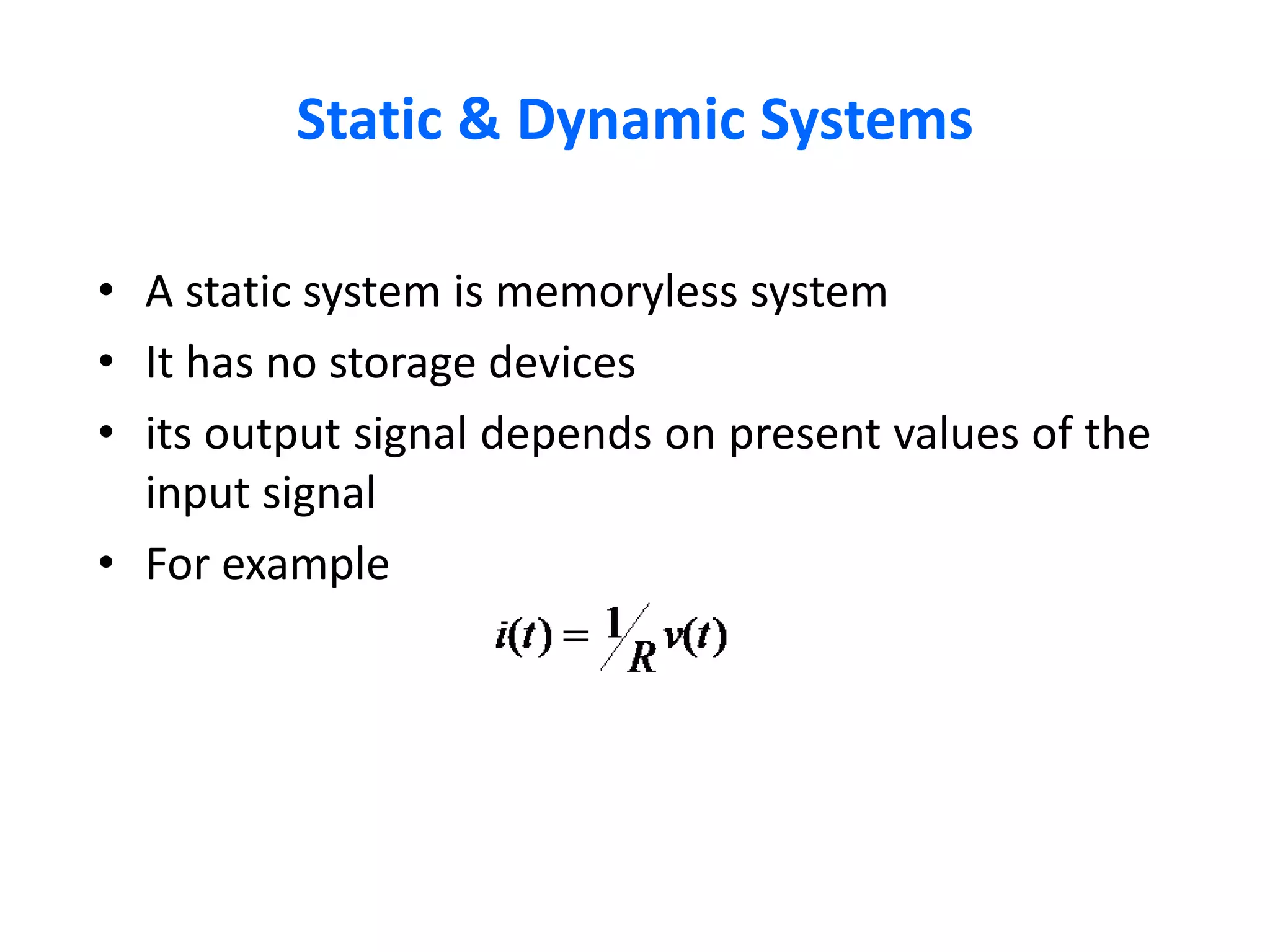
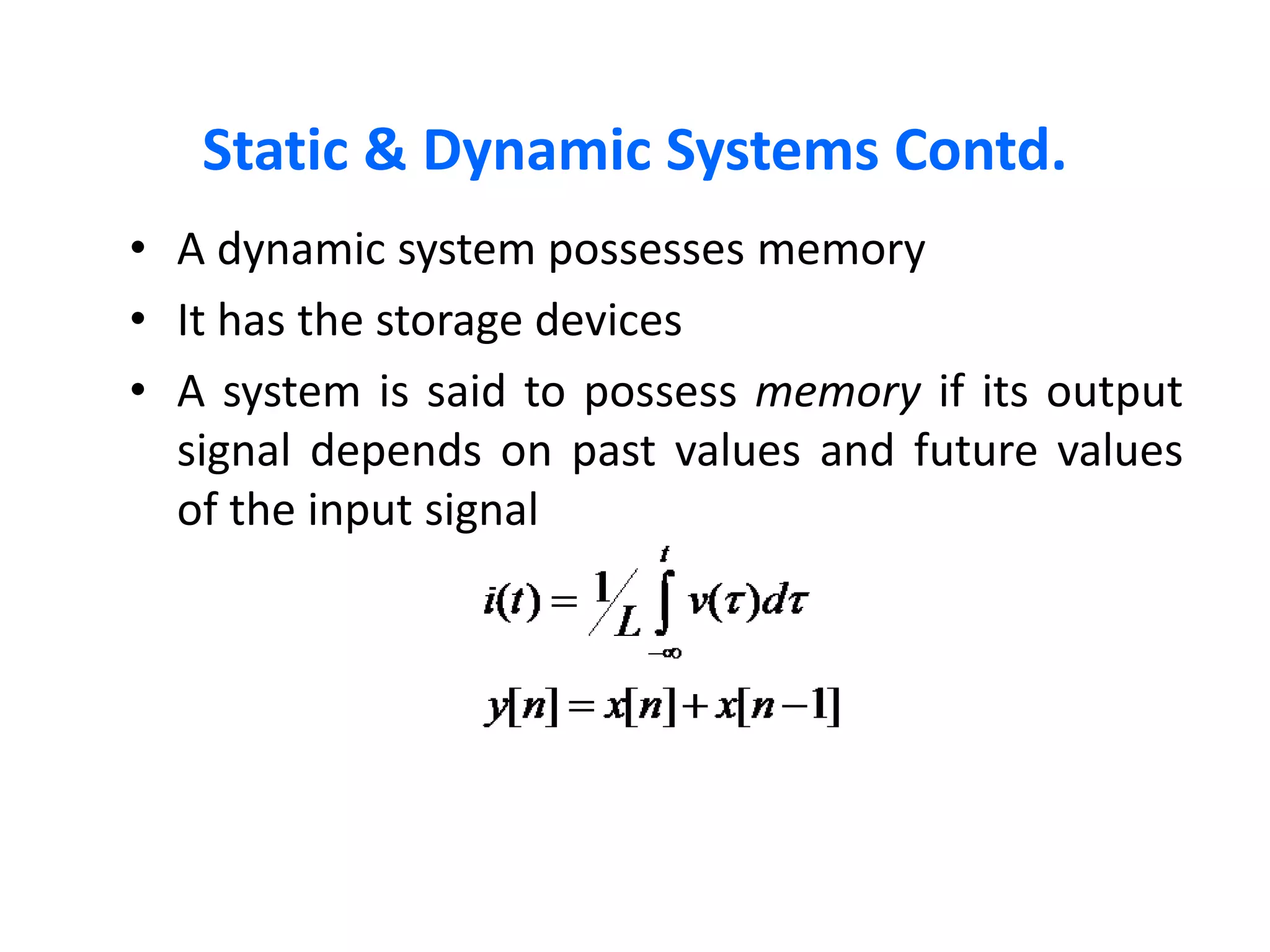
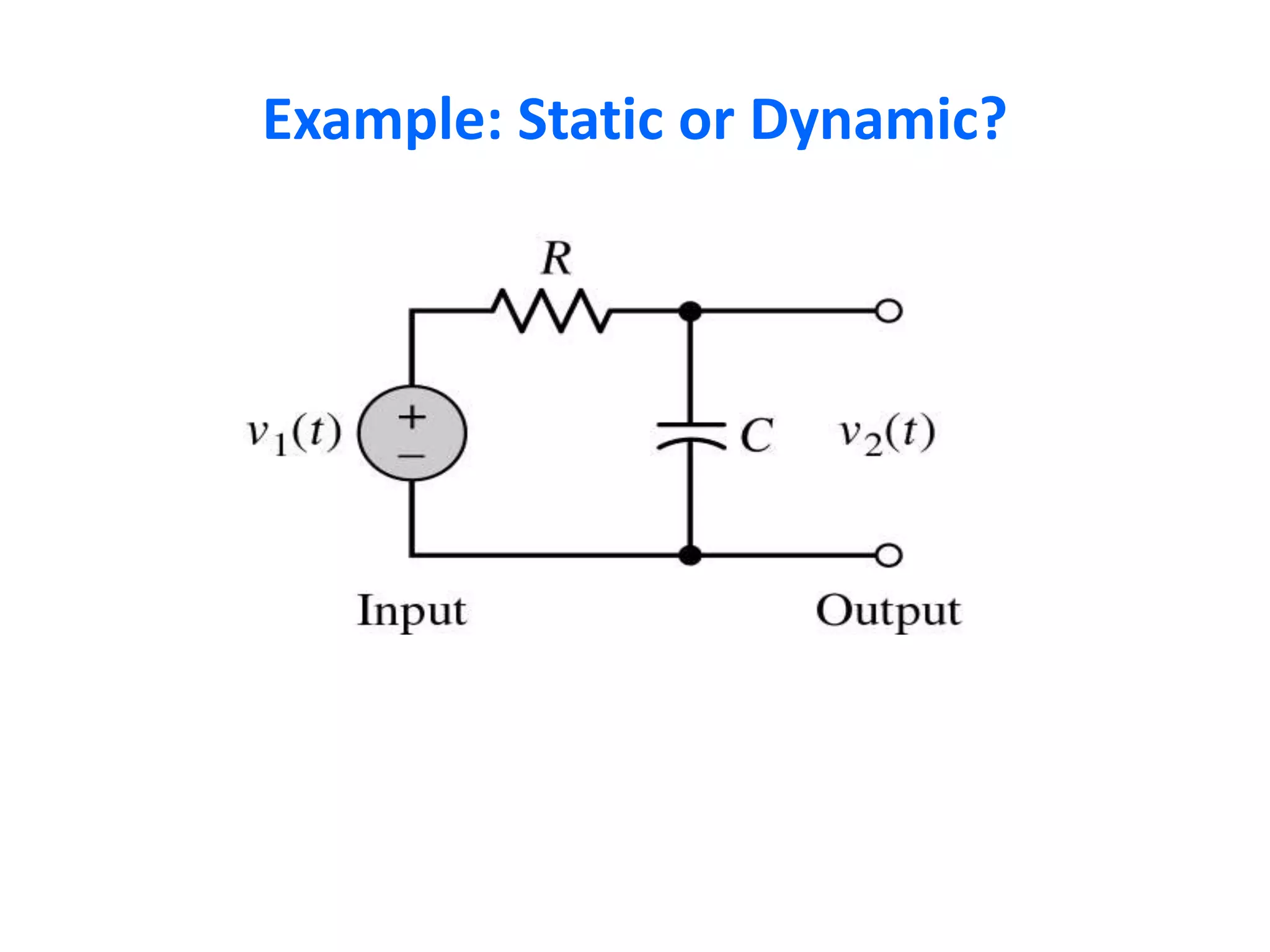
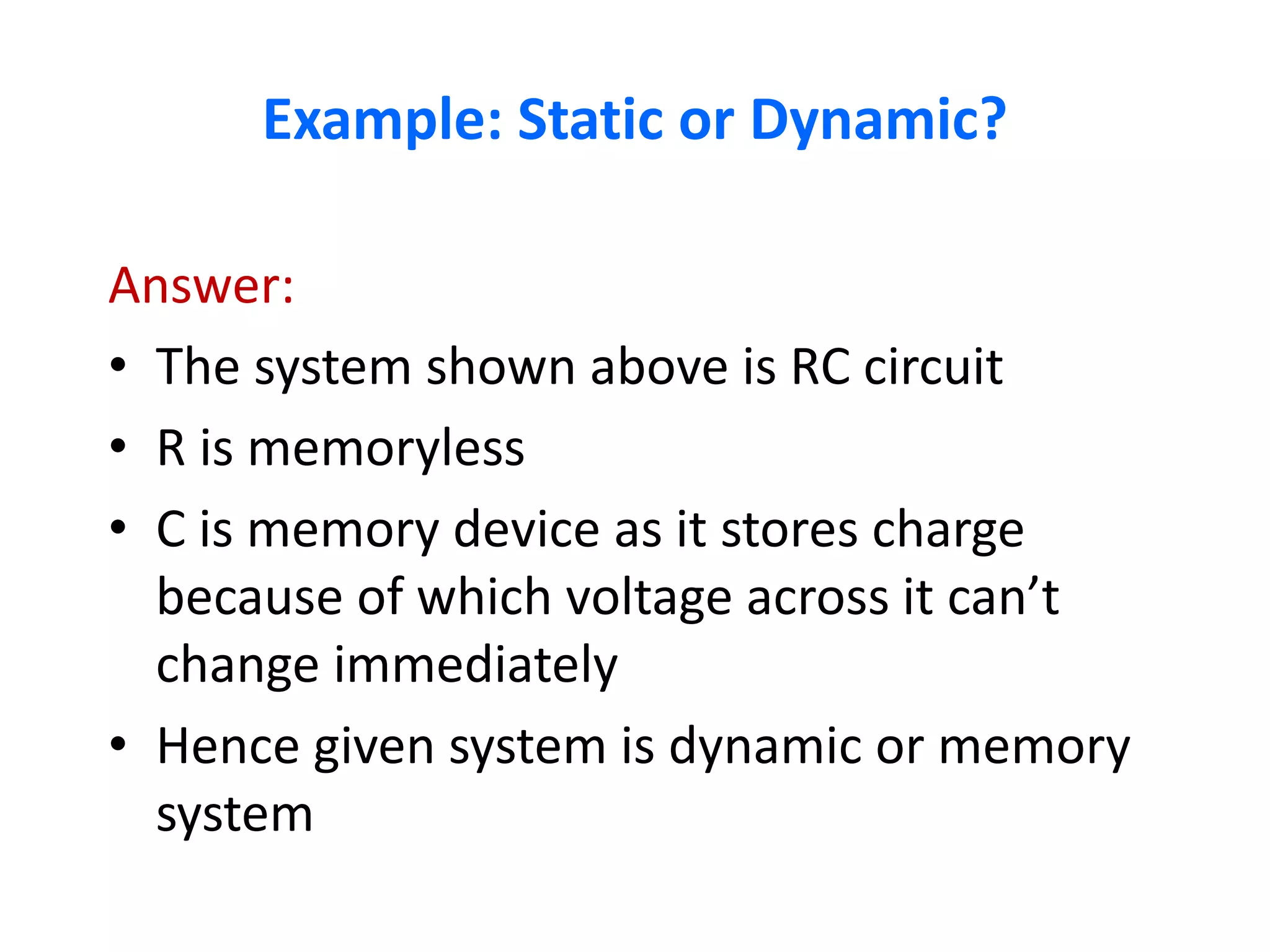
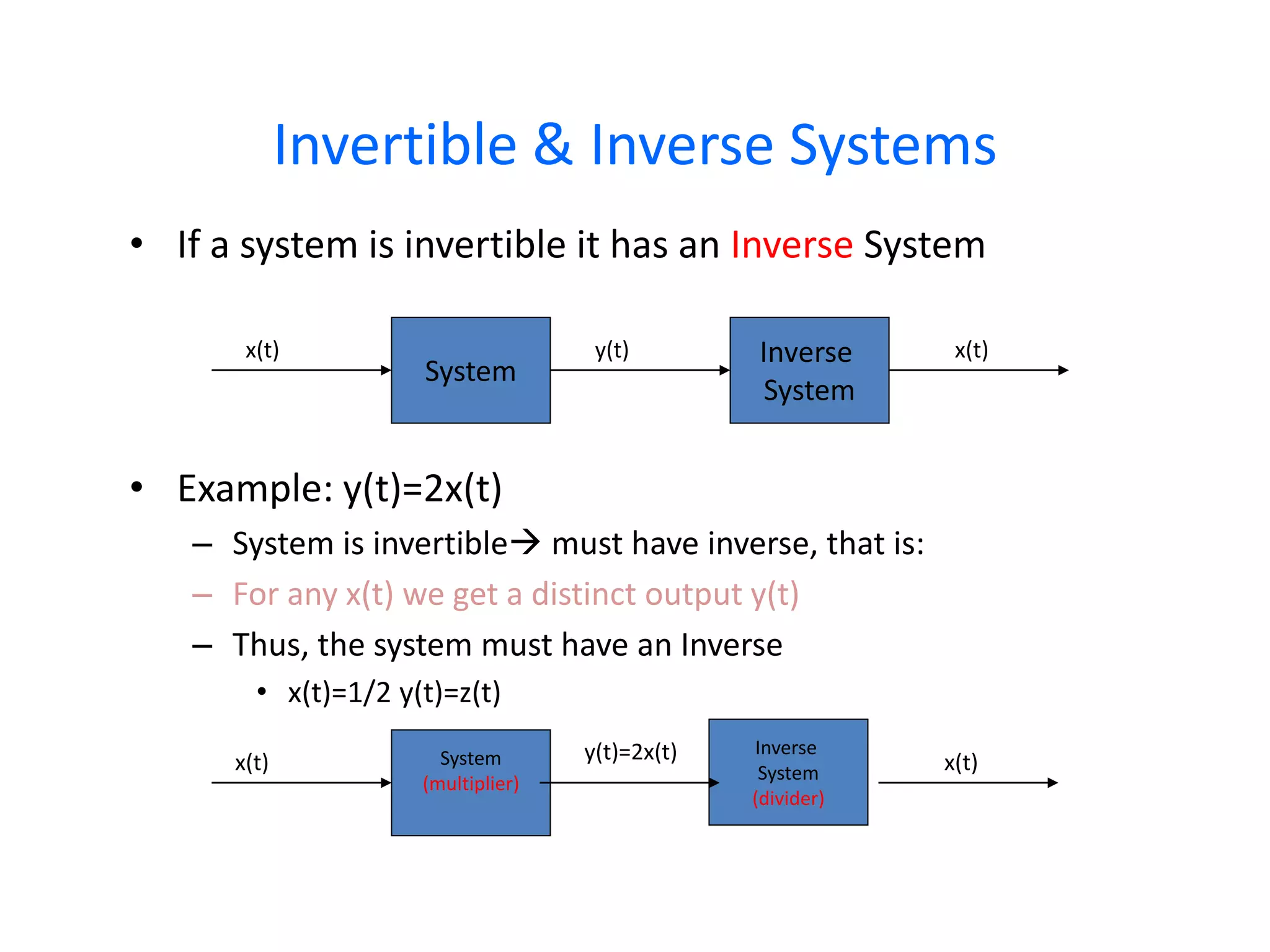
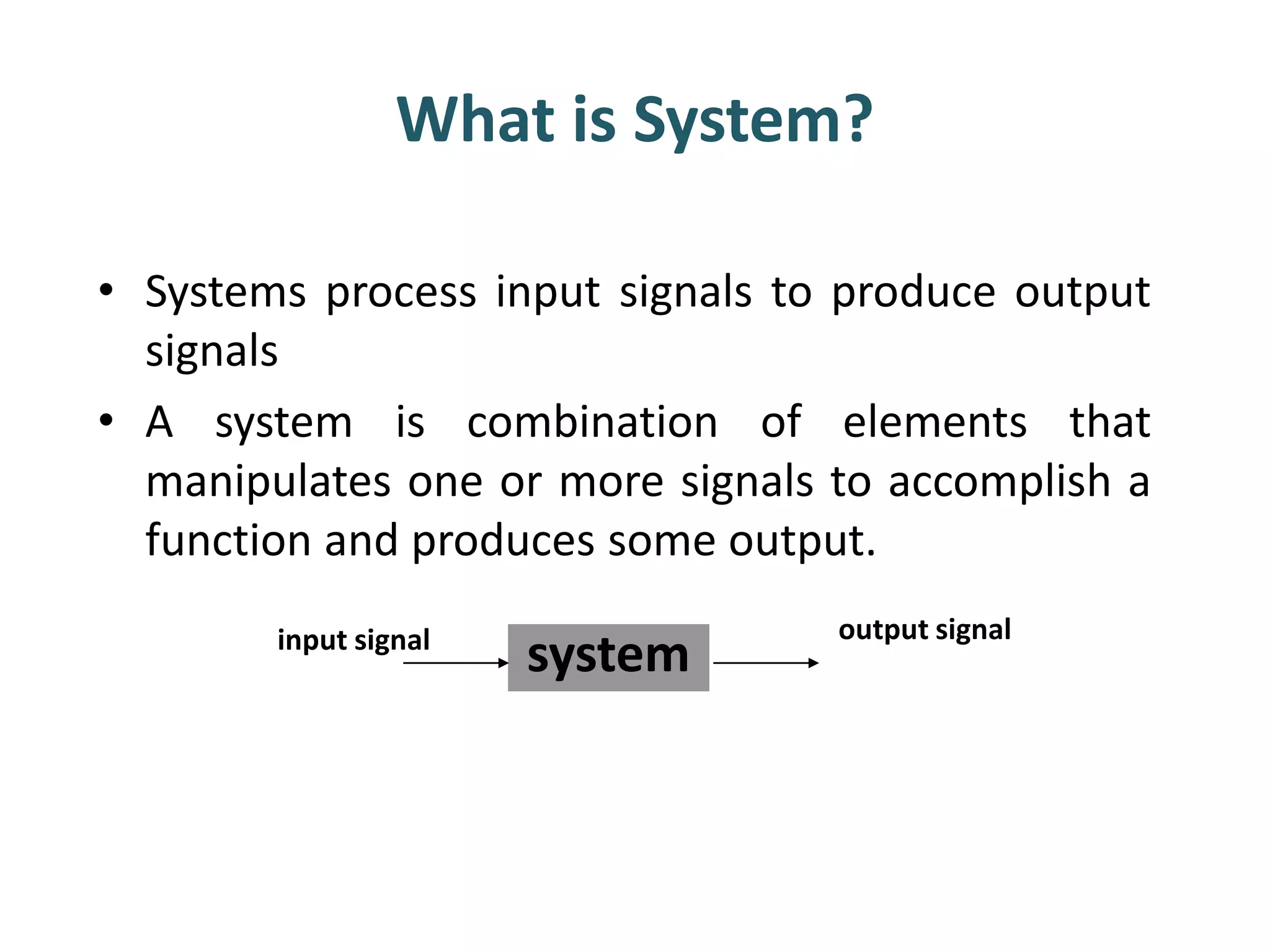
