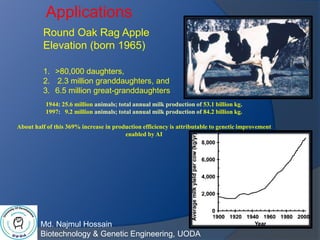
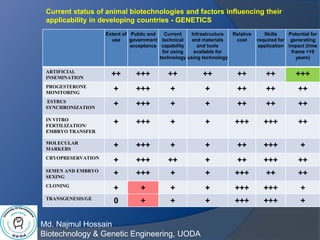
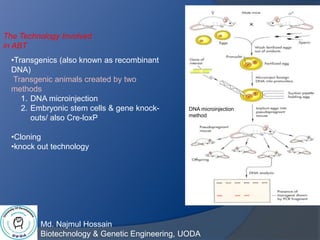
Animal biotechnology is the use of science and engineering to modify living organisms, with the goals of making products, improving animals, and developing microorganisms for agricultural uses. Examples include creating transgenic animals through gene knock out or knock in technology. Round Oak Rag Apple, an influential dairy cow born in 1965, had over 80,000 daughters who produced a total of 53.1 billion kg of milk in 1944, which increased to 84.2 billion kg in 1997 due to genetic improvement through artificial insemination. Common animal biotechnologies include artificial insemination, progesterone monitoring, estrus synchronization, in vitro fertilization/embryo transfer, molecular markers, cryopreservation, semen and embryo sexing, cloning,