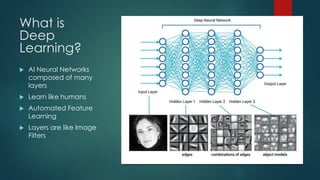
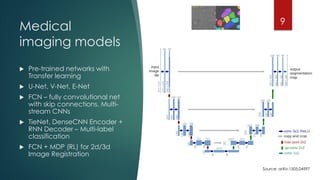
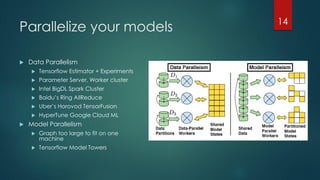
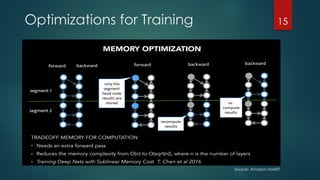
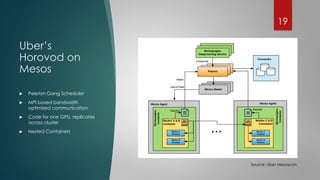
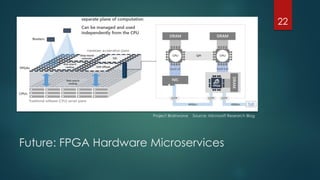
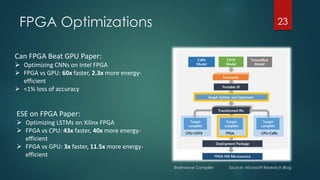
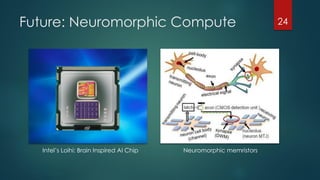
The document discusses the role of deep learning in medical imaging, including its use cases, models, and optimization techniques. It highlights the challenges and advancements in specialized computing for model training and inference as well as the future of medical imaging technology. Additionally, it provides a roadmap for individuals starting their journey in deep learning for medical applications.