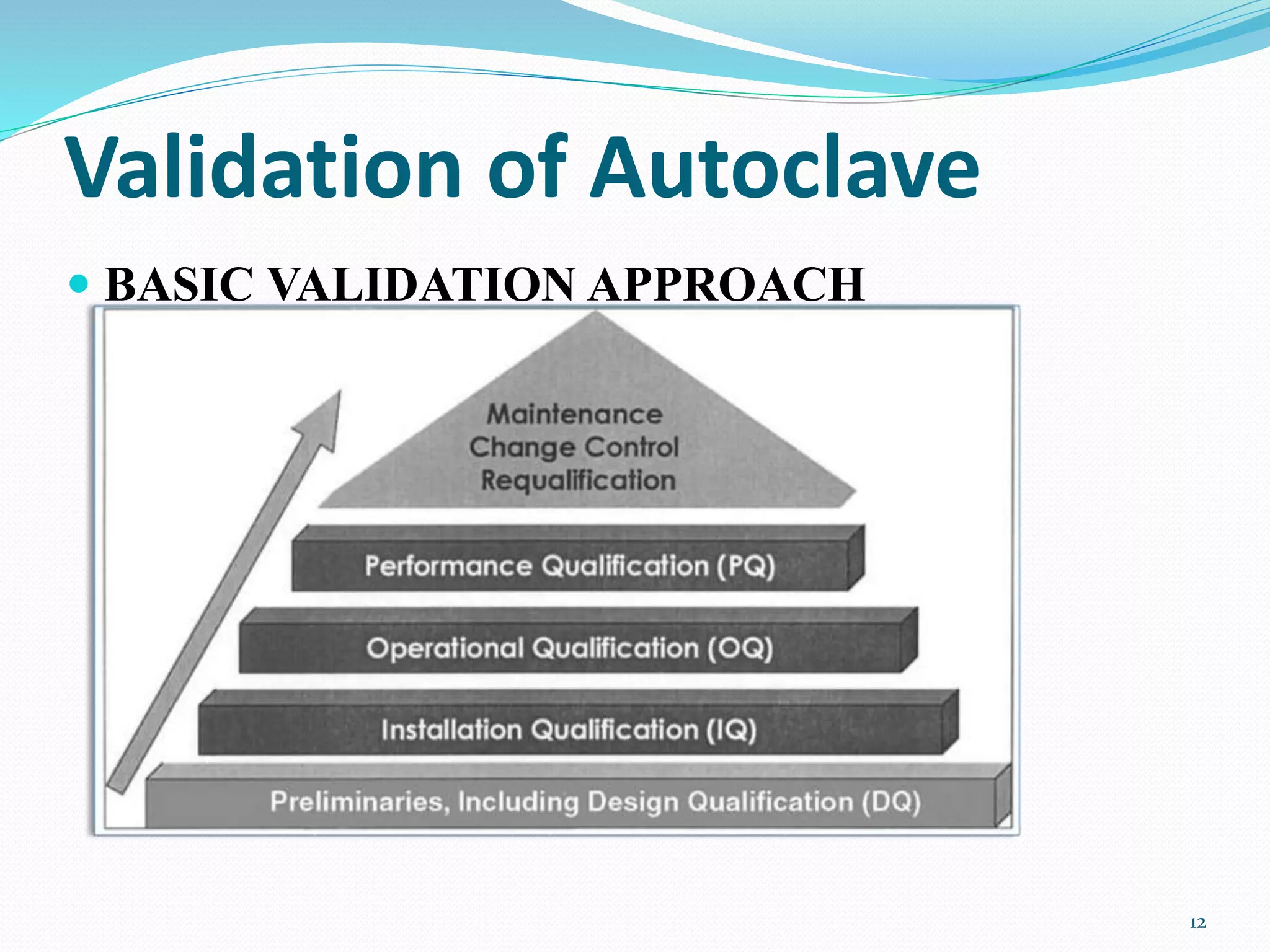
The document discusses the importance of instrument validation in the pharmaceutical industry, outlining the key processes involved, including installation qualification and performance qualification. It emphasizes regulatory requirements for validating instruments and provides detailed steps for validating an autoclave, including various tests and criteria to ensure proper functioning. The conclusion stresses the necessity of qualified personnel for conducting these validations to ensure product quality.