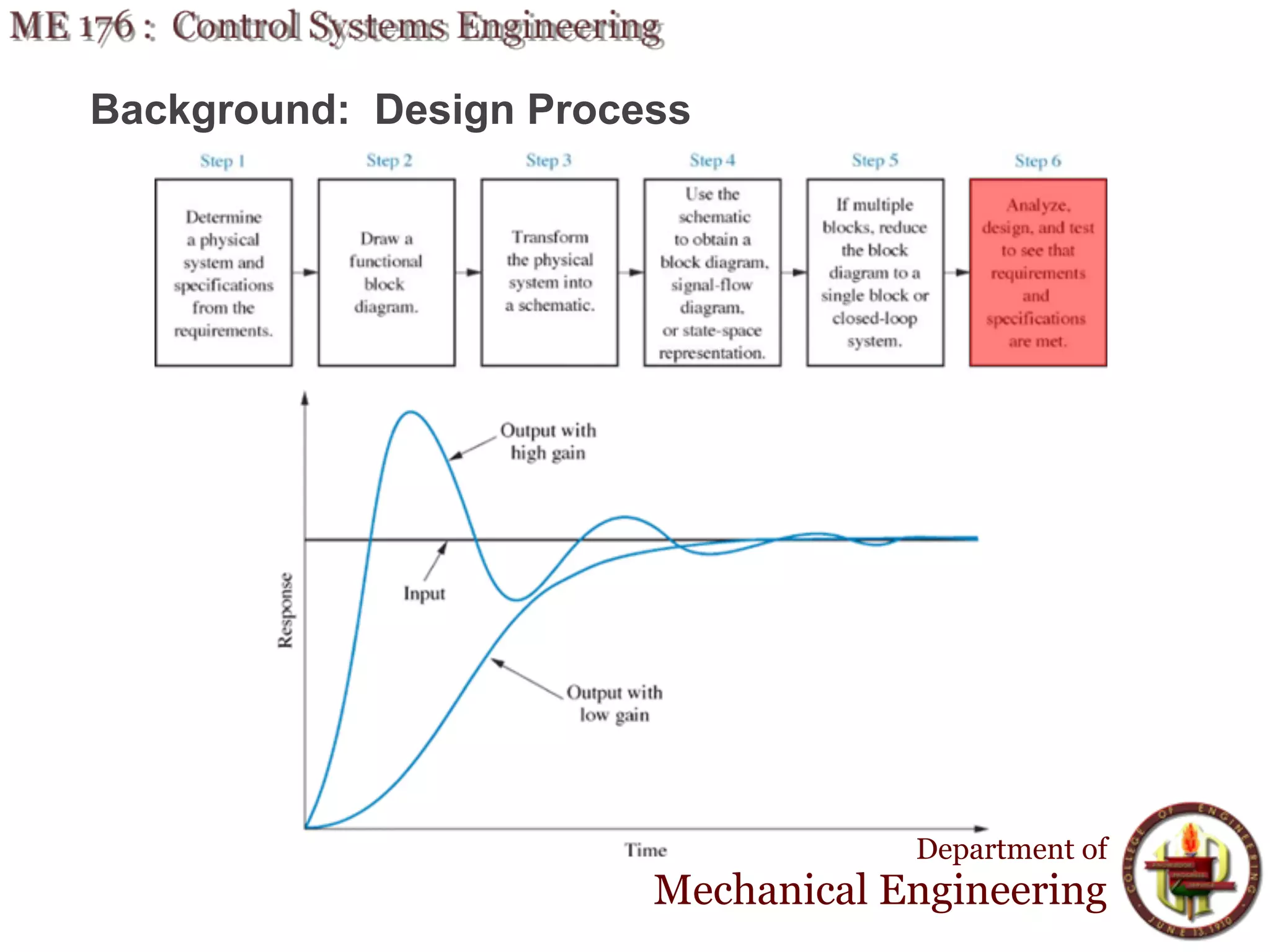
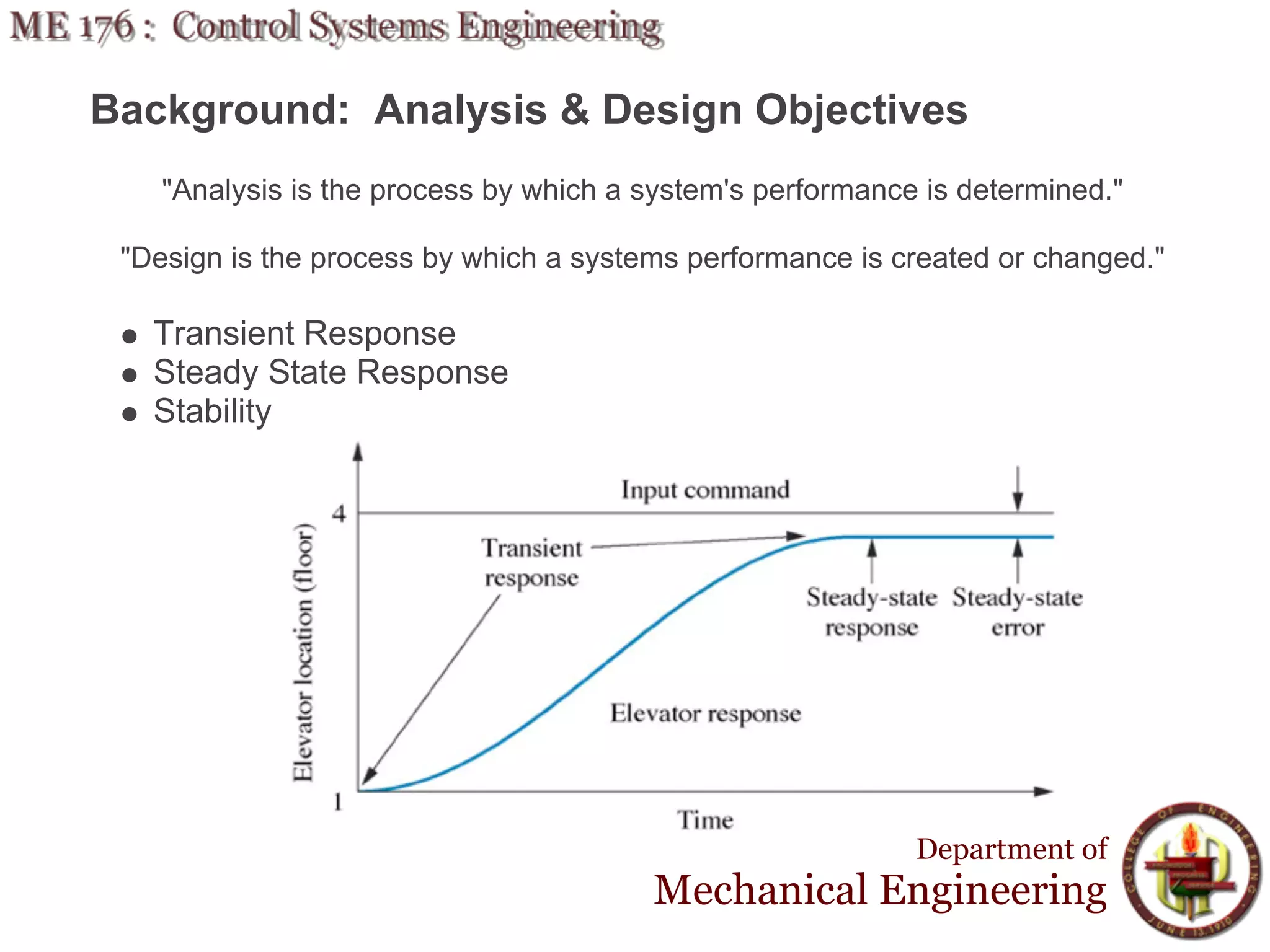
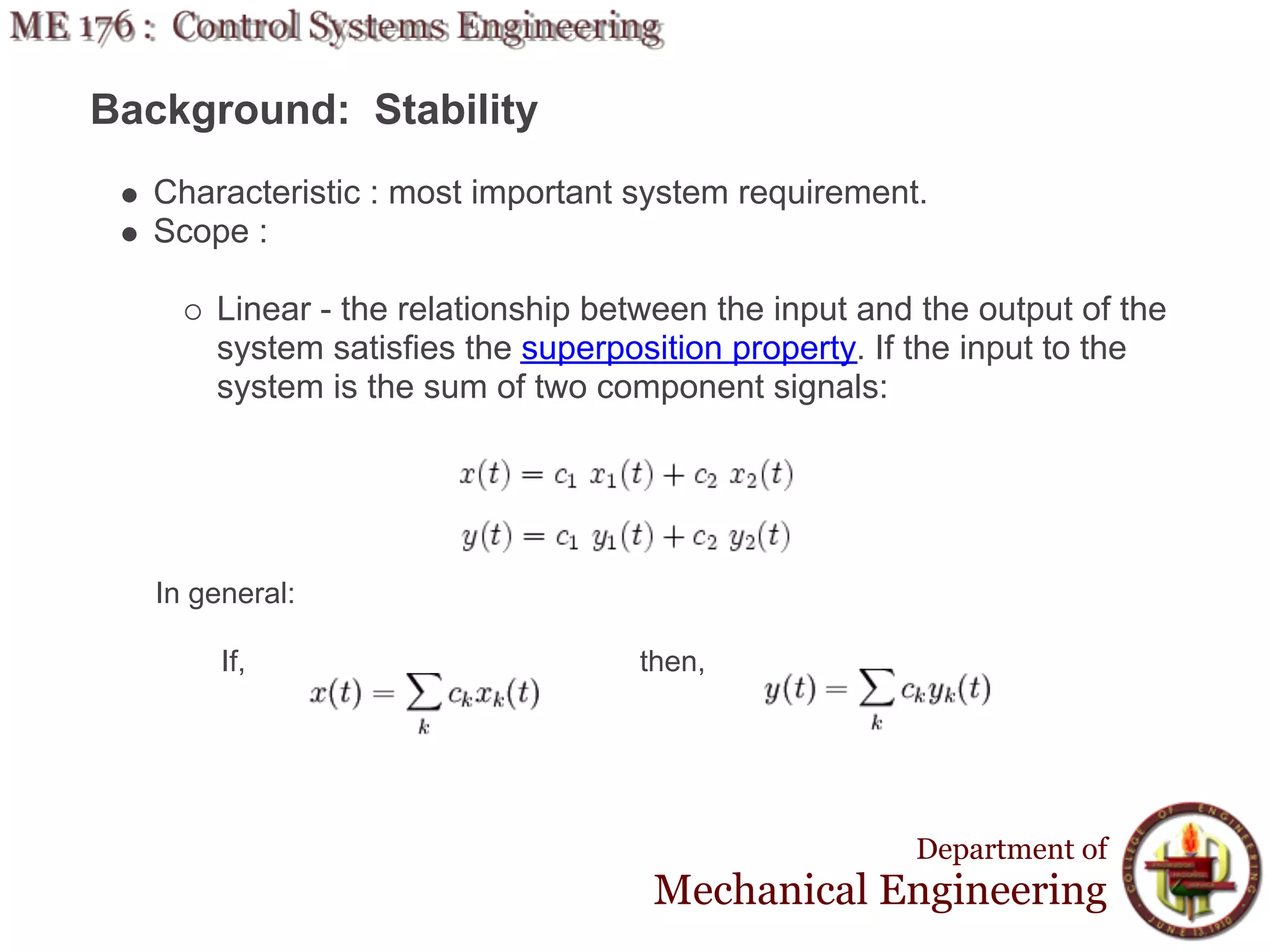
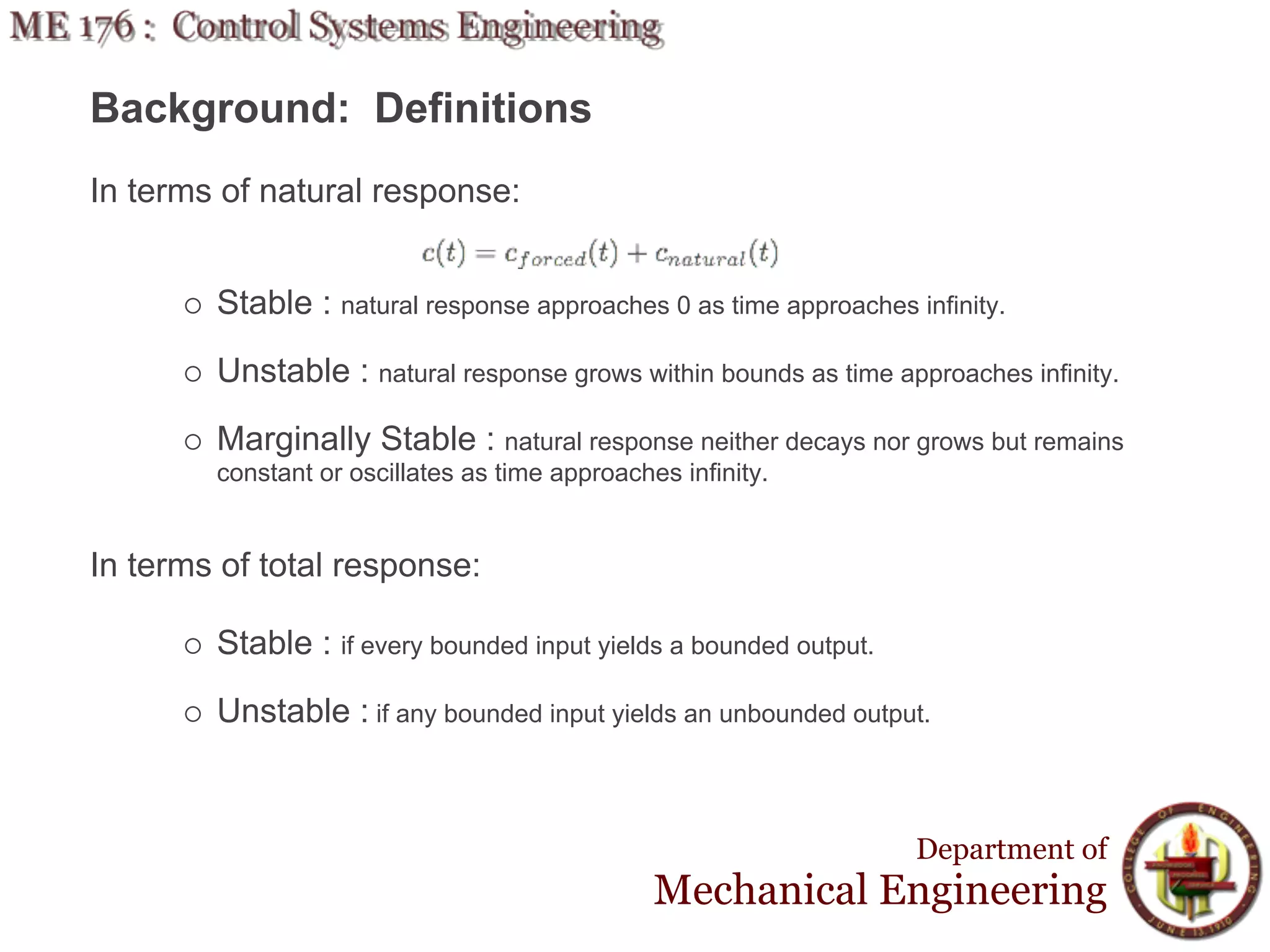
