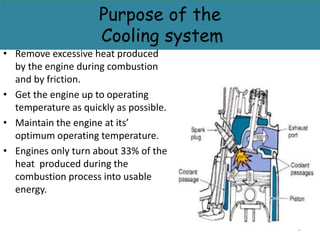
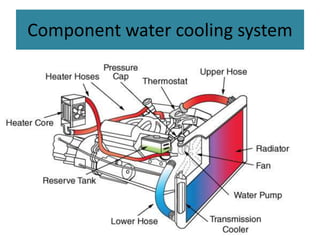
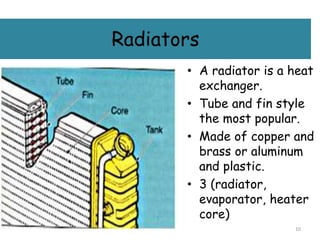
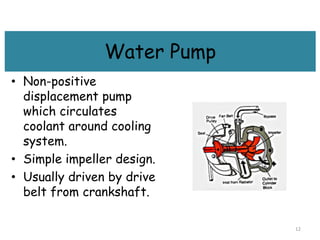
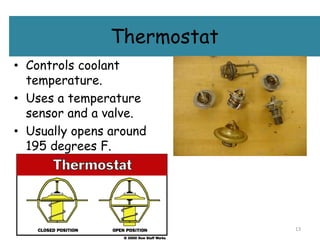
The cooling system serves to remove excess heat from the engine through combustion and friction. It works to quickly bring the engine up to optimal operating temperature and maintain it there. There are two main types - air cooling, which radiates heat through fins to the atmosphere, and liquid/water cooling, which circulates coolant through water jackets and a radiator. Water cooling cools more uniformly and improves fuel efficiency but requires more components and depends on the water supply. The main components of a water cooling system are the radiator, water jackets, water pump, and thermostat.