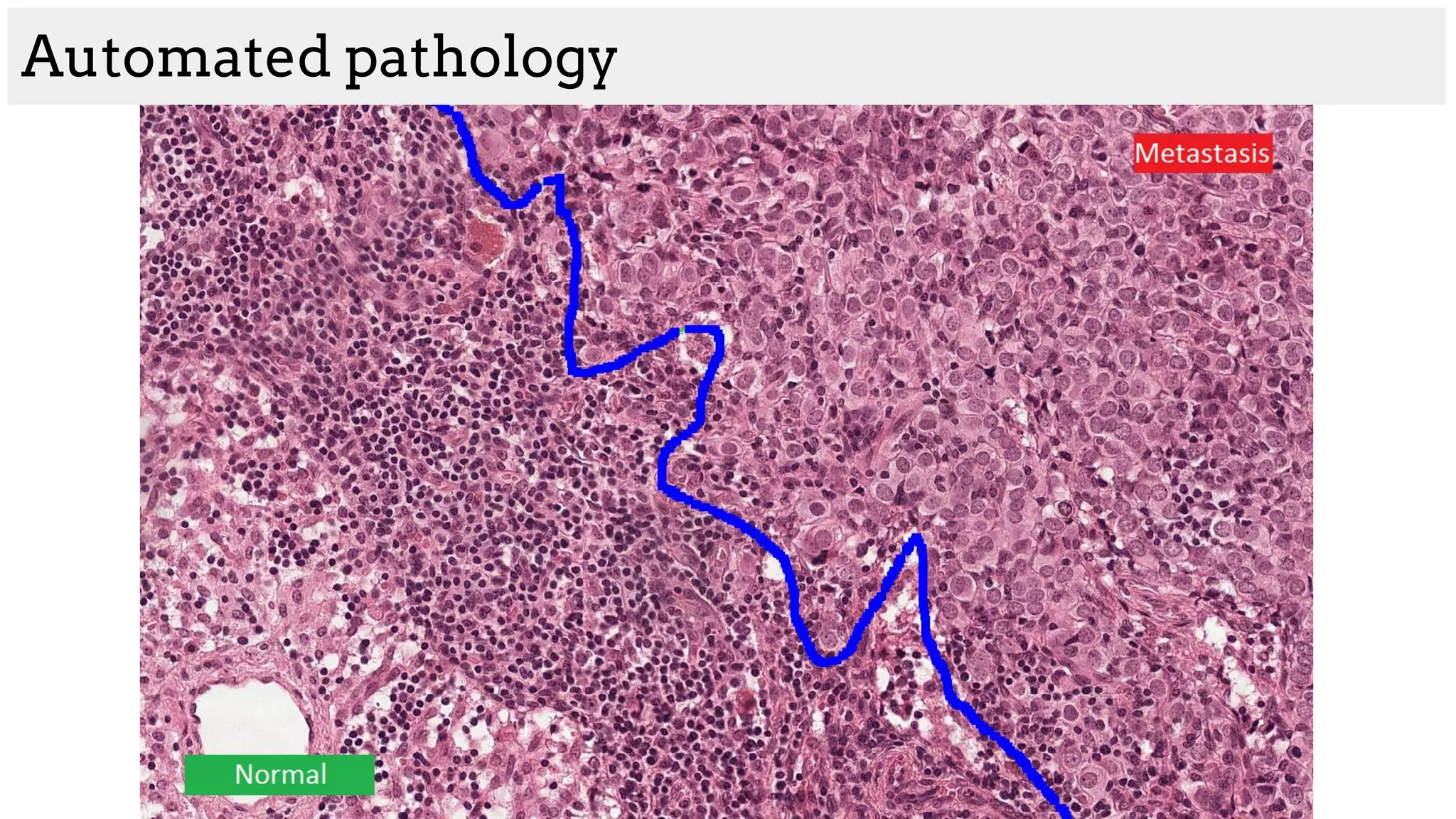
