Embed presentation


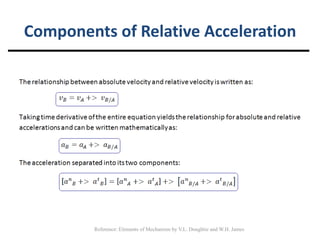
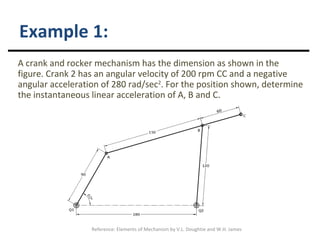
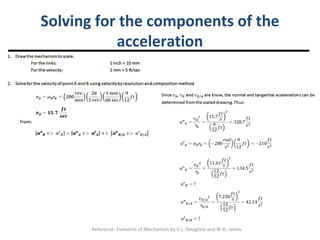
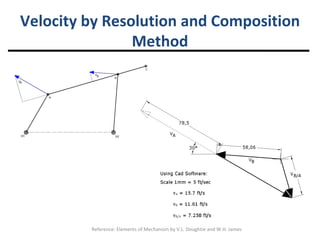



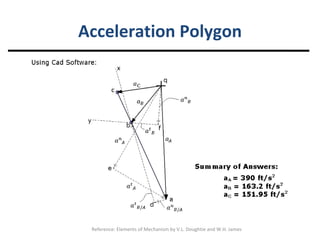

Relative acceleration is the acceleration of one object as observed from another reference object that is also moving. The document discusses relative acceleration and provides an example of using a crank and rocker mechanism to determine the instantaneous linear acceleration of points A, B, and C based on the angular velocity and acceleration of crank 2. It outlines the steps to solve for the components of acceleration using a velocity resolution and composition method and constructing an acceleration polygon.