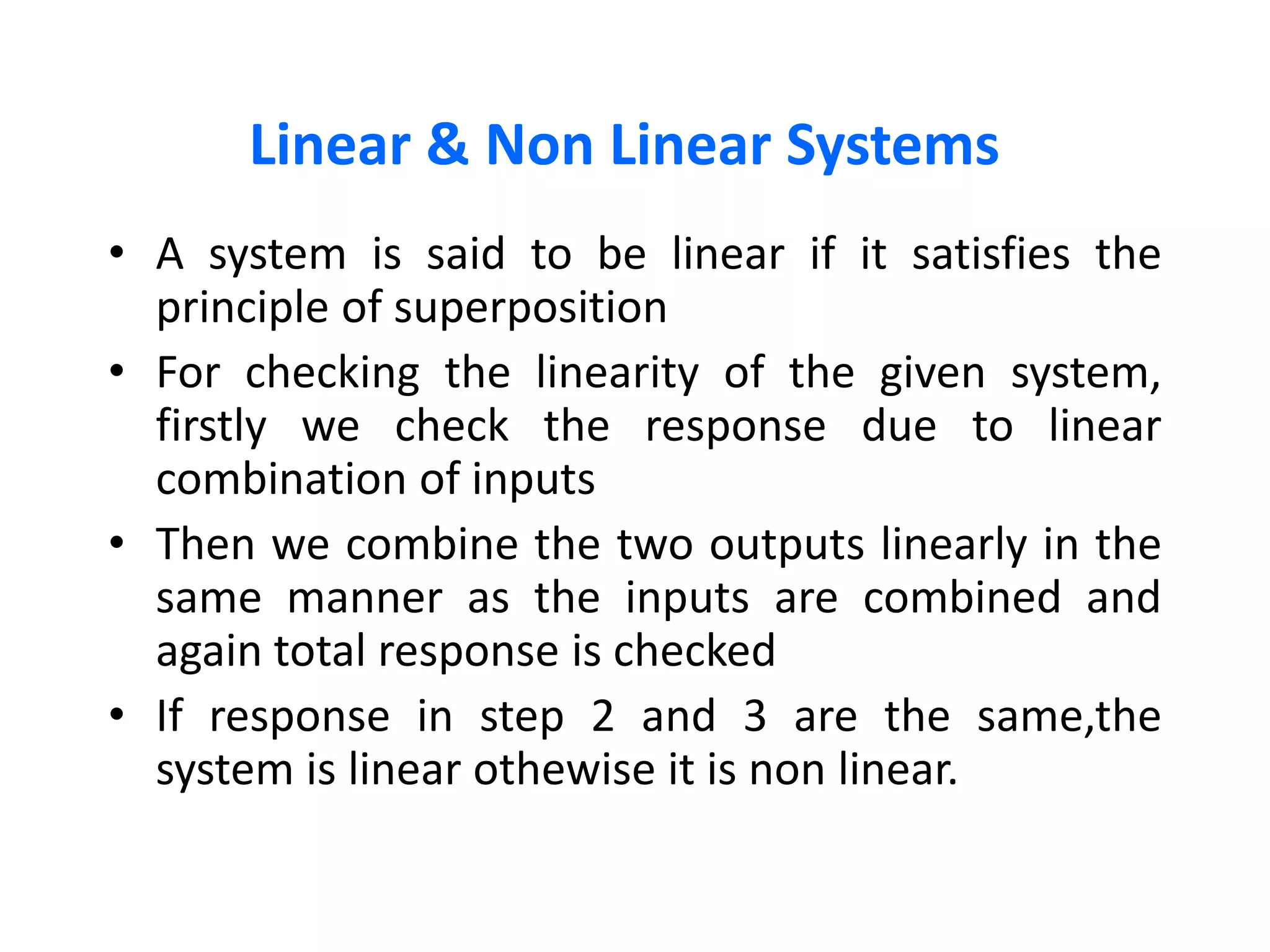
A system processes input signals to produce output signals. It is a combination of elements that manipulate one or more signals to accomplish a function. There are different types of systems including