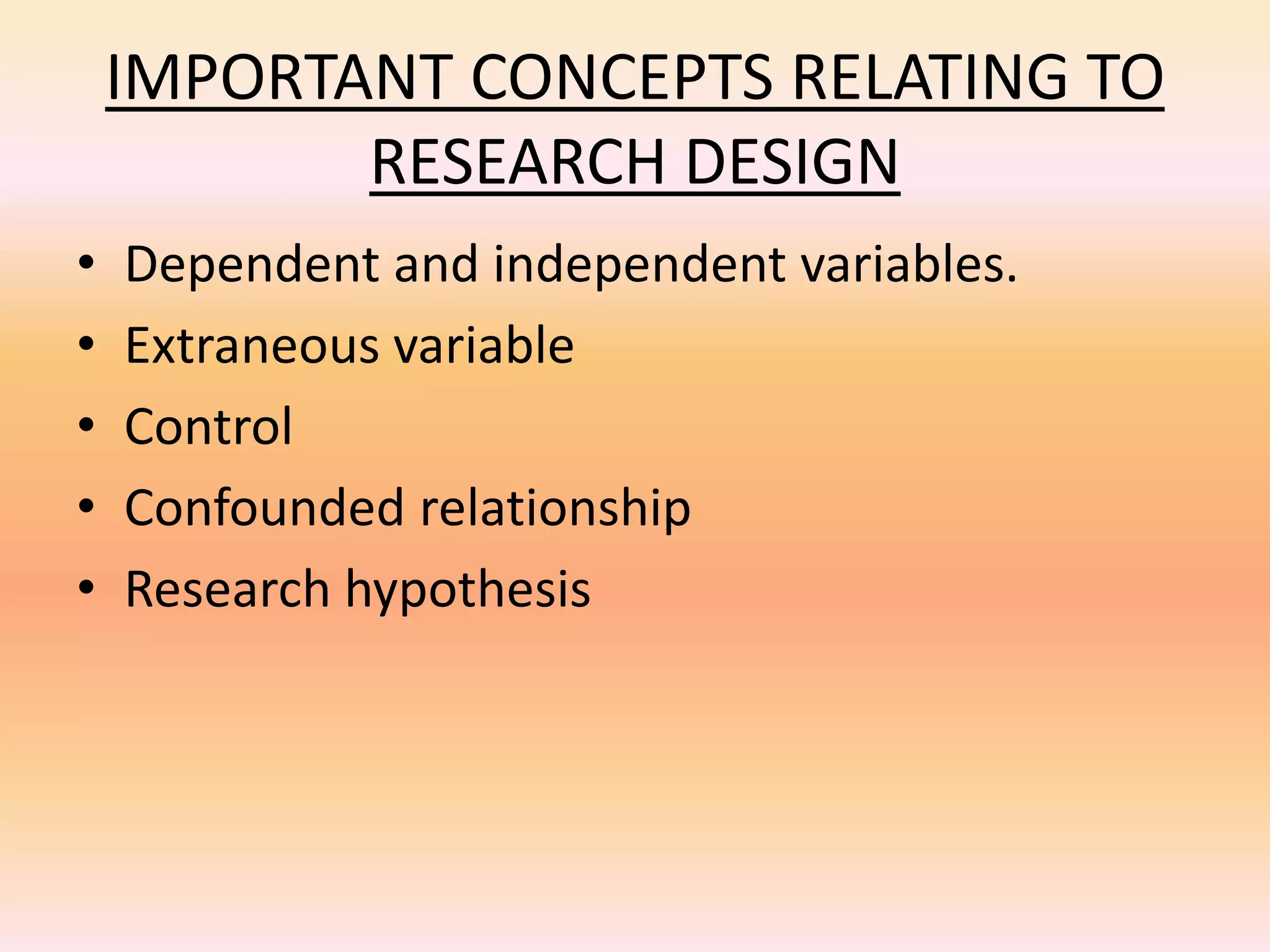
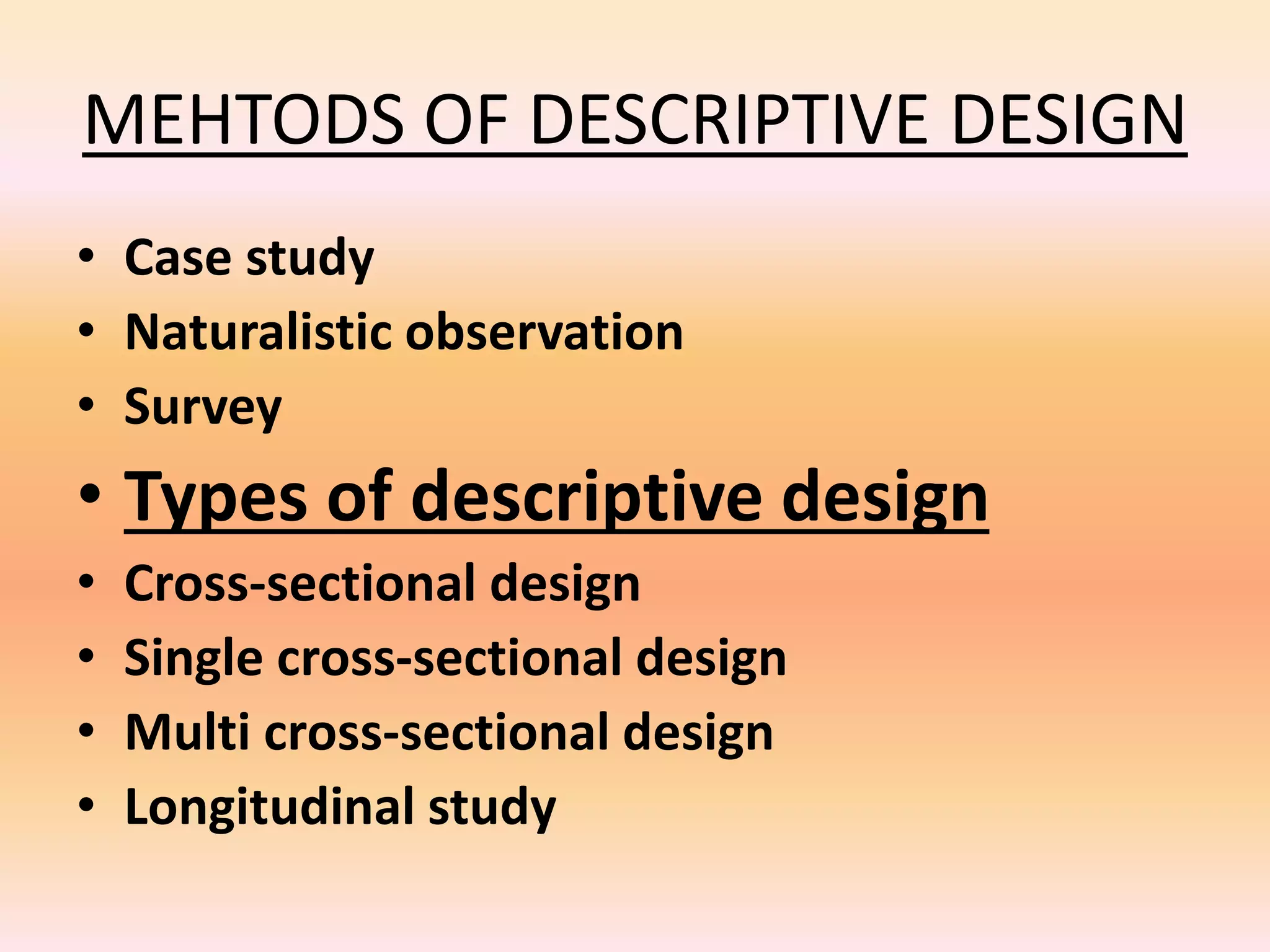
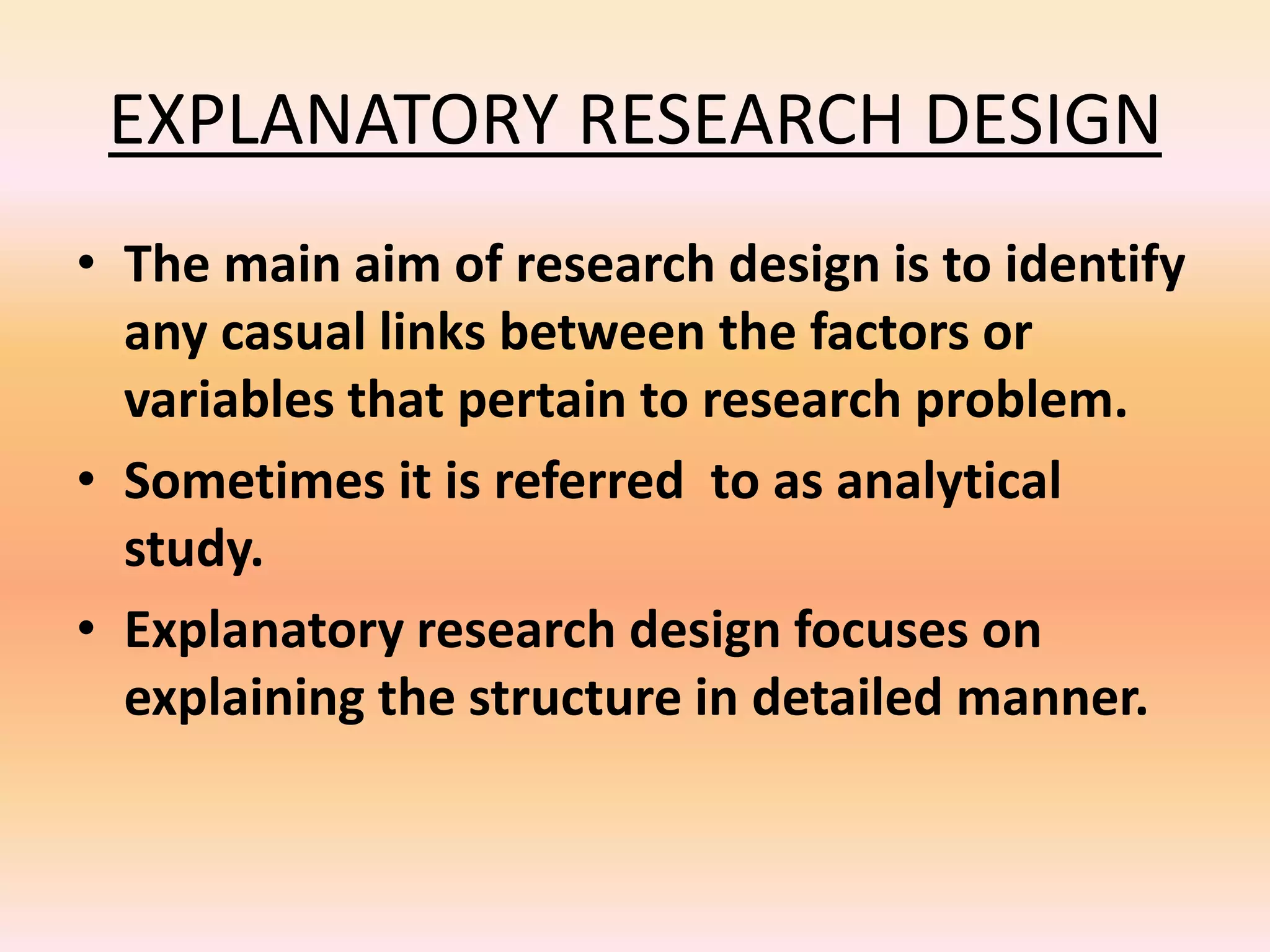
This document discusses different types of research design: exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory. Exploratory design is used to investigate a new area and form hypotheses. Descriptive design aims to describe a problem and its solutions. Methods include surveys, observations, and case studies. Explanatory design identifies causal links between variables through methods like literature reviews, in-depth interviews, and case analysis. The document emphasizes that research design provides a logical plan for conducting a study to maximize valid answers to research questions through the appropriate use of exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory approaches.