This document discusses databases and the relational database model. It covers key concepts like data, records, fields, and tables. It also explains entity relationship diagrams and how they are used to represent relationships between entities. Different types of relationships like one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many are defined. An example entity relationship diagram is provided for a company database with employees, departments, and projects. Finally, it shows how to design tables from an entity relationship diagram by creating fields for each entity's attributes and adding foreign keys to represent relationships between tables.




![Al Karma Language School
CHAPTER THREE
Relational Database Model
First: Drawing a table for each entity in [ERD], we find that the fields are the attributes
of this entity:
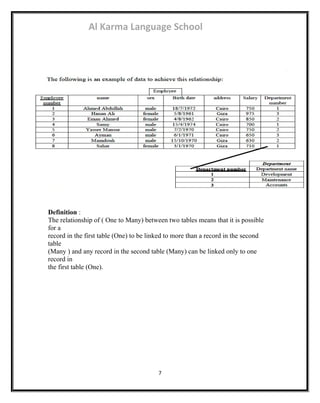
Employee:
Employee number name gender Birth date address salary
Department
Department number Department name
Project
project number name Location
Notes:
· The name of the table is put at the top before the field name.
· One of the entity key attributes is selected to be a primary key and underline
the field name to highlight it.
· The field of (Employees number) has not been put for each "department" in
(Department Table), because the number of employees is a derived attribute.
In other words, it can be counted from the relationship between (department)
and (employee).
· Field location has not been put for the (Department table) because
(Department location) represents a multi- valued attribute. In other words, a
certain department can have more than a location as shown in the following
example; this is in case of putting the field of (Department location) in
(Department table).
Definition :
The composite key is more than a field in a table whose components together do
not recur. It distinguishes each record where as each field can be repeated solo.
1-Between the tables of (Department and Employee)
a-The relationship of "working in department ":
As the relationship "One to Many" in department table as shown in the previous
chapter from the ERD. Therefore, we will add a field in the table that represents
(Many) in the "employee table", In this case, it expresses (Department Number)
where an employee works. In other words, this field is linked to the field of
(Department number) in (Department table). In this case, it is called (Foreign Key
Field)
Definition
The Foreign Key is a strange field in a table linked to "Primary Key" in another table.
NOTE:
It is not required to nominate the foreign key with the primary field name linked
to it. However, it must be of the same type and size as shown in designing the table
using the computer.
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-sec2-1stterm-141027112212-conversion-gate02/85/Computer-sec2-1st-term-6-320.jpg)