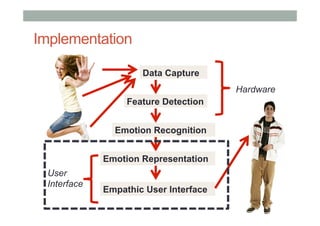
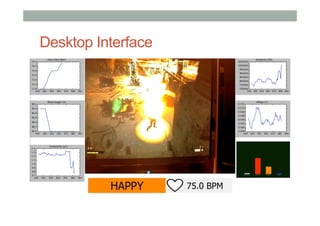
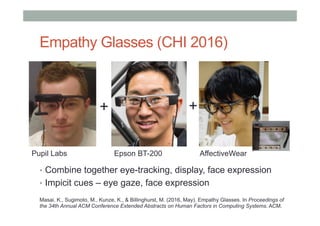
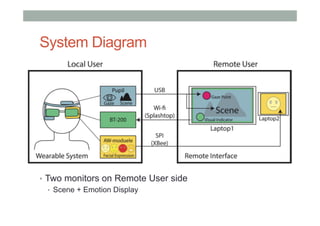
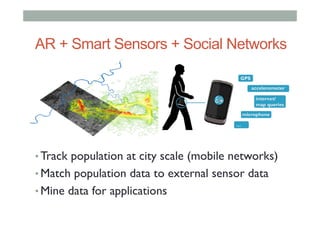
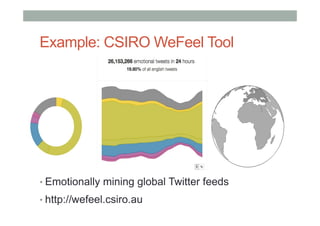
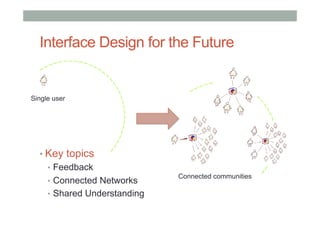
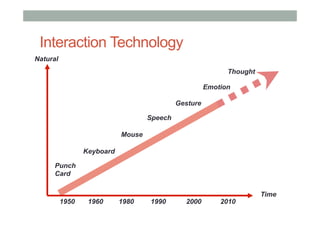
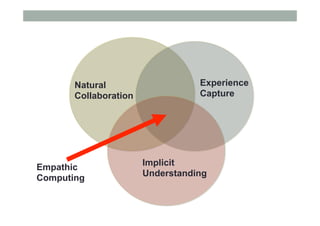
The document discusses advancements in empathic computing and interface technology, emphasizing the importance of shared understanding and connected networks in enhancing user interactions. It highlights various technologies such as augmented reality and wearable devices designed to foster empathy through experience sharing and emotional recognition. Future research directions are suggested, focusing on scaling experiences to broader populations and improving collaborative technologies.
























![Social Panoramas (ISMAR 2014)
• Capture and share social spaces in real time
• Supports independent views into Panorama
Reichherzer, C., Nassani, A., & Billinghurst, M. (2014, September). [Poster] Social panoramas using
wearable computers. In Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), 2014 IEEE International Symposium
on (pp. 303-304). IEEE.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chiuxid2016-160414221331/85/From-Interaction-to-Empathy-38-320.jpg)