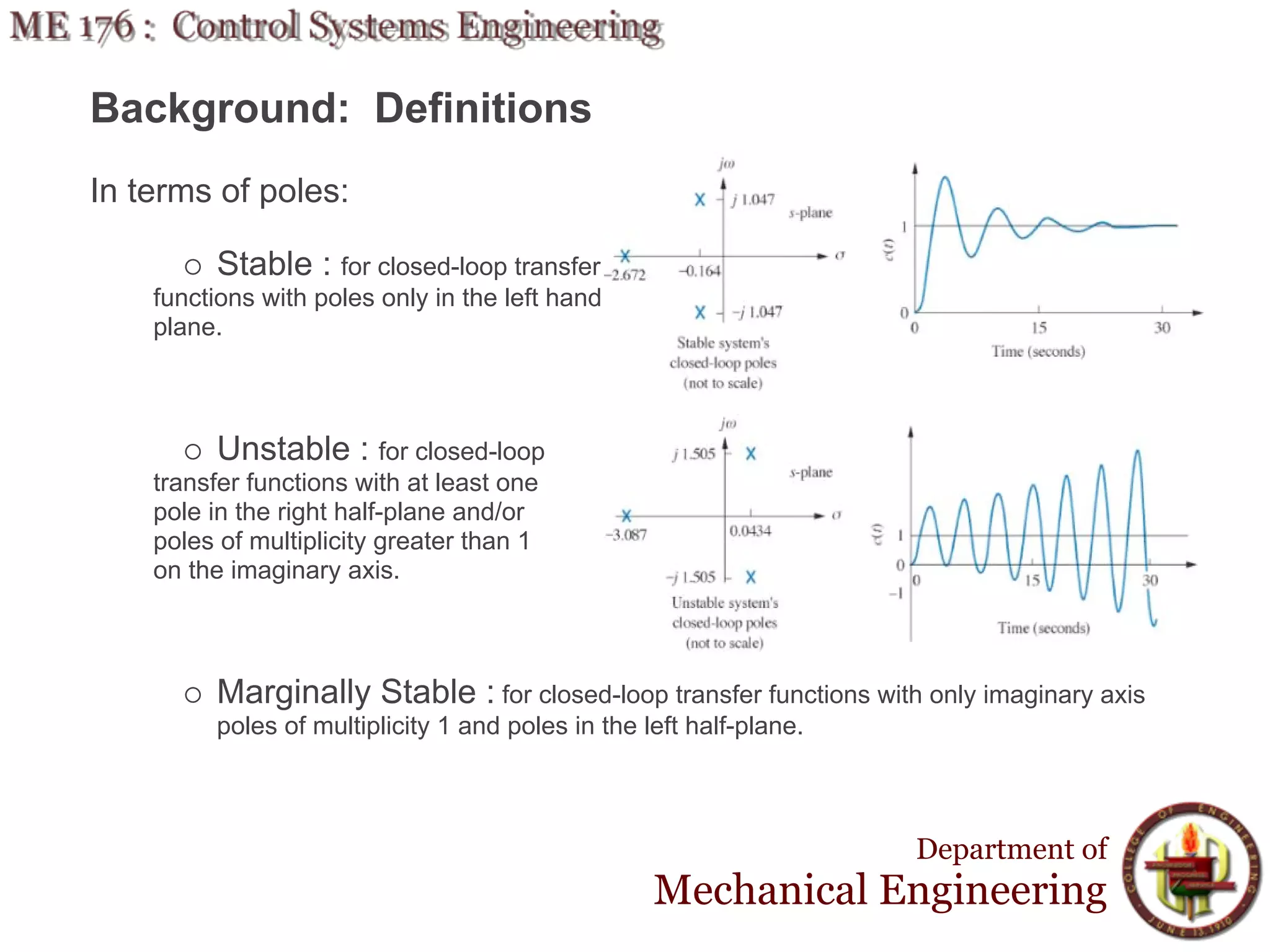
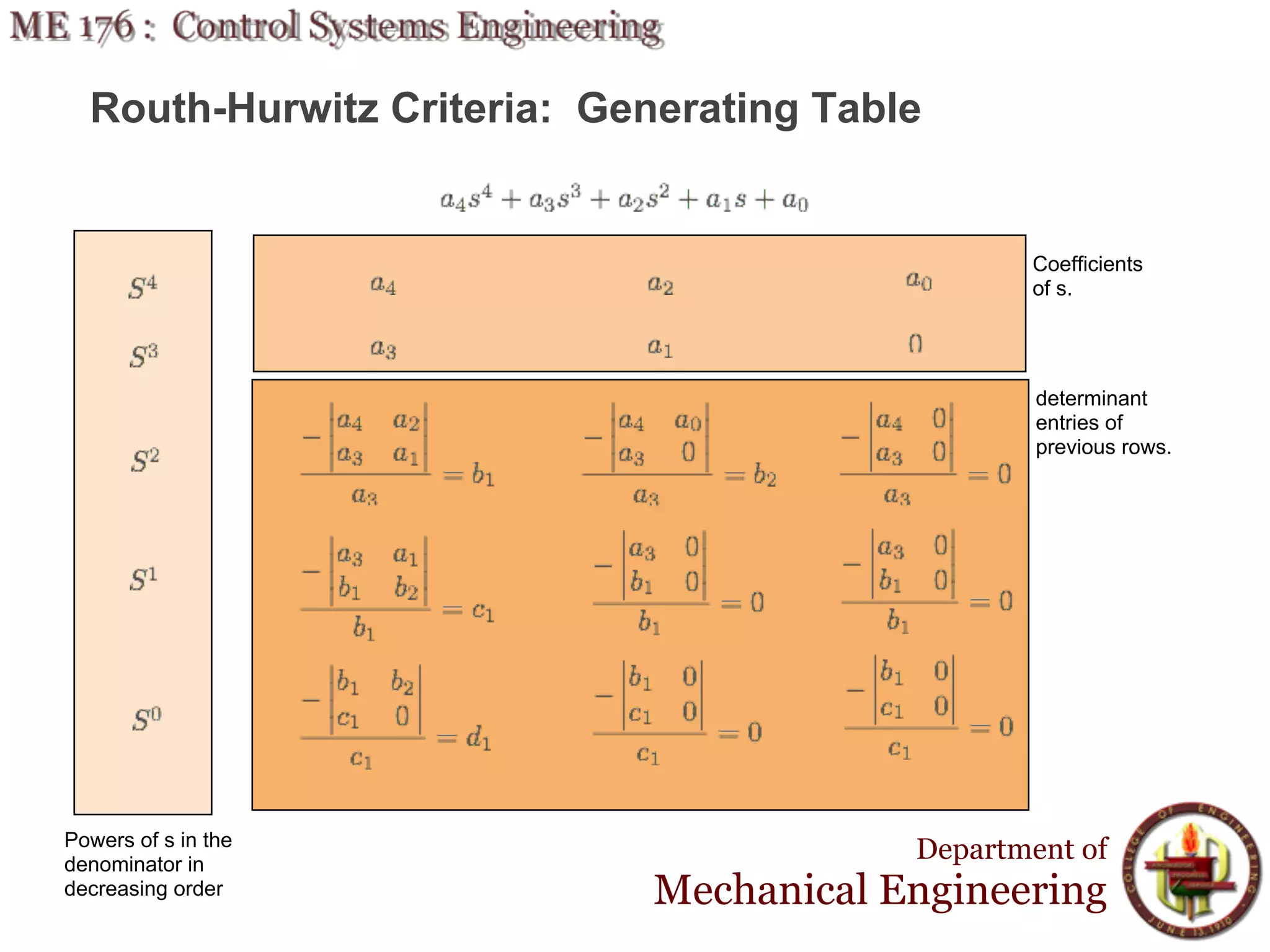
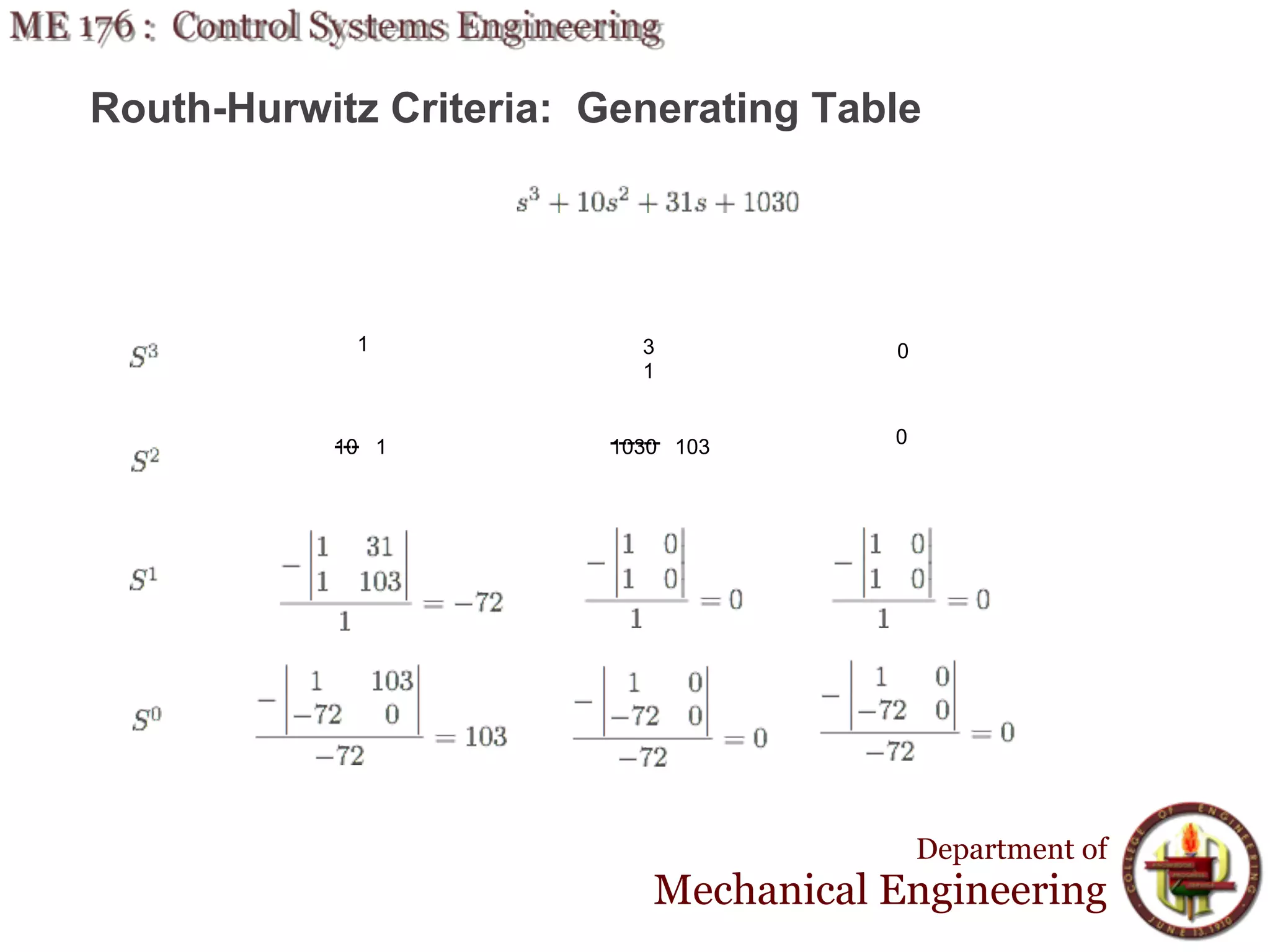
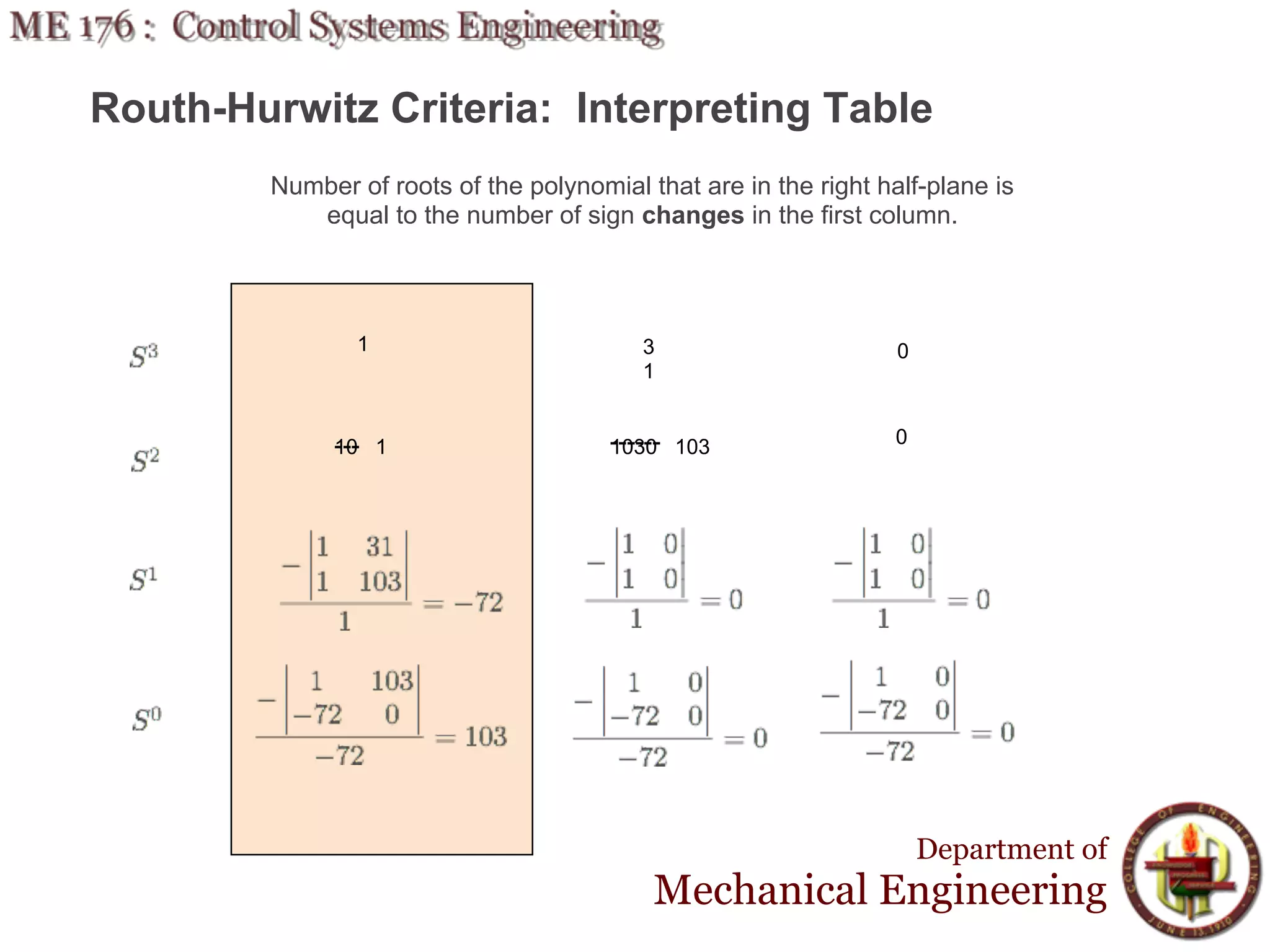
