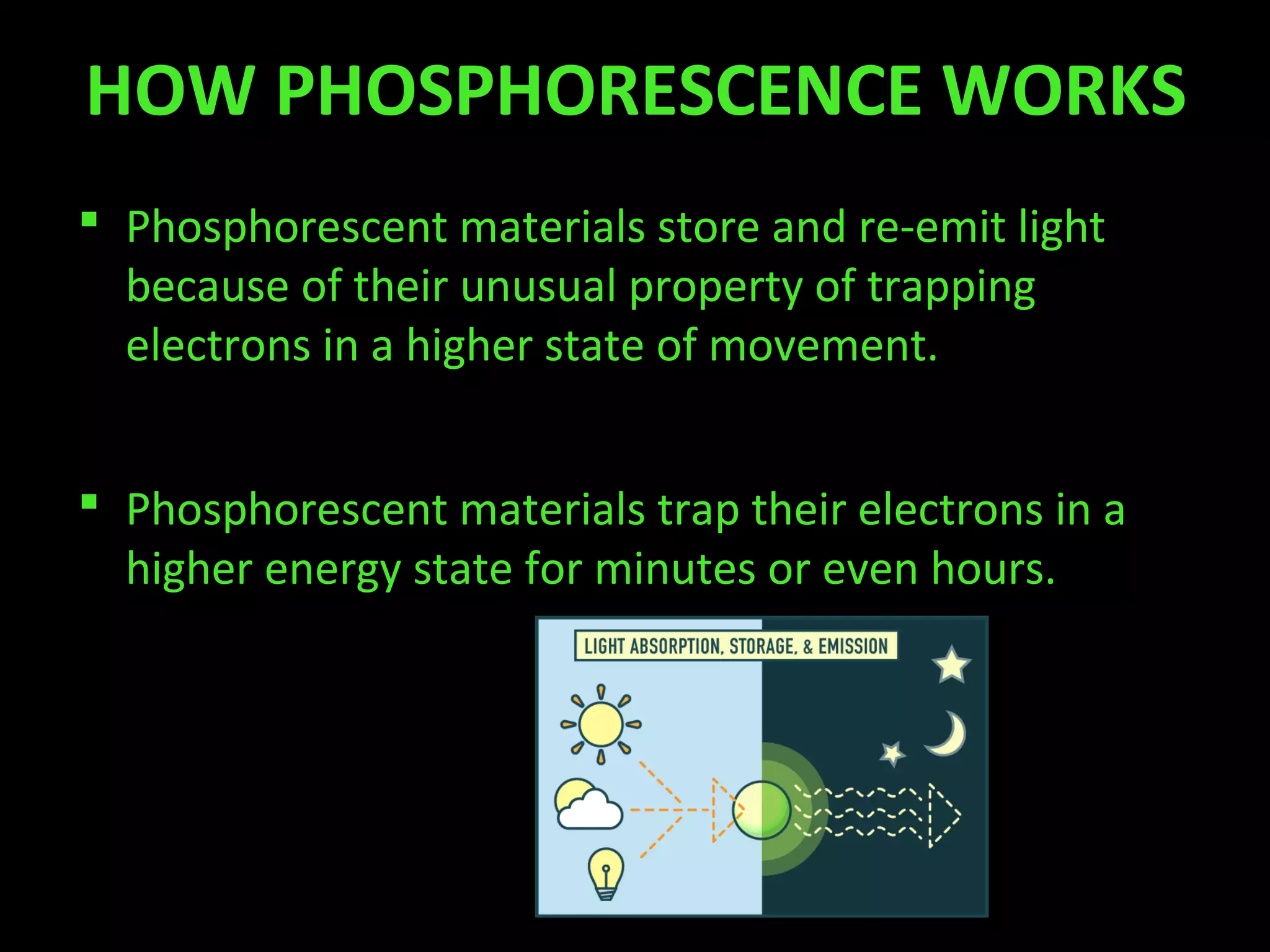
Phosphorescence is the process by which materials emit light after absorbing radiation or energy. It was first observed in the 17th century but not studied scientifically until the 19th century. Phosphorescent materials store absorbed energy and release it slowly as light over minutes or hours by trapping electrons in an excited state. There are two types of photoluminescence - fluorescence which emits light quickly, and phosphorescence which emits light slowly. Common phosphorescent materials include zinc sulfide and strontium aluminate.