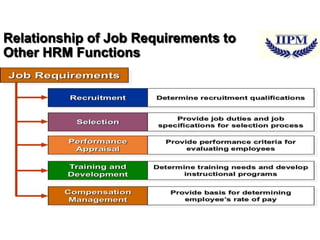
Job analysis is the process of obtaining information about jobs to determine their duties, tasks, and activities. This information is used by HR managers to develop job descriptions and specifications that form the basis for recruitment, training, performance appraisal, and career development. The goal is to improve organizational performance and productivity. Job analysis involves studying workflows, reengineering processes, and designing jobs. It identifies the tasks, duties, responsibilities, knowledge, skills, abilities, and competencies required for each position. The results inform other HR functions like recruitment, selection, training, and compensation. Information can be gathered through interviews, questionnaires, observation, diaries, and computer systems.