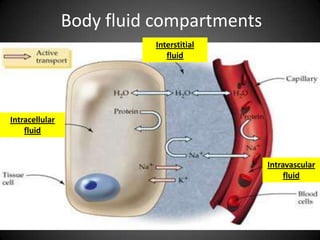
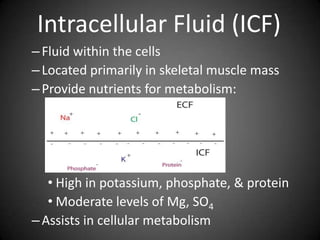
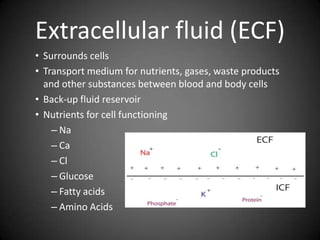
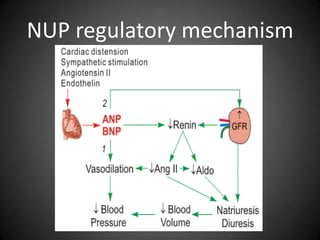
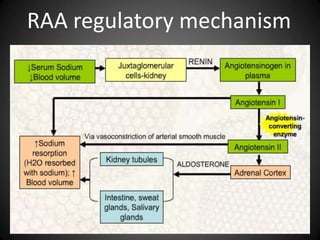
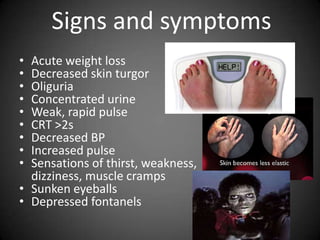
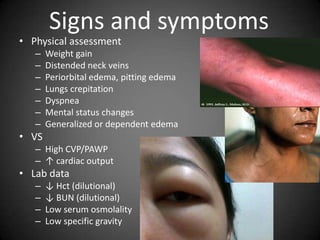
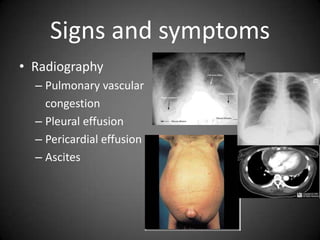
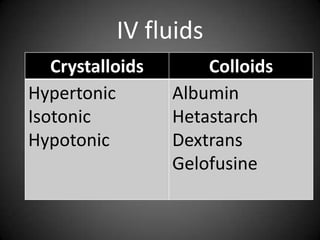
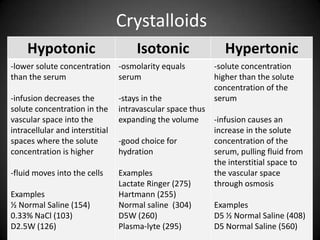
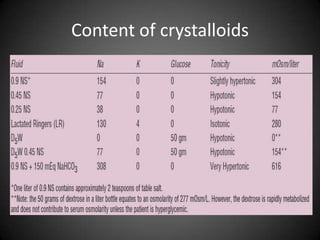
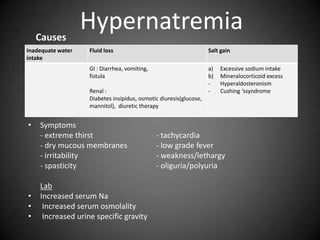
This document summarizes fluid and electrolyte physiology. The body contains 40L of total body water, with 60% intracellular fluid and 40% extracellular fluid. Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride are regulated and important for cellular function. Fluid balance is maintained through intake, output, and hormonal control. Abnormalities in fluid volume or electrolyte levels can cause various signs and symptoms.