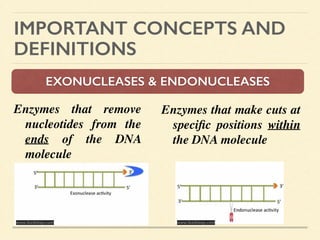
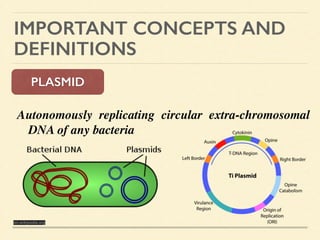
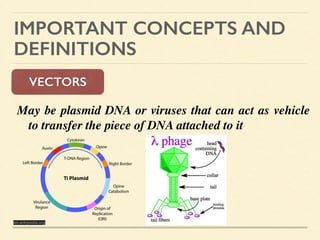
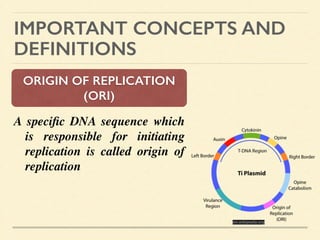
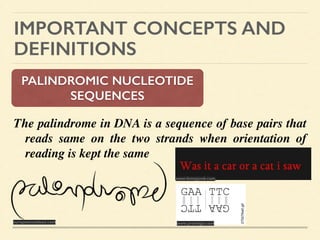
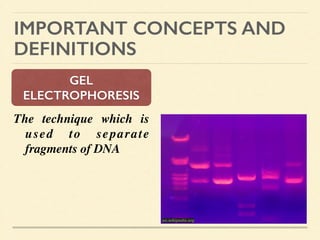
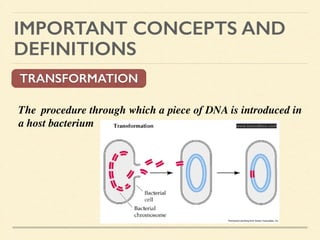
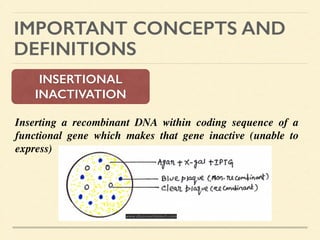
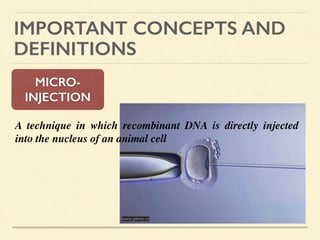
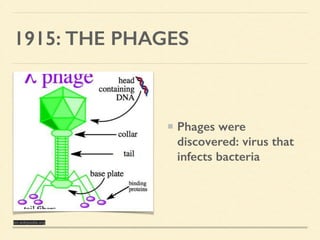
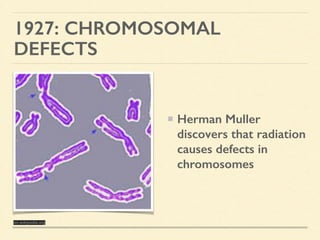
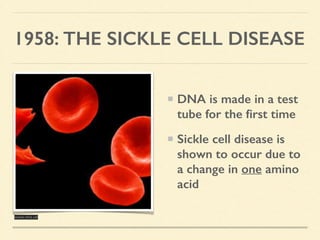
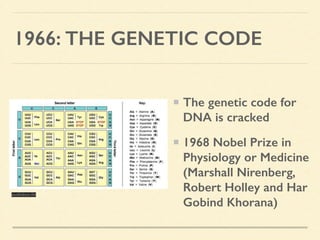
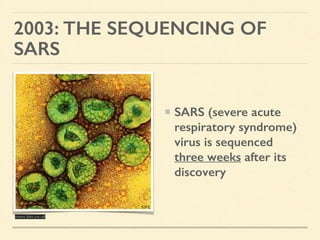
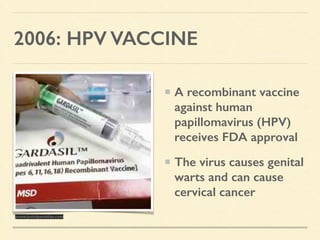
This document provides an introduction and overview of biotechnology, including definitions of key terms and an historical timeline of important developments in the field. It begins with definitions of biotechnology and genetic engineering. It then outlines the timeline of biotechnology from early domestication and farming in Mesopotamia through modern developments like recombinant vaccines, cloning, and the human genome project. The document concludes with a note about an upcoming meeting to level off on the material.