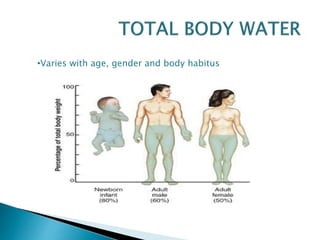
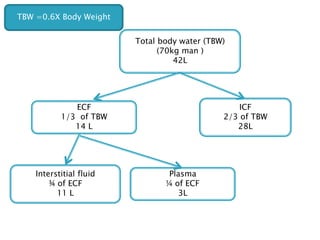
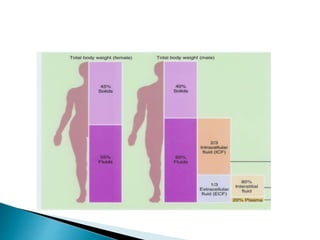
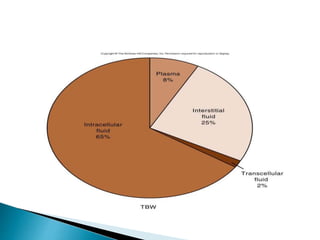
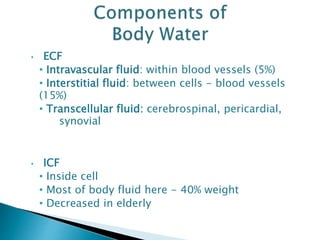
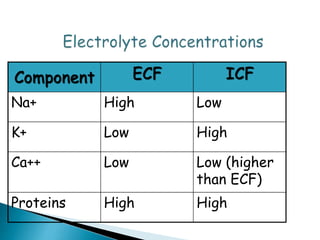
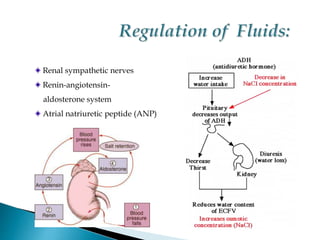
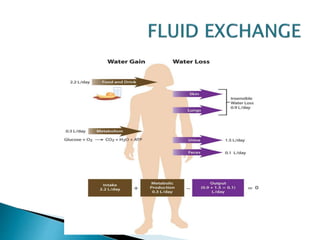
The document discusses water and electrolyte balance, which is important for homeostasis. The kidney plays a key role in maintaining circulating volume, osmolality, and electrolyte balance. Fluid volume and electrolyte composition can change pre, intra, and postoperatively due to factors like trauma or sepsis. Total body water is about 60% of body weight, with two thirds being intracellular fluid and one third extracellular fluid including plasma and interstitial fluid. Key electrolytes include sodium, potassium, calcium, and proteins. Precise fluid management is important during the pre, intra, and postoperative periods.








![ Colloid solutions –
Gelatinous solutions containing particles
suspended in solution. These particles will not
form a sediment under the influence of gravity and
are largely unable to cross a semi-permeable
membrane. e.g. Albumin, Dextrans, Hydroxyethyl
starch [HES]; Haemaccel and Gelofusine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluidtherapy-160118001011/85/Fluid-therapy-17-320.jpg)







![(1) 0.9% Normal Saline – Think of it as ‘Salt and
water’
Principal fluid used for intravascular resuscitation and replacement
of salt loss e.g diarrhoea and vomiting
Contains: Na+ 154 mmol/l, K+ - Nil, Cl- - 154 mmol/l; But K+ is
often added
IsoOsmolar compared to normal plasma
Distribution: Stays almost entirely in the Extracellular space
Of 1 litre – 750ml Extra cellular fluid; 250ml intravacular fluid
So for 100ml blood loss – need to give 400ml N.saline [only 25%
remains intravascular]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluidtherapy-160118001011/85/Fluid-therapy-26-320.jpg)

![(1) 5% Dextrose (often written D5W) – Think of it
as ‘Sugar and Water’
Primarily used to maintain water balance in patients
who are not able to take anything by mouth; Commonly
used post-operatively in conjuction with salt retaining
fluids ie saline; Often prescribed as 2L : 1L N.Saline
[‘Physiological replacement’ of water and Na+ losses]
Provides some calories [ approximately 10% of daily
requirements]
Regarded as ‘electrolyte free’ – contains NO Sodium,
Potassium, Chloride or Calcium
Distribution: <10% Intravascular; > 66% intracellular
When infused is rapidly redistributed into the
intracellular space; Less than 10% stays in the
intravascular space therefore it is of limited use in fluid
resuscitation.
For every 100ml blood loss – need 1000ml dextrose
replacement [10% retained in intravascular space
Common cause of iatrogenic hyponatraemia in surgical
patient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluidtherapy-160118001011/85/Fluid-therapy-28-320.jpg)































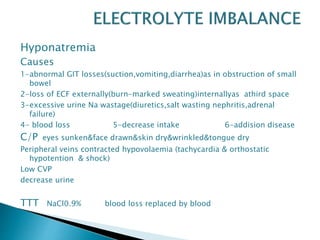




![ Metabolic Acidosis
Causes
Over production of organic acid DKA-Lactic acidosis
of sepsis and shock[ HIGH ANION GAP ]
Renal failure(acute-chronic)
Excessive loss of HCO3(diarrhea,pancreatic or small
intestinal fistula,uretro sigmoidostmy [ NORMAL
ANION GAP ]
C/P increased rate&depth of breathing
TTT mild to moderate ttt of cause
Sever (IV HCO3 causes (1/2body weight X (15-
HCO3))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluidtherapy-160118001011/85/Fluid-therapy-68-320.jpg)

