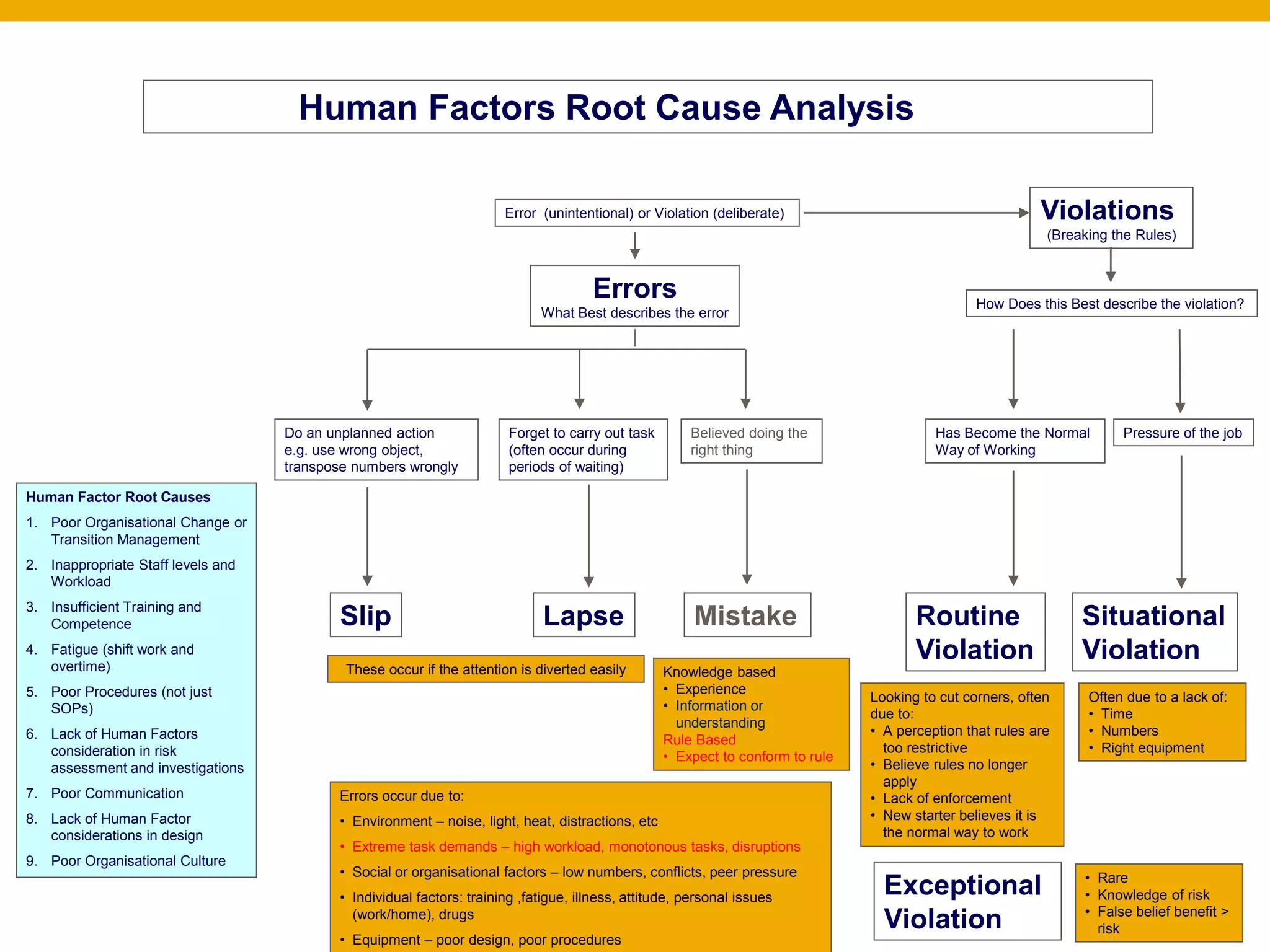
This document outlines different types of human errors and violations that can occur. It describes errors as unplanned actions like using the wrong object or transposing numbers. Errors can be slips from forgetting tasks or lapses from easily diverted attention. Violations are deliberate breaks of rules that can be routine from believing incorrect actions are normal, situational due to lack of resources, or exceptional when risks are known. Nine root causes of human factor issues are identified, including poor organizational change management, inappropriate staffing levels, insufficient training, fatigue, poor procedures, lack of human factors in risk assessment and investigations, poor communication, lack of human factors in design, and poor organizational culture.