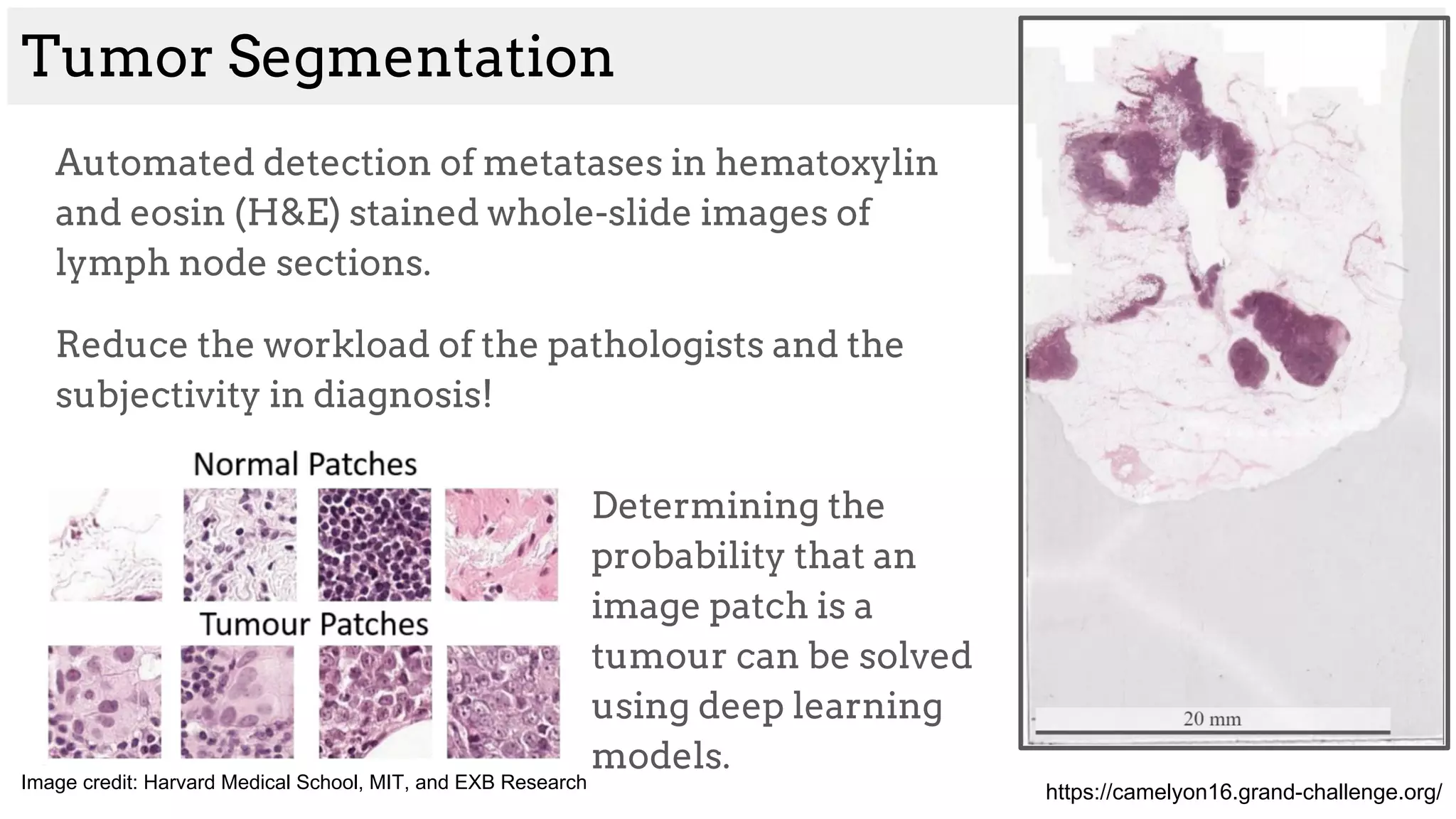
