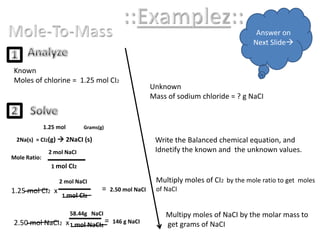
Stoichiometric calculations involve using balanced chemical equations and mole ratios to determine unknown quantities in chemical reactions from known values. The key tools needed are a balanced chemical equation, mole ratios based on the coefficients in the equation, and conversions between moles, grams, and molar mass. An example problem is provided that shows how to calculate the mass of sodium chloride products from a known number of moles of chlorine reactants using mole ratios from the balanced equation, molar mass, and stoichiometric relationships between coefficients. The mass to mass calculation process is similar, using inverse molar mass and molar mass conversions.