This document discusses key concepts related to stoichiometry including:
- The mole, molar mass, and Avogadro's number are defined. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance and is measured in g/mol.
- Atomic mass is calculated using the ratio of isotopes multiplied by their individual masses. Molar/molecular mass has the same value as atomic mass but is measured in g/mol rather than atomic mass units.
- Examples are given for calculating the molar mass of compounds like CO2, H2O, and relating mass, moles, and molar mass.
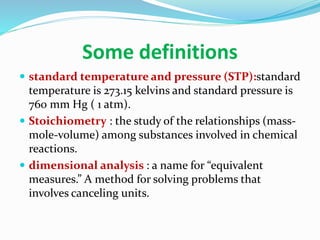
- Standard temperature and pressure, stoichiometry, and dimensional analysis are also defined