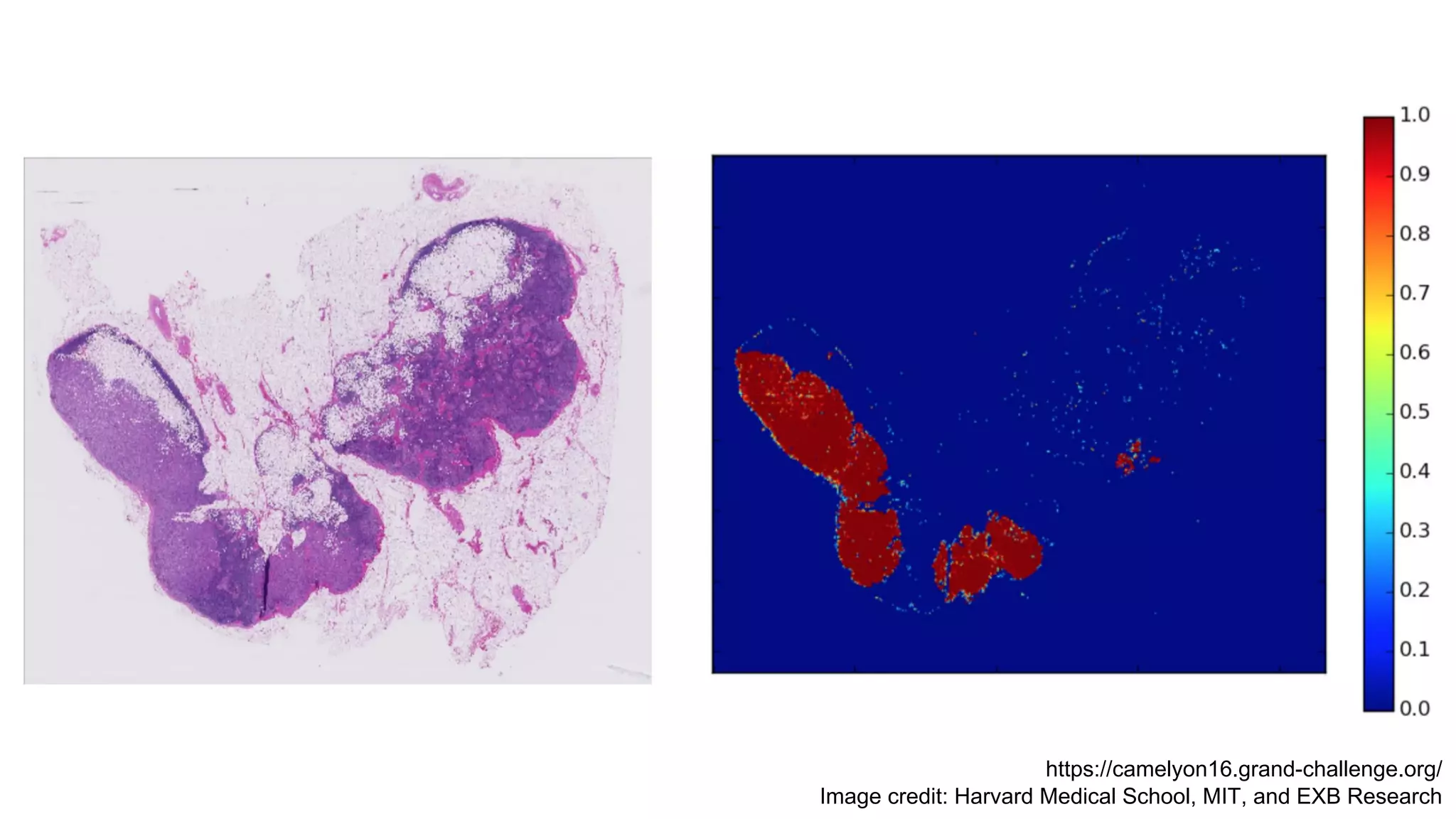