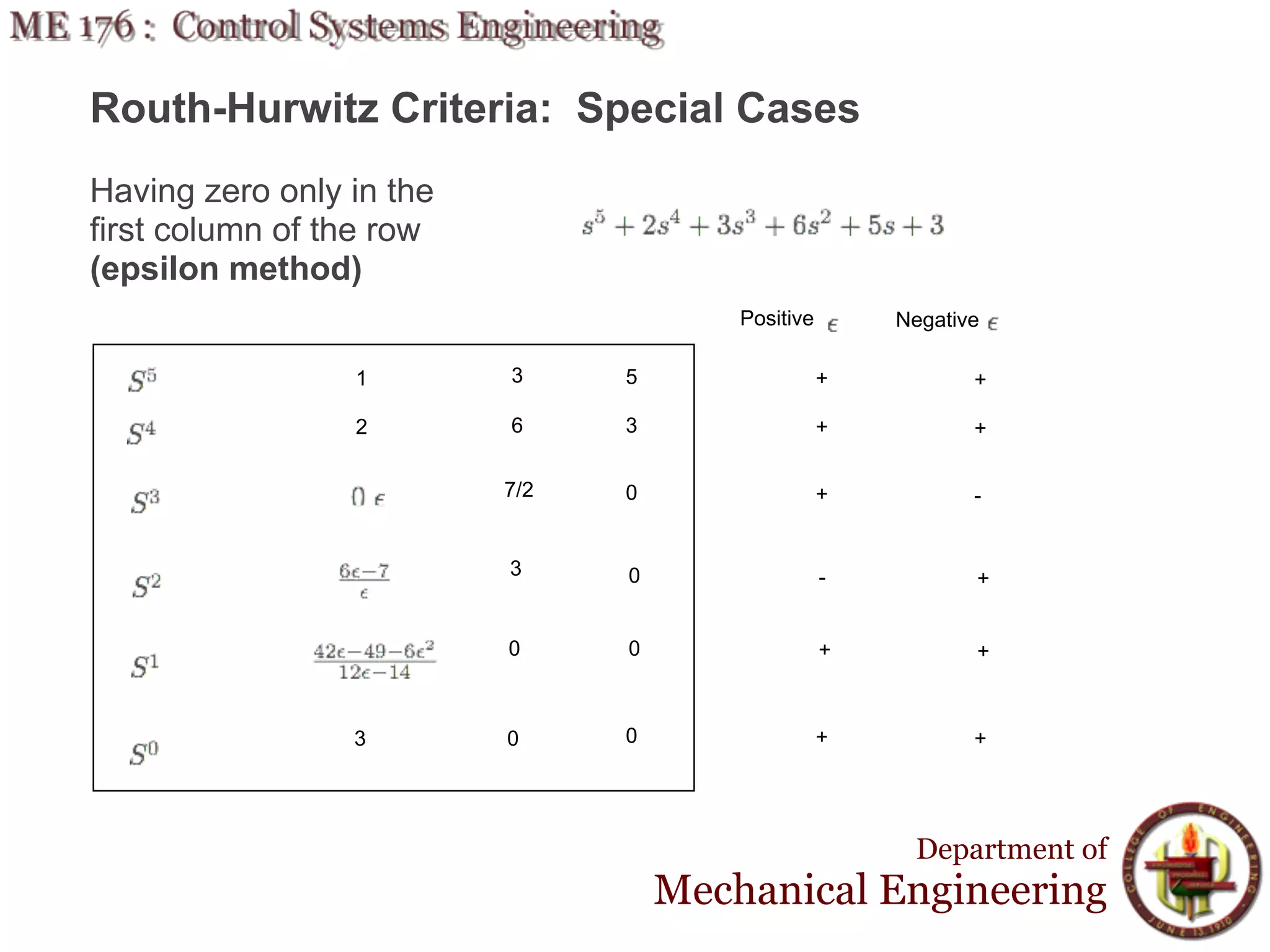
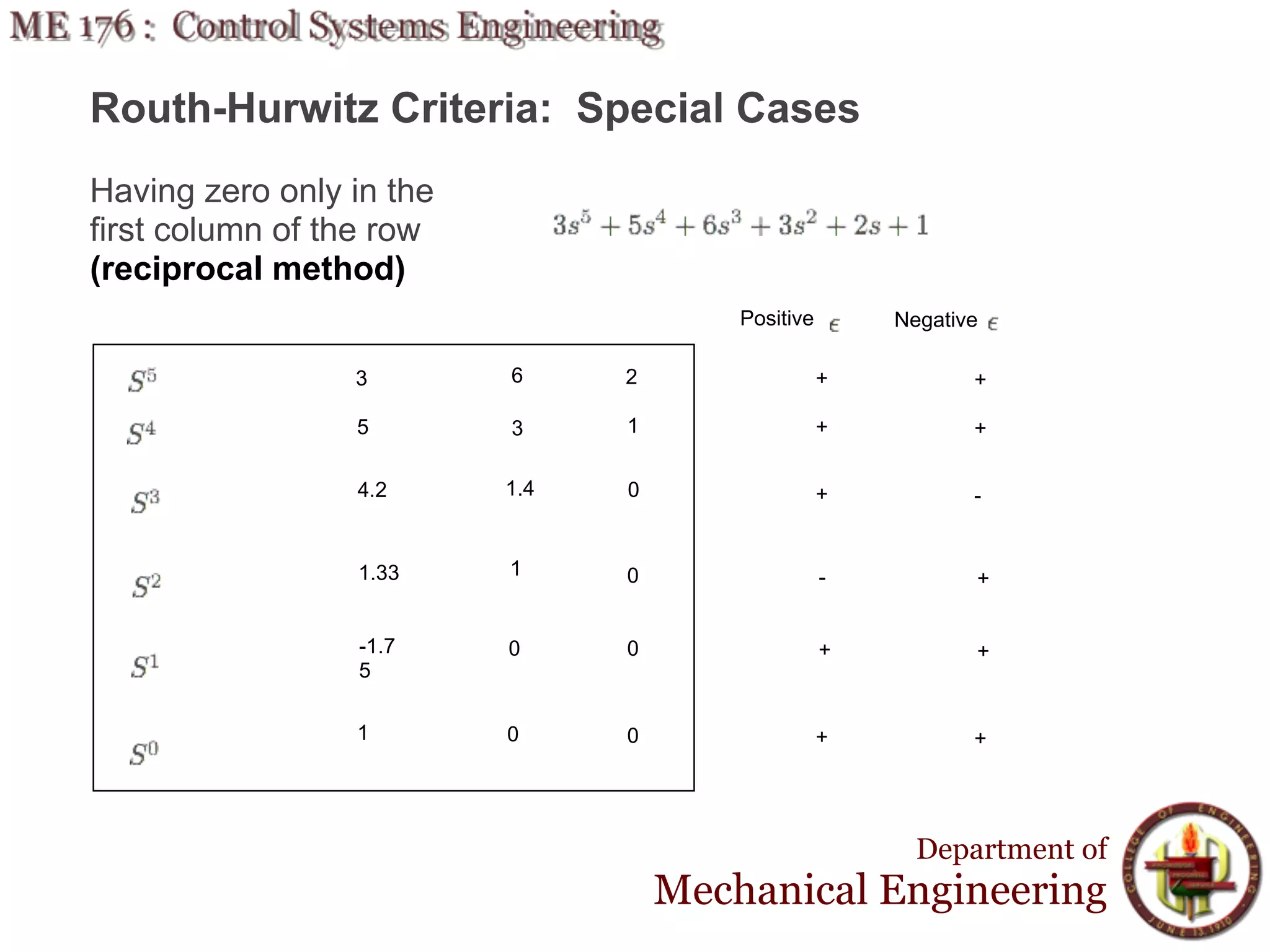
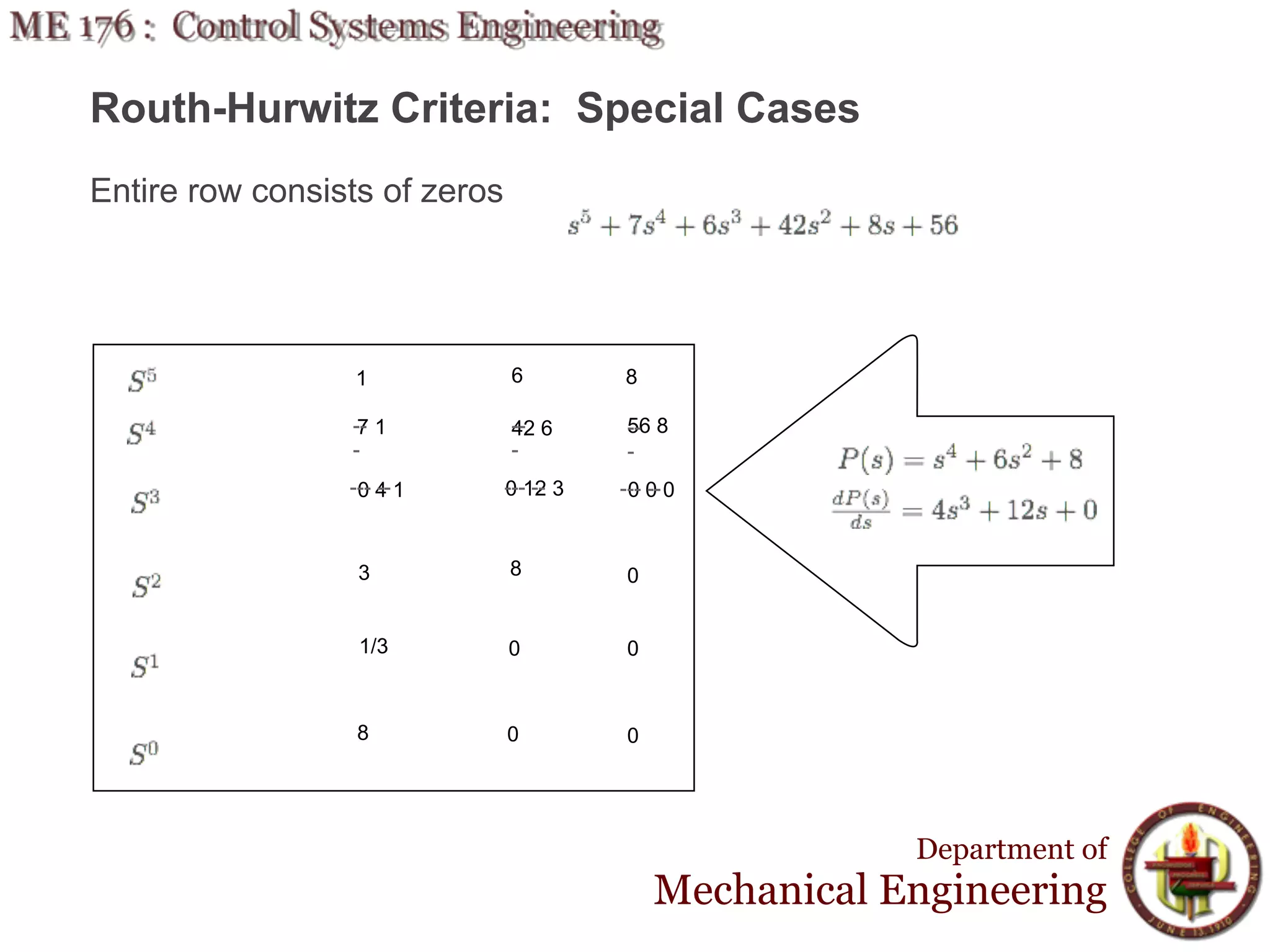
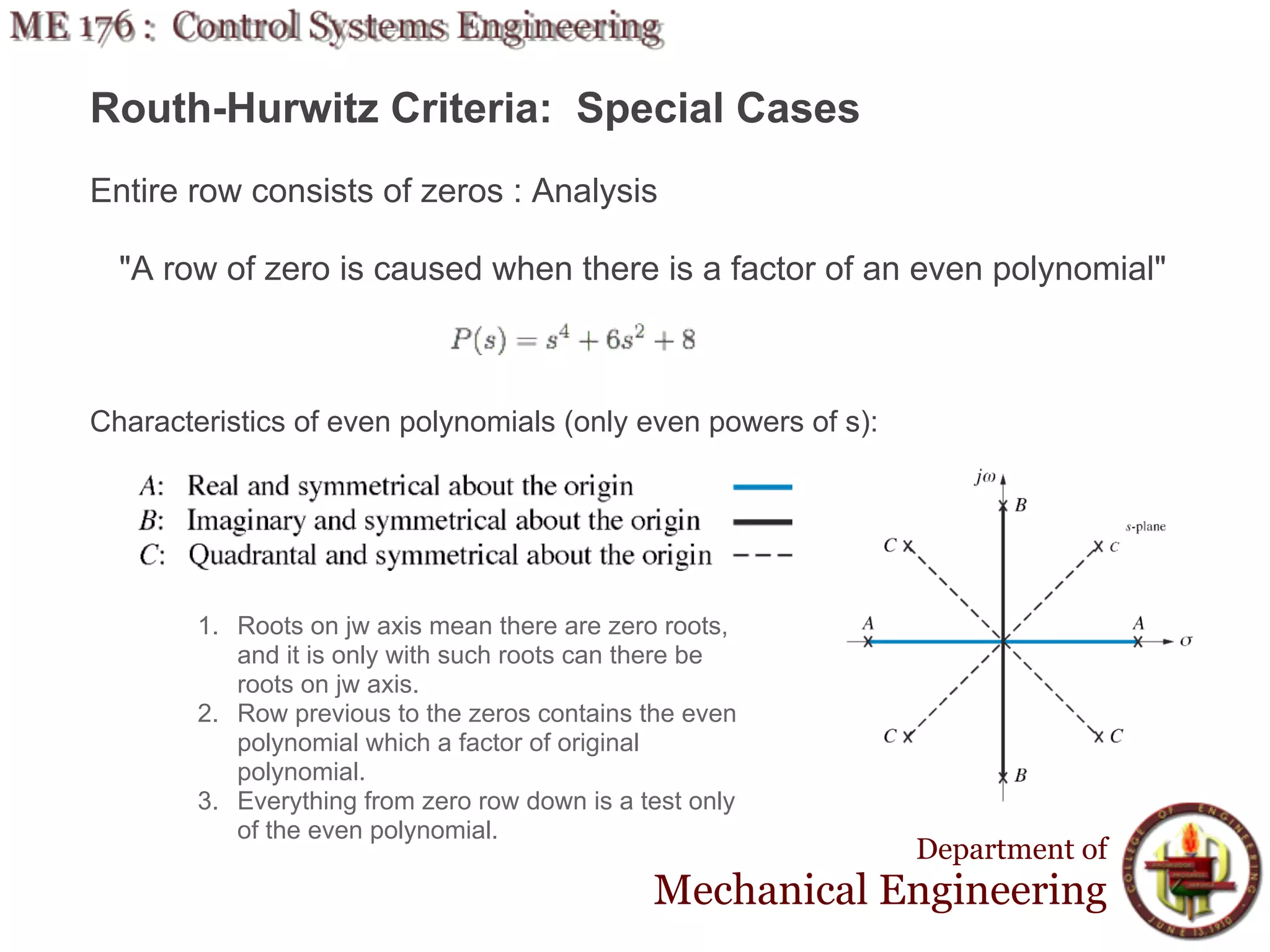
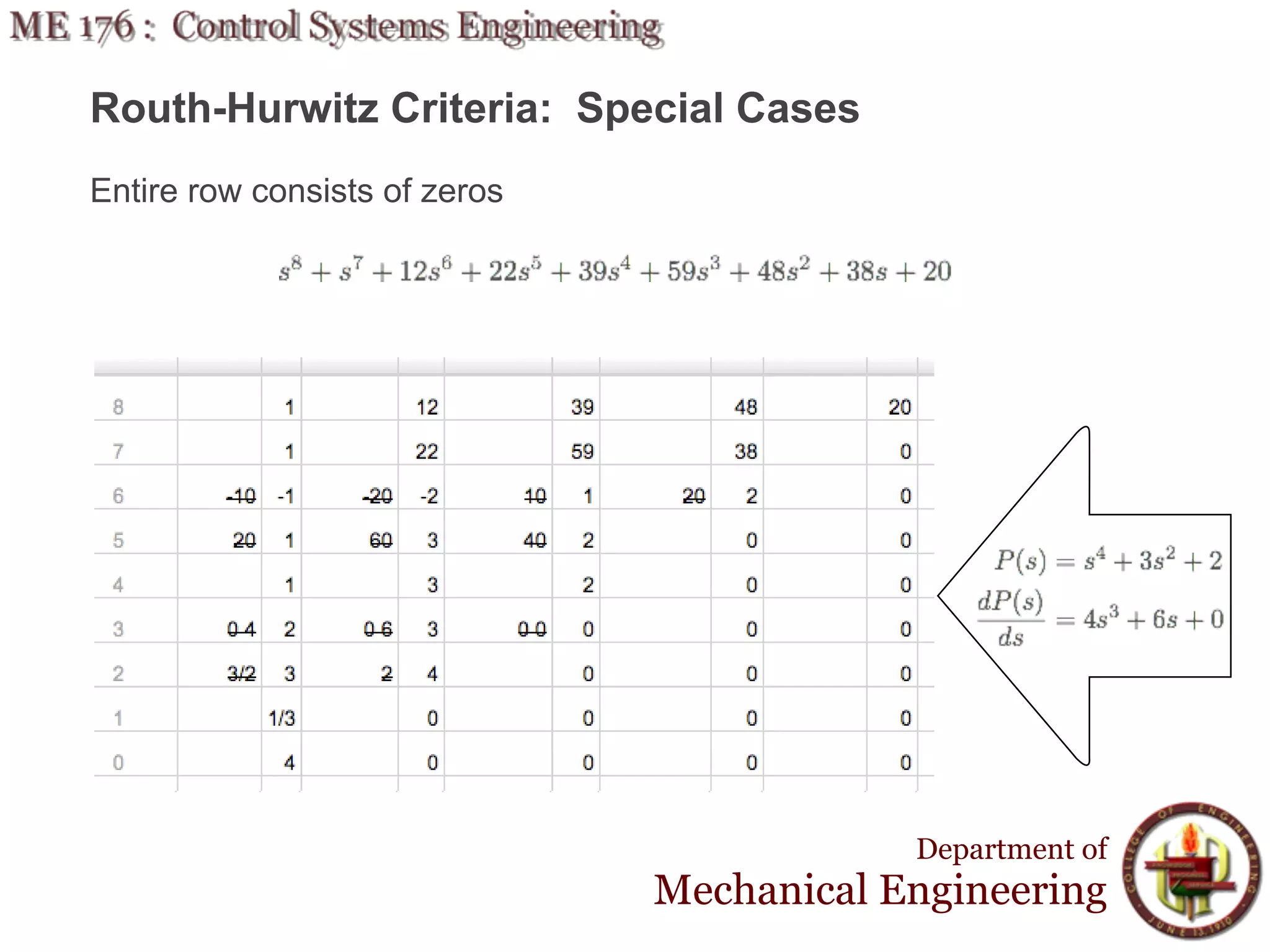
