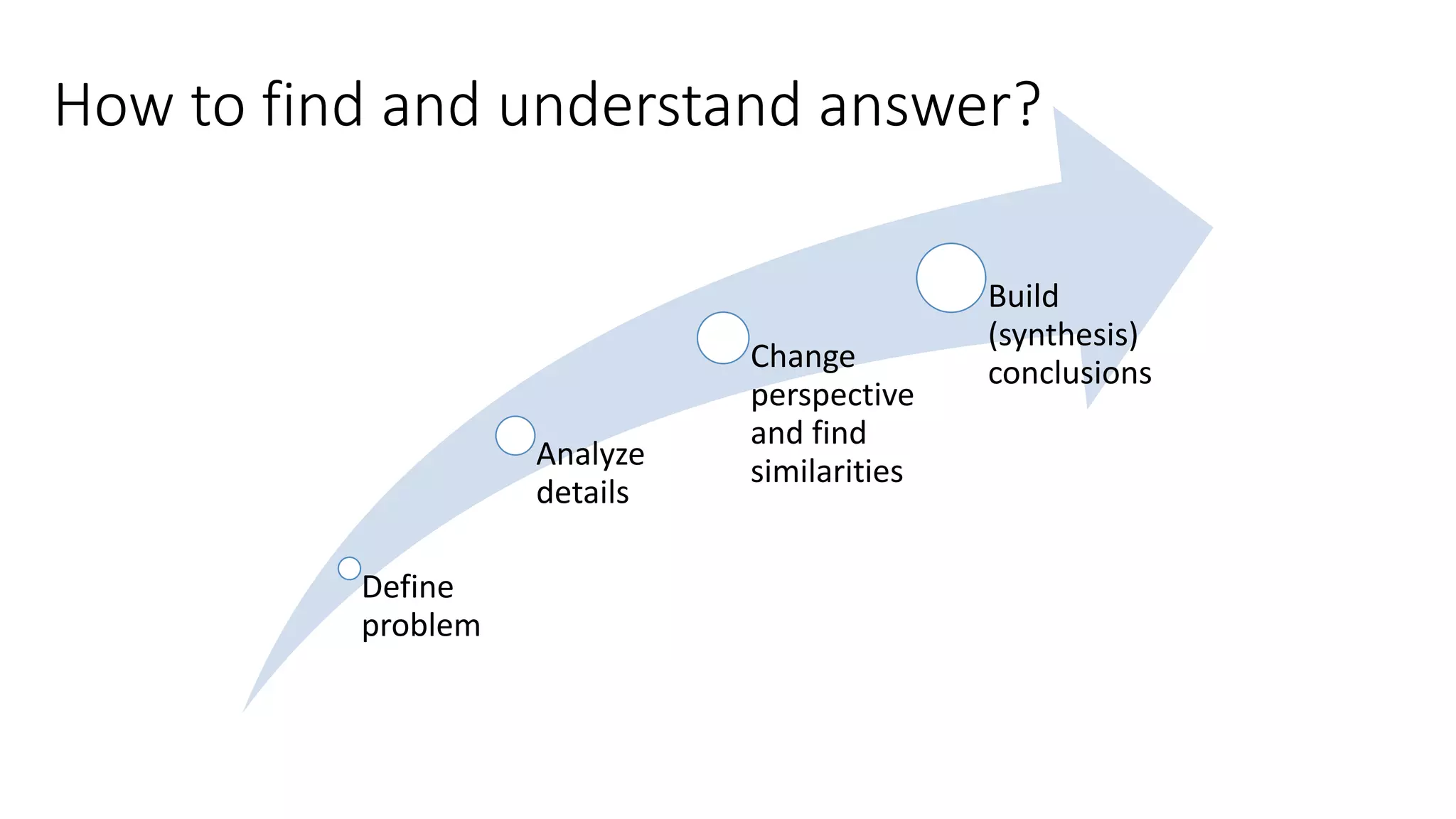
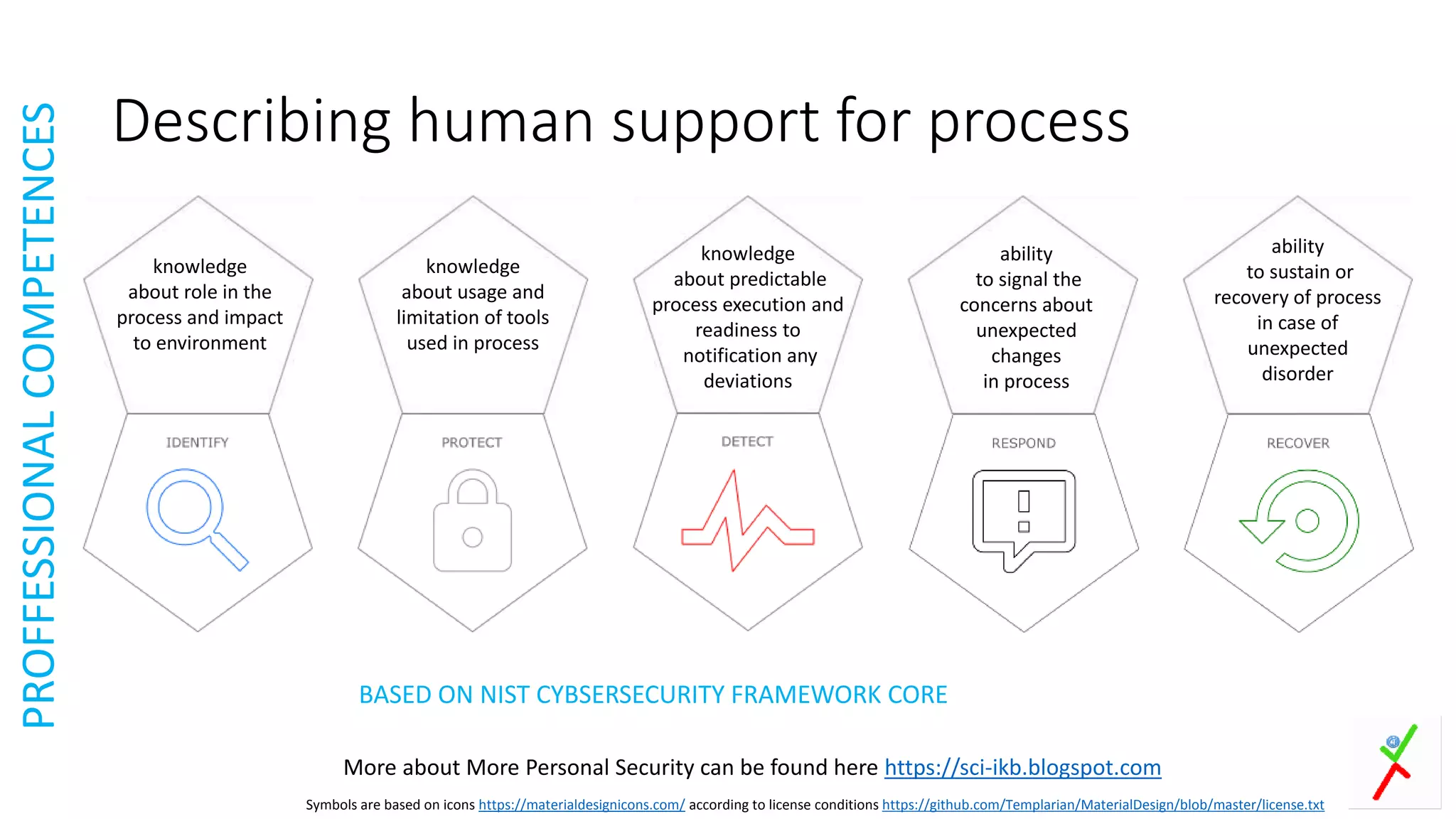
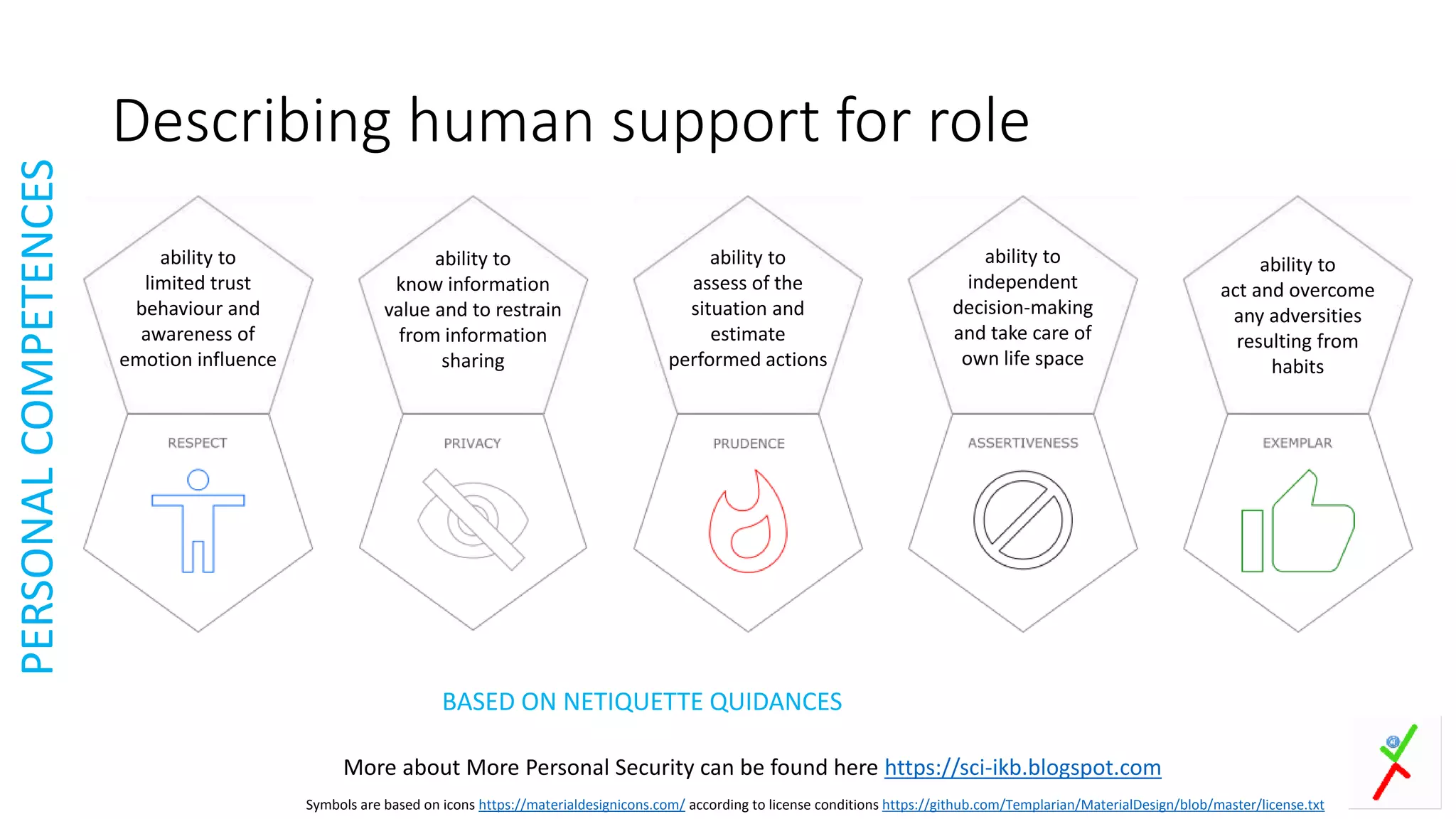
The document provides an extensive overview of human factor safety, detailing the complexities of human behavior and its impact on safety in various environments. It identifies the 'dirty dozen' human errors and offers strategies for mitigating these issues through improved communication, teamwork, and awareness. A key focus is on developing human competencies and creating a supportive environment to enhance safety practices and reduce errors.