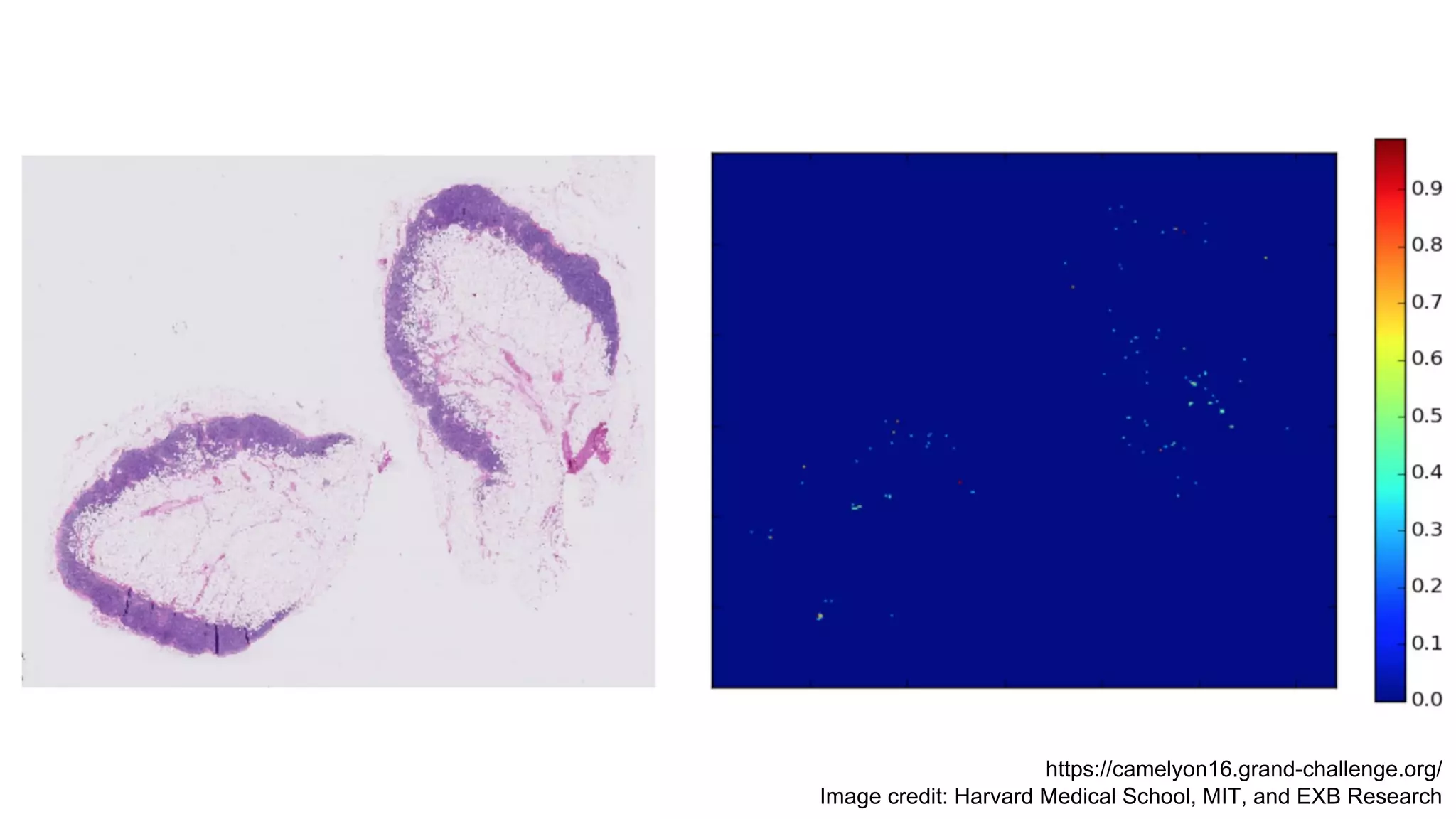