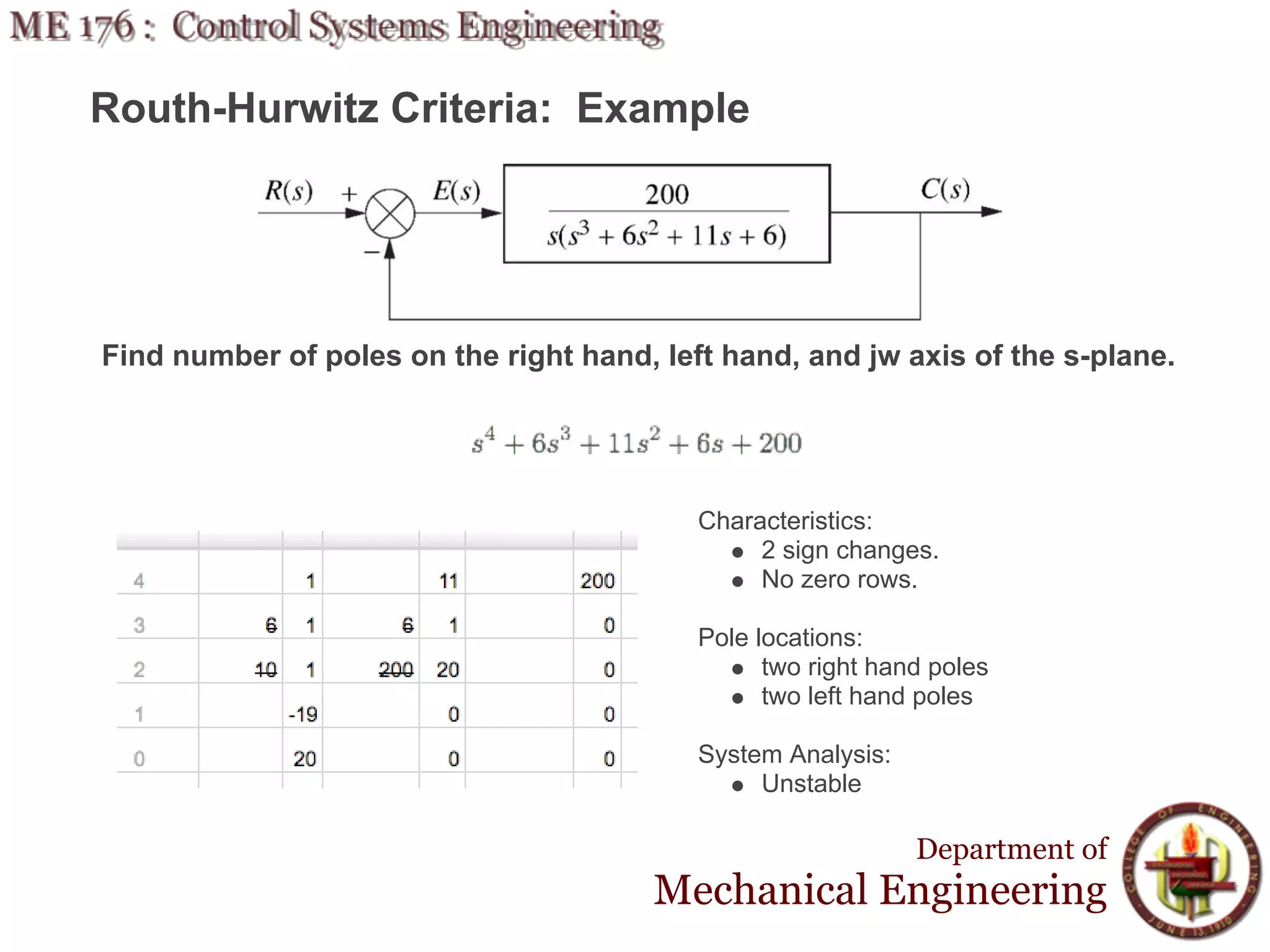
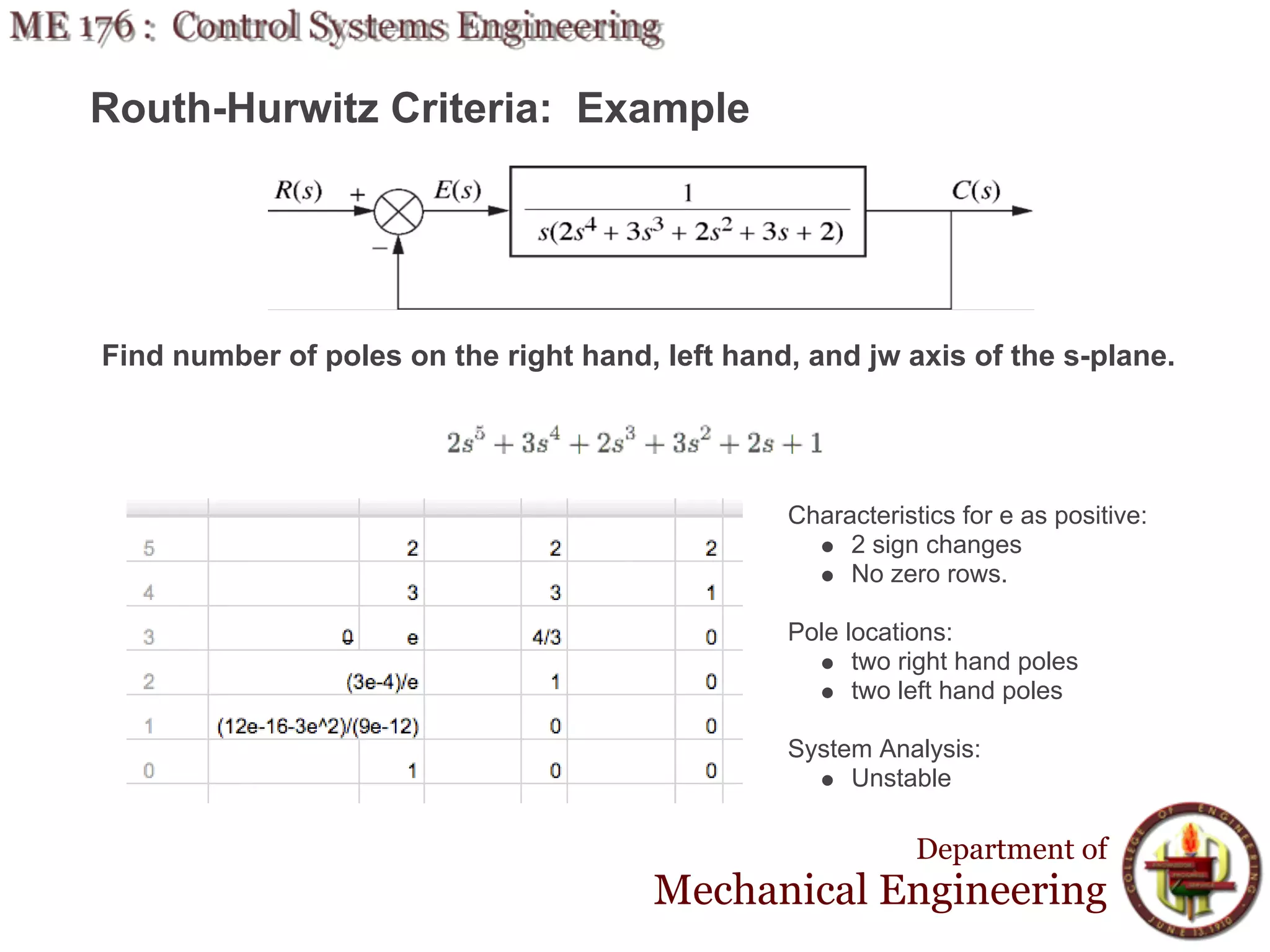
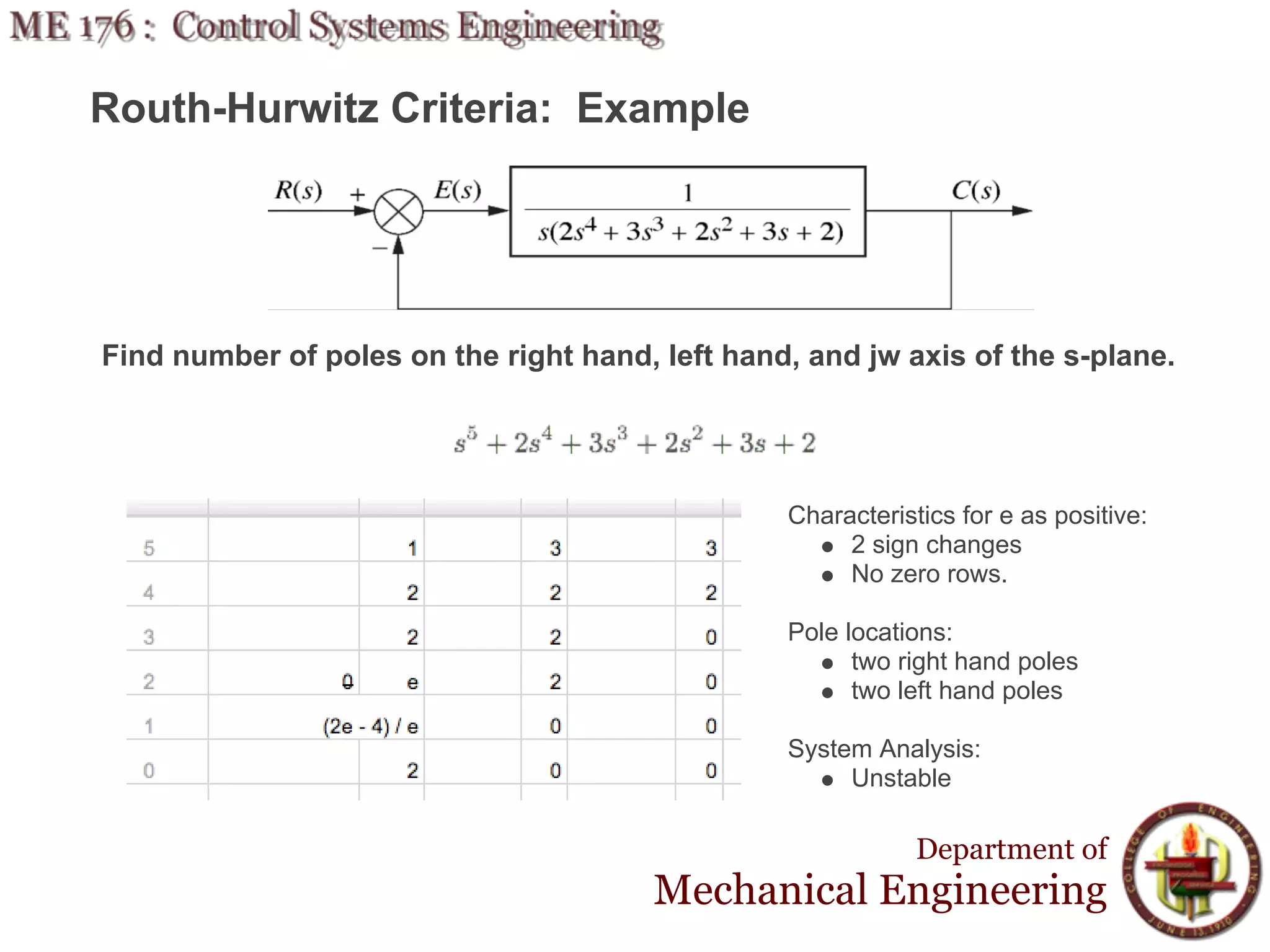
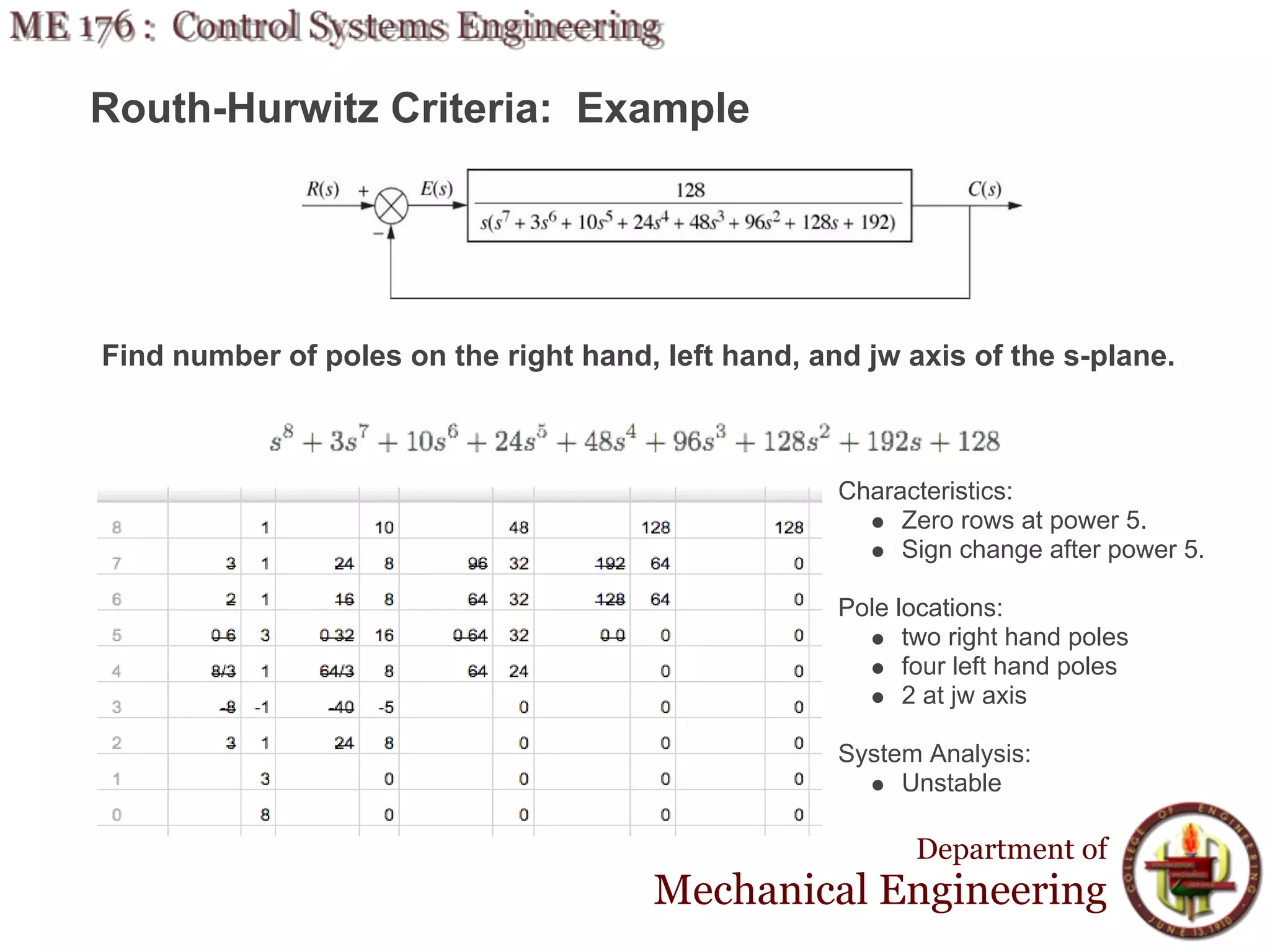
