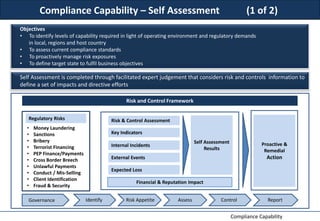
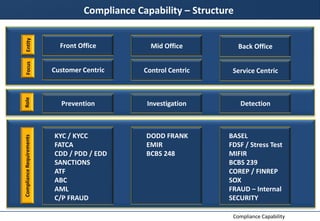
This document discusses developing a compliance capability for an organization. It outlines principles for taking an end-to-end view of business processes to ensure compliance. Ownership and accountability for compliance must be clear from leadership down. Compliance processes should be integrated into business functions from the start. Automating compliance functions and integrating compliance into transaction lifecycles can help comprehensively control processes. Self-assessments can identify compliance capabilities and gaps to help define a target compliance state.