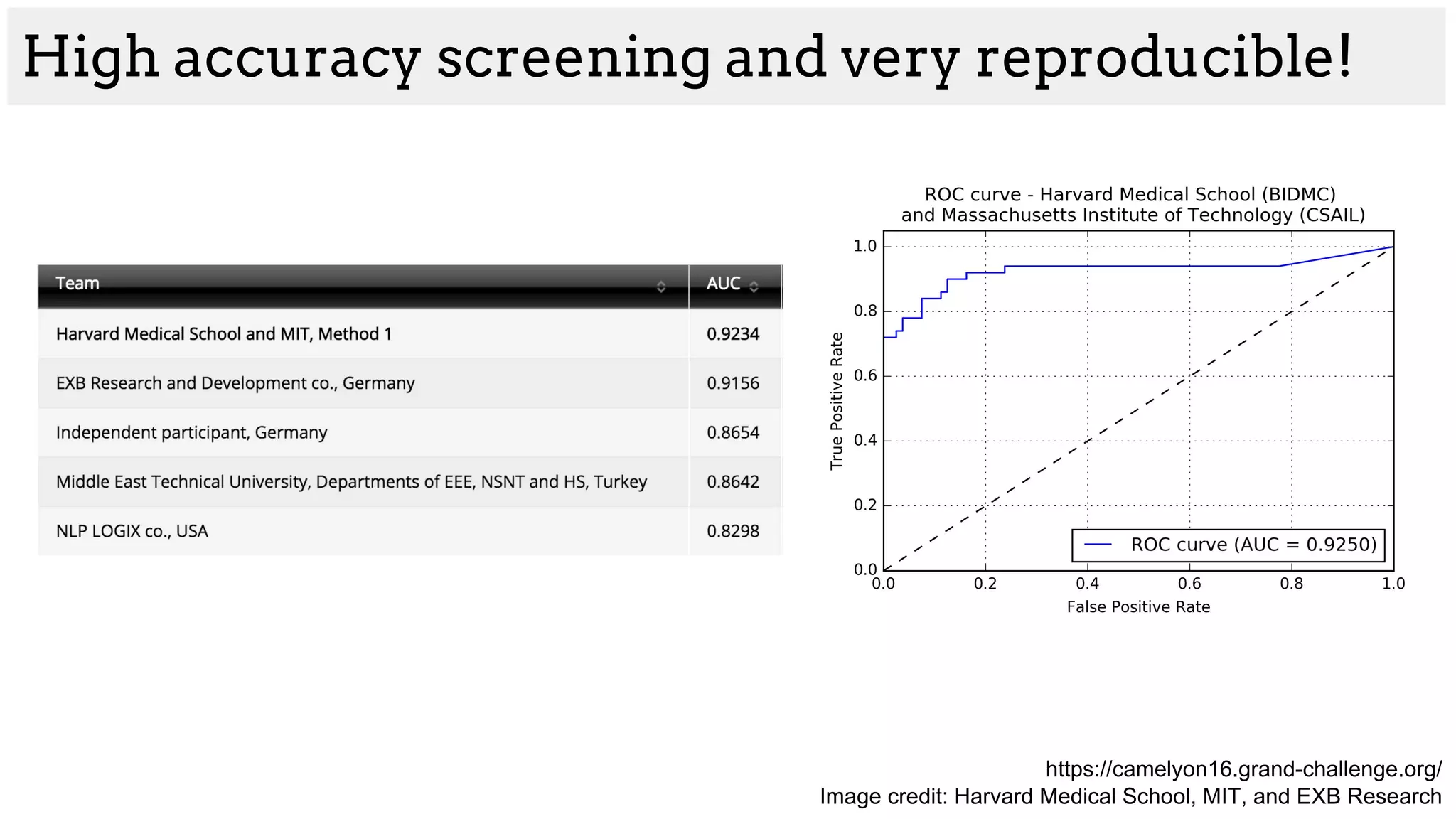