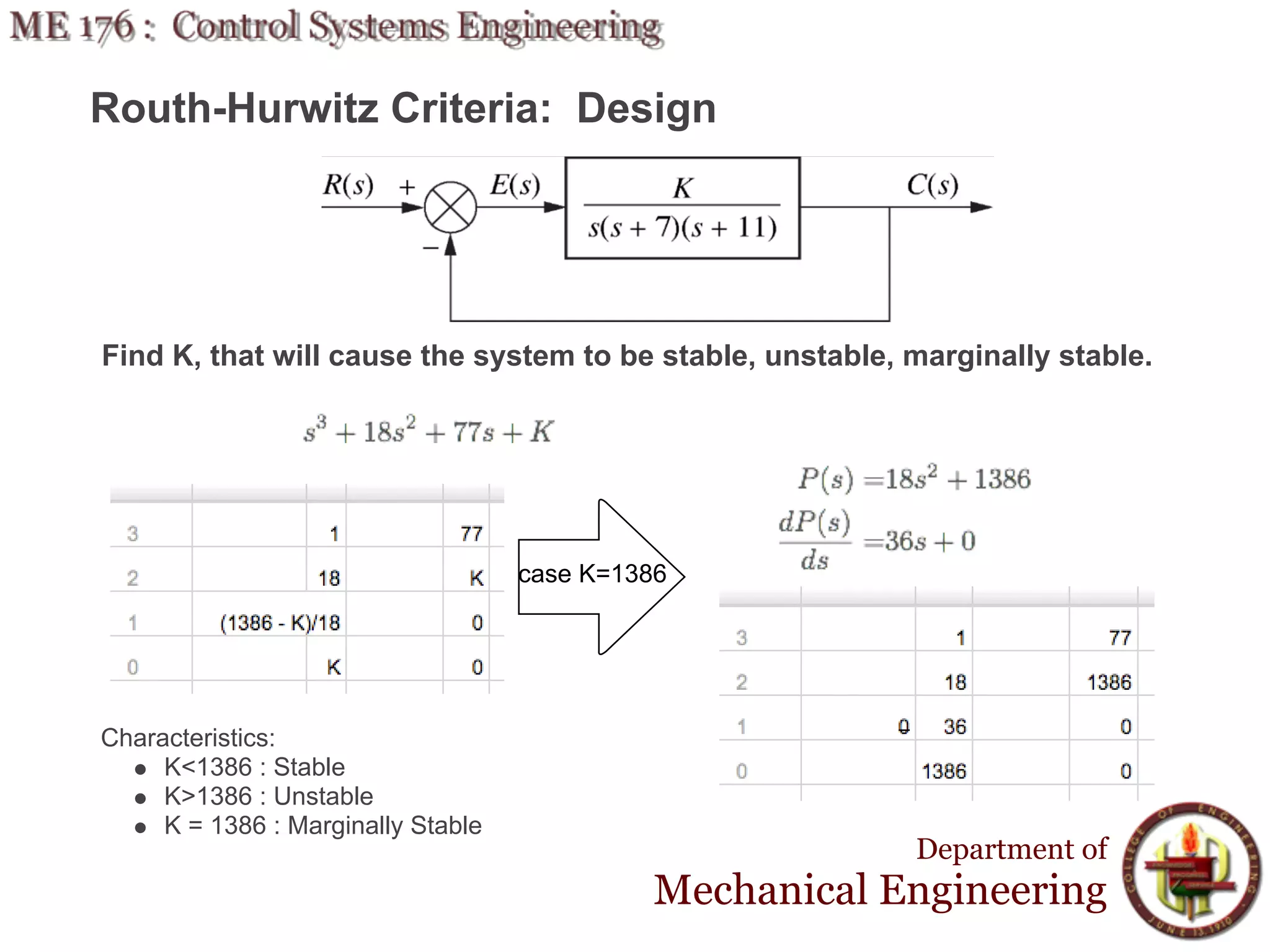
This document discusses stability analysis and design of control systems using the Routh-Hurwitz criteria. It provides definitions of stable, unstable, and marginally stable systems and describes how to generate and interpret the Routh table to determine the number and location of poles. The Routh-Hurwitz criteria allows determining stability based on the number of sign changes in the first column of the table and identifying marginally stable systems with poles only on the imaginary axis. Examples are provided to illustrate applying the method to determine stability and finding design parameters that achieve different stability conditions.