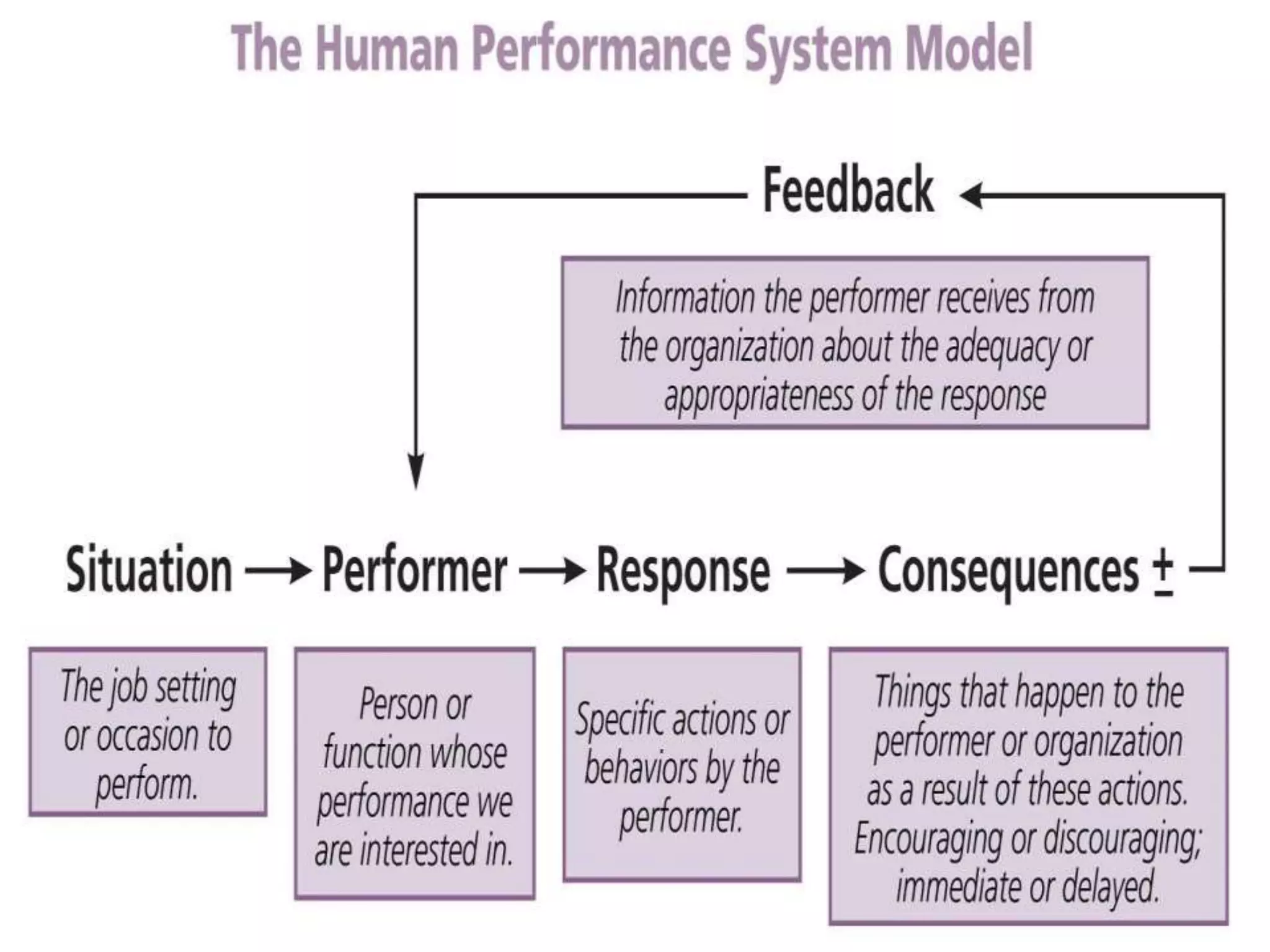
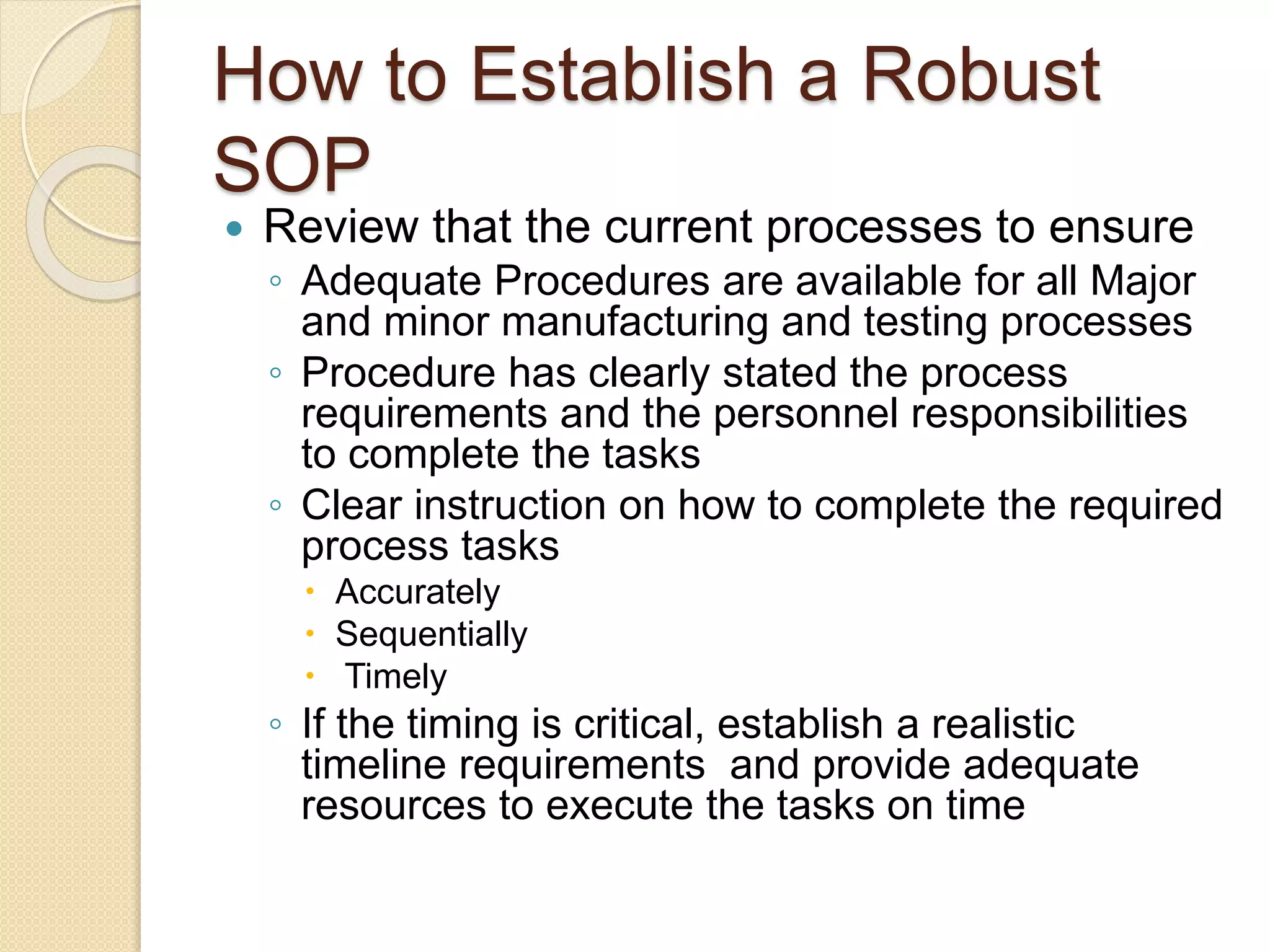
This document discusses human errors, how to identify and reduce them. It defines human error as an inappropriate decision or behavior that reduces system effectiveness, safety or performance. It notes that errors can be due to individual factors as well as external factors like equipment design or procedures. There are three types of errors - skill-based from routine tasks, rule-based from familiar situations, and knowledge-based from unique situations. The document recommends reducing errors through better recruitment, training, design of equipment/procedures, and feedback systems to continuously improve performance.