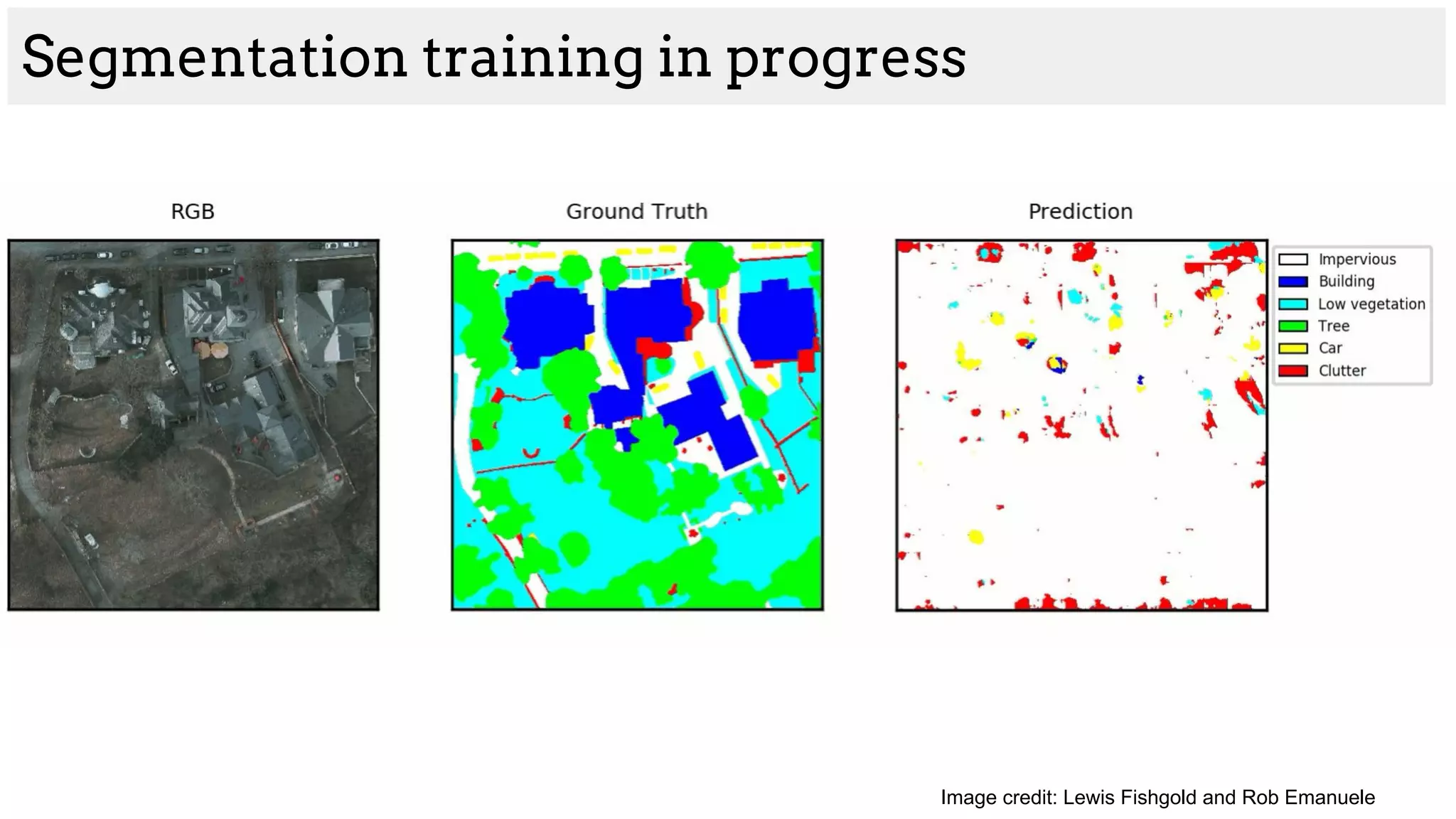
