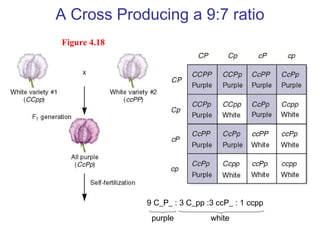
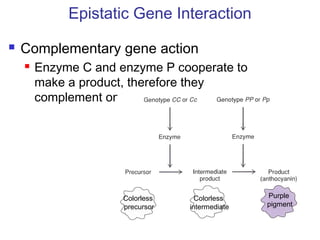
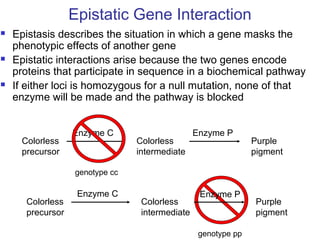
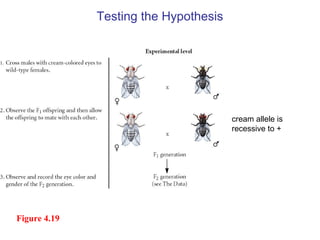
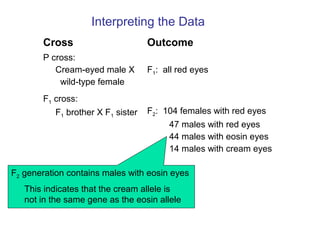
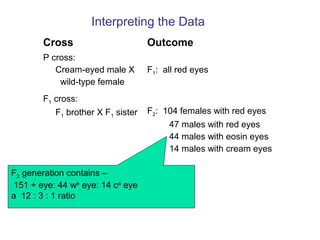
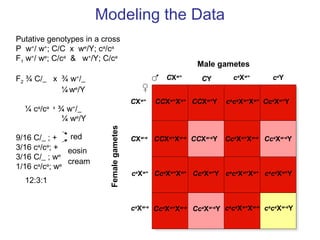
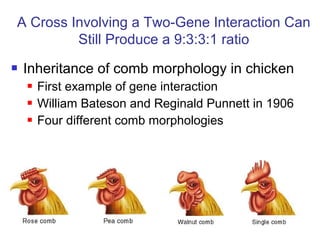
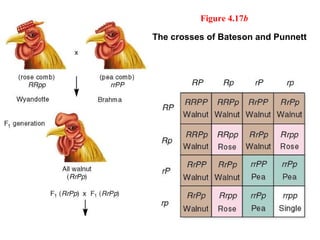
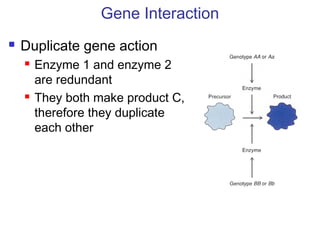
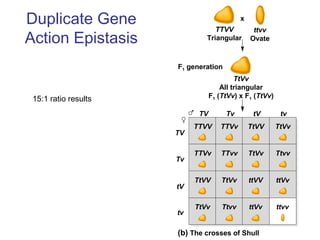
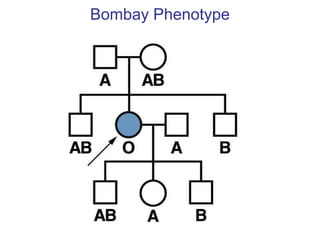
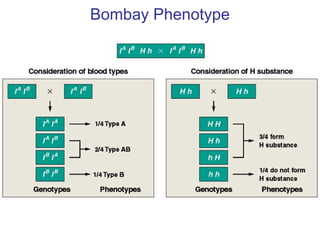
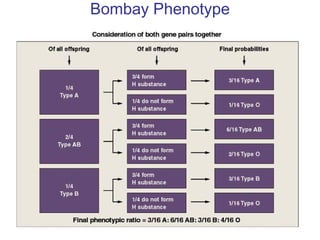
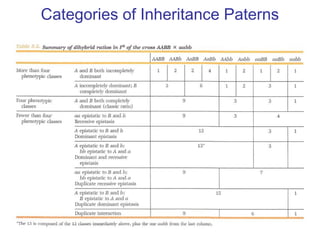
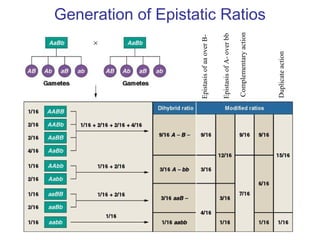
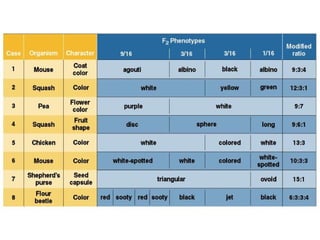
This document discusses gene interactions and epistasis. It provides several examples of gene interactions that result in ratios other than the expected 9:3:3:1 ratio for dihybrid crosses. These include complementary gene action between two enzymes that produce a product, duplicate gene action where two genes encode redundant enzymes, and different forms of epistasis where one gene is masked by the other. Specific examples discussed include interactions governing pigment production in fruit flies and comb morphology in chickens.