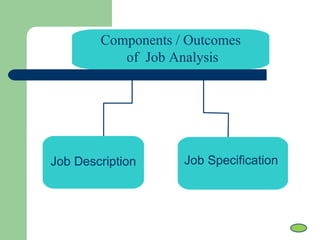
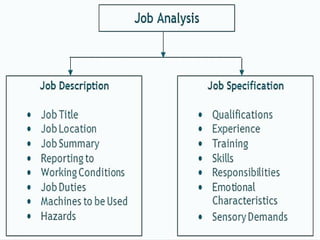
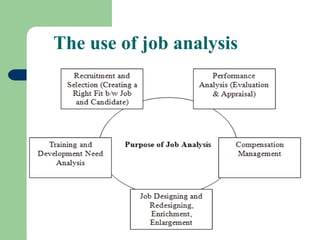
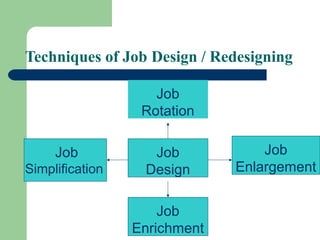
Job analysis is the systematic study of job tasks, duties, and responsibilities to define specific job positions within an organization. It results in a job description and job specification, outlining the necessary qualifications and skills for performing the job effectively. The analysis aids in recruitment, performance evaluation, training needs assessment, compensation management, and job redesign.