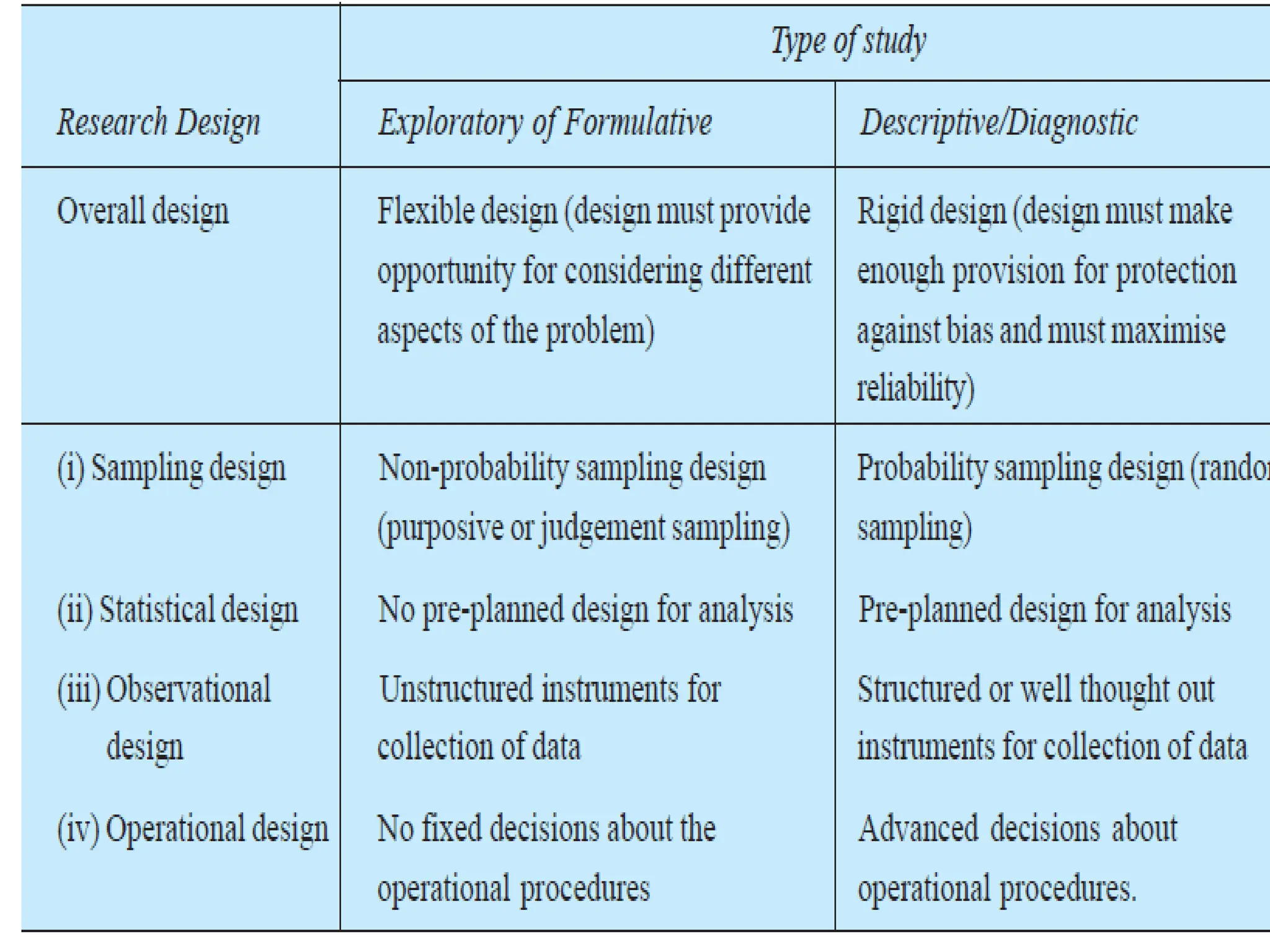
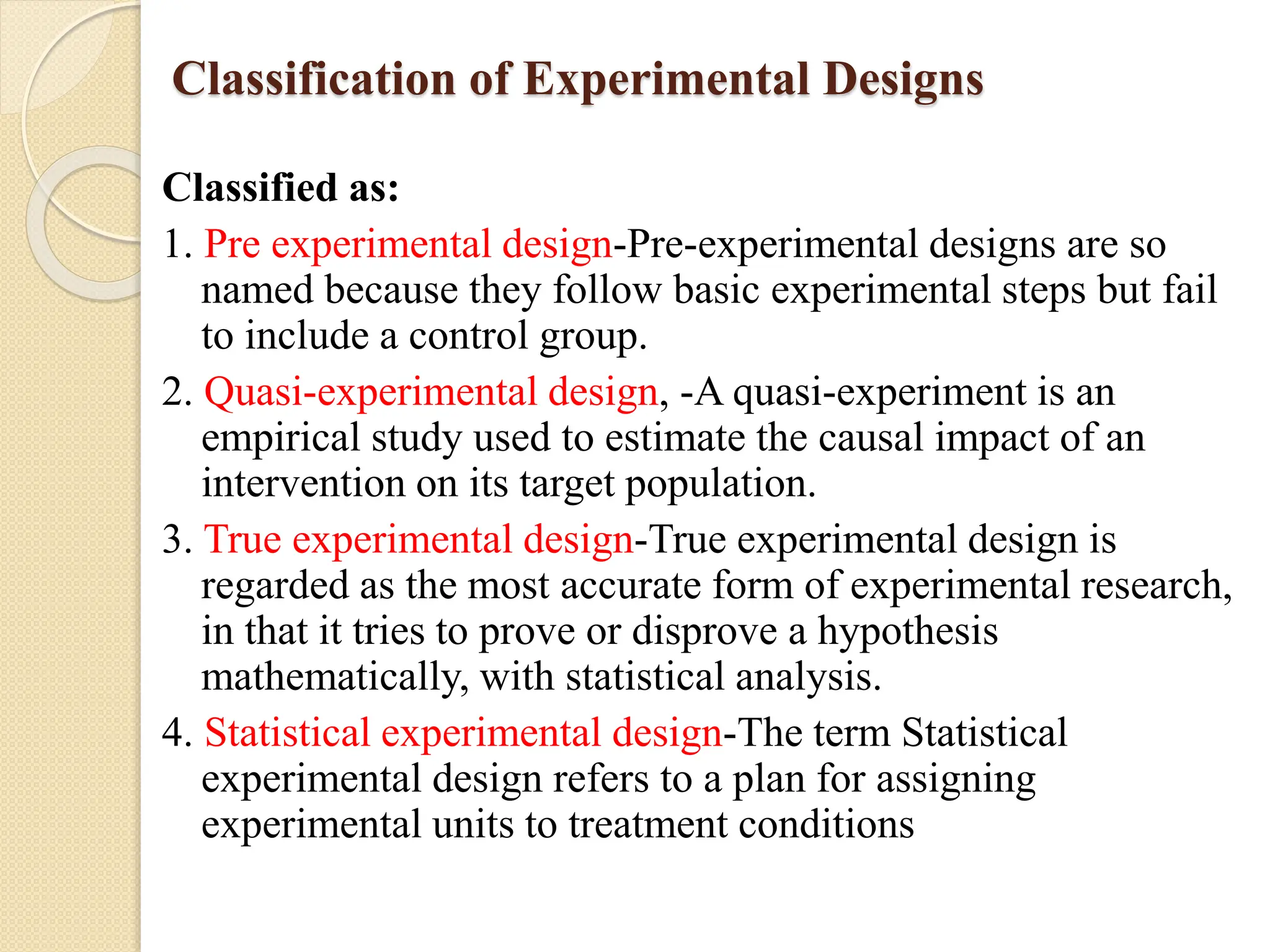
The document outlines the essential components and considerations involved in business research design, focusing on decision-making aspects such as objectives, data types, and analysis techniques. It distinguishes between different types of research designs, including exploratory, descriptive, diagnostic, and experimental studies, each serving unique purposes in research methodology. Important characteristics of good research design include flexibility, efficiency, and the minimization of bias while maximizing data reliability.