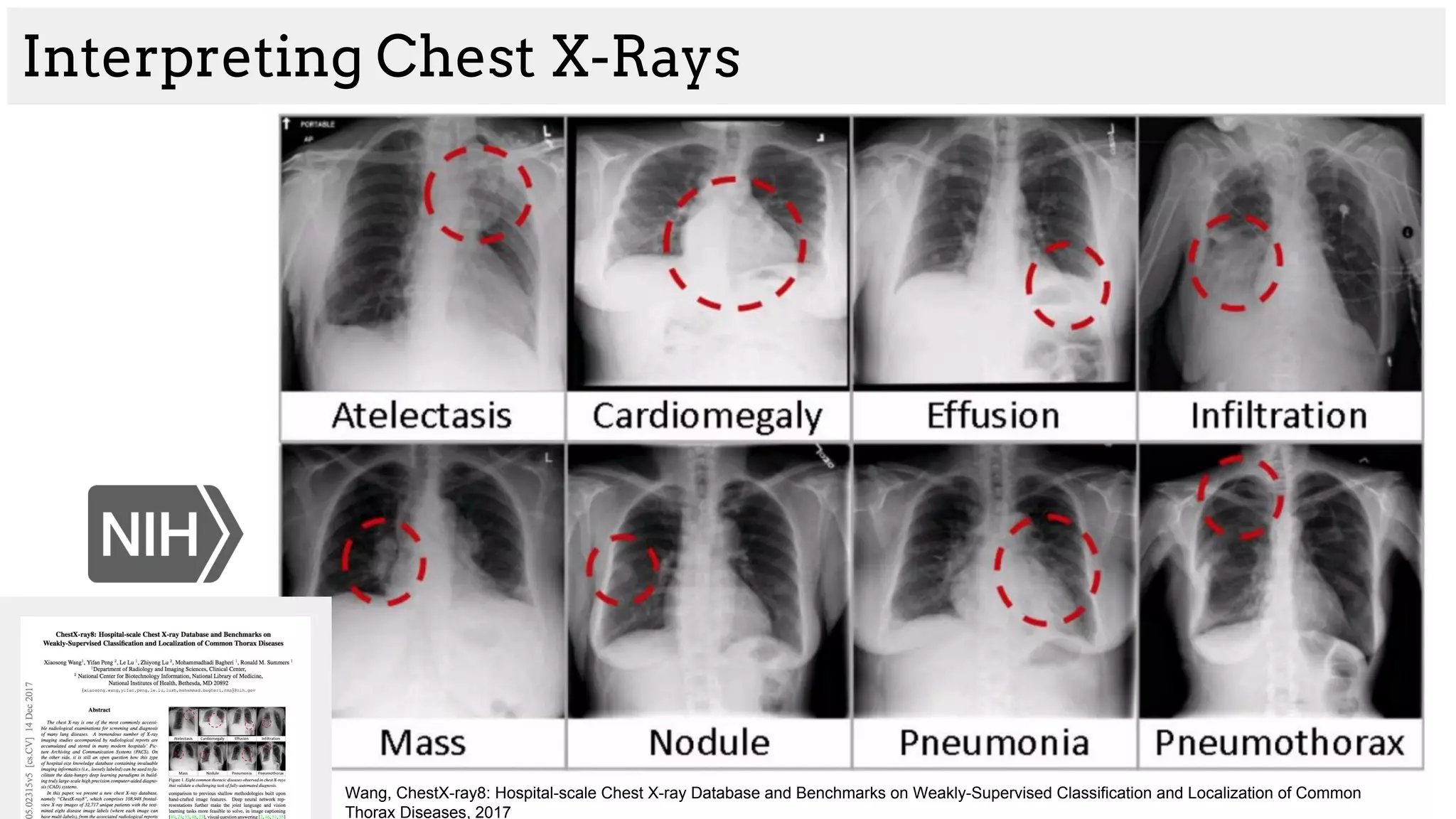
