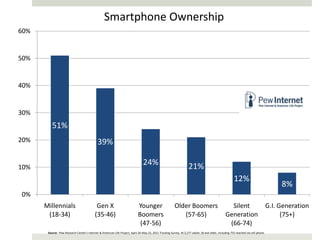
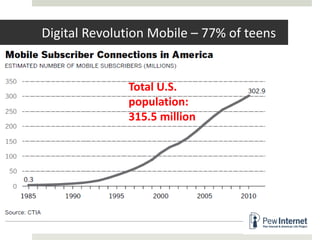
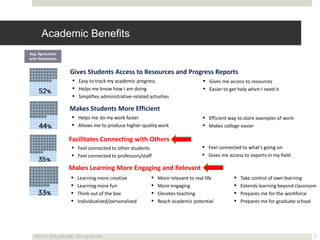
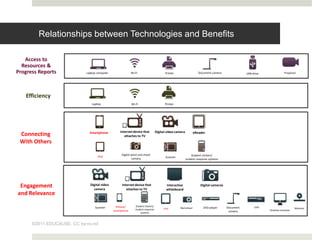
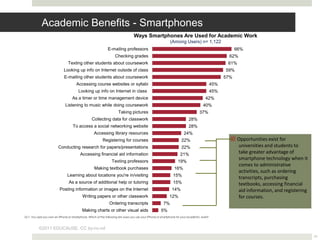
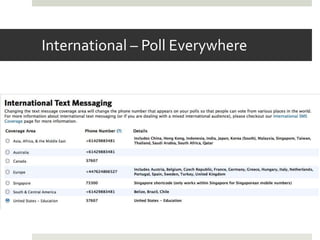
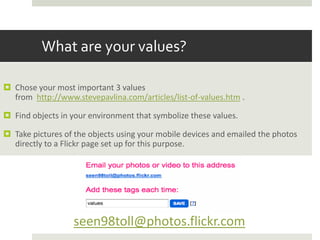
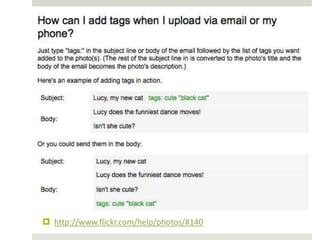
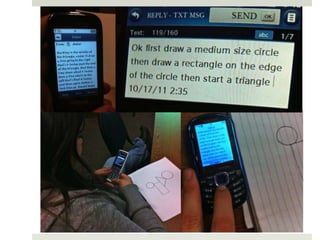
The document discusses using mobile devices to build community in schools. It notes that schools with strong community see benefits like increased academic motivation and social skills. However, few schools successfully build community, especially for low-income and minority students. The document then discusses how mobile devices are widely used by today's youth and how collaborative mobile learning can support relationship-building and engagement. It provides examples of activities like sharing photos or comments that can be used on mobile devices to facilitate teamwork and community.