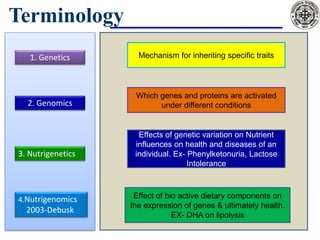
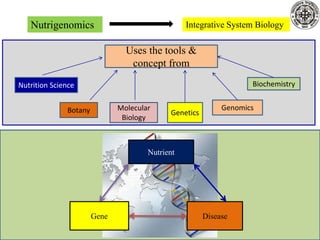
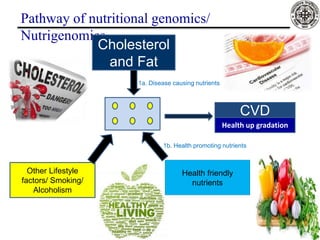
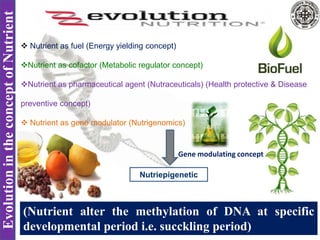
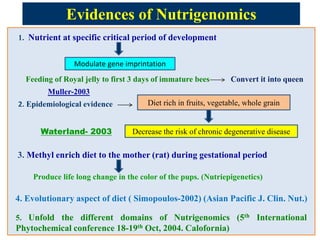
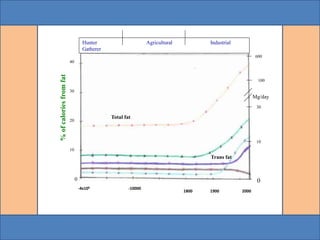
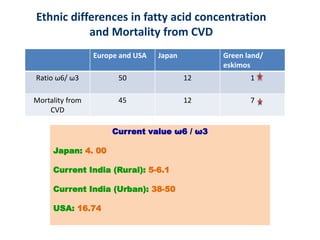
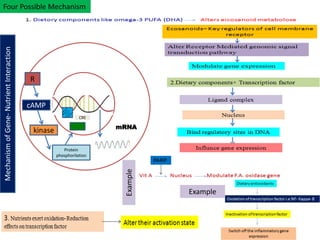
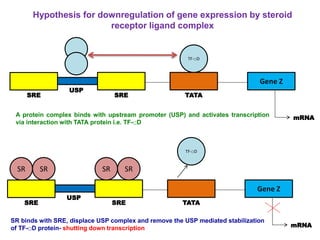
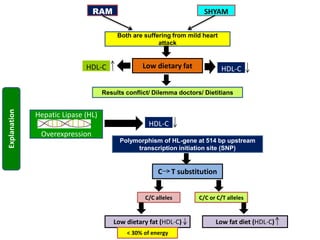
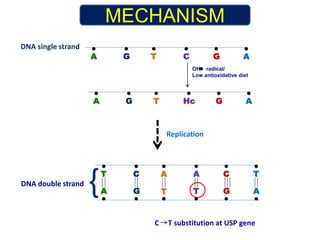
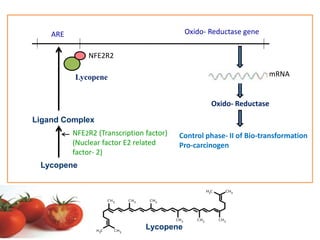
Nutrigenomics is an emerging scientific discipline that studies the effects of foods and dietary components on gene expression. It explores how nutrients and bioactive compounds in food can turn genes on and off and influence our health. Some key points covered in the document include:
- Nutrigenomics uses tools from fields like genetics, molecular biology, and genomics to study nutrient-gene interactions.
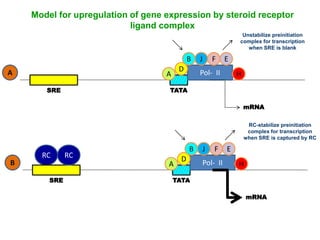
- Certain nutrients consumed during critical periods of development can modulate gene imprinting and influence long-term health outcomes.
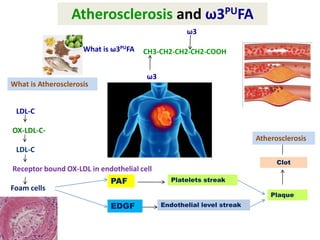
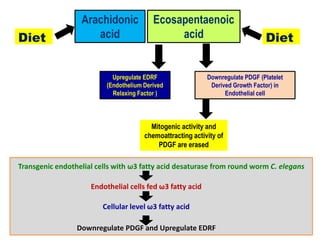
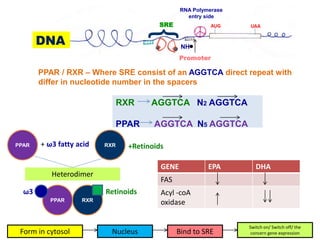
- Omega-3 fatty acids from foods like fish have been shown to downregulate genes associated with heart disease and upregulate genes related to cardiovascular health.
- Nutrigenomics research is providing insights into personalized