causal/anticausal, linear/nonlinear, time-invariant/time-variant, stable/unstable, static/dynamic, and invertible/non-invertible systems. Causal systems depend on past and present input values, while anticausal systems depend on future input values. Linear systems satisfy superposition principles, while nonlinear systems do not. Time-invariant systems produce identical output shifts for identical input shifts. Stable systems produce bounded outputs for bounded inputs. Dynamic systems possess memory while static systems do not. Invertible systems have inverse systems that can
![Causal & Anticausal Systems
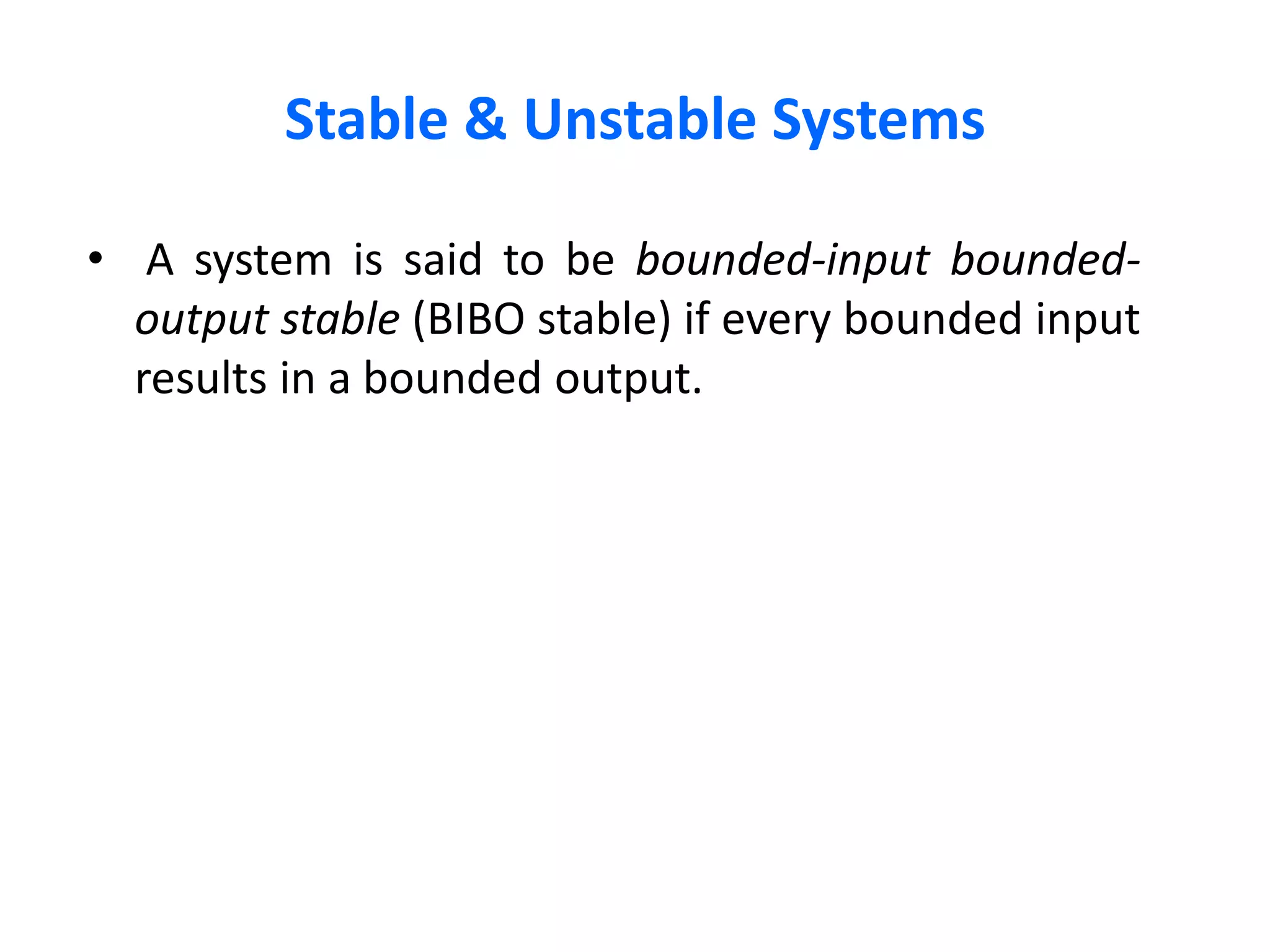
• Causal system : A system is said to be causal if the
present value of the output signal depends only
on the present and/or past values of the input
signal.
• Example: y[n]=x[n]+1/2x[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofsystem-150506134405-conversion-gate02/75/Types-of-system-3-2048.jpg)
![Causal & Anticausal Systems Contd.
• Anticausal system : A system is said to be
anticausal if the present value of the
output signal depends only on the future
values of the input signal.
• Example: y[n]=x[n+1]+1/2x[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofsystem-150506134405-conversion-gate02/75/Types-of-system-4-2048.jpg)

![Stable & Unstable Systems Contd.
Example
- y[n]=1/3(x[n]+x[n-1]+x[n-2])
1
[ ] [ ] [ 1] [ 2]
3
1
(| [ ]| | [ 1]| | [ 2]|)
3
1
( )
3
x x x x
y n x n x n x n
x n x n x n
M M M M
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofsystem-150506134405-conversion-gate02/75/Types-of-system-8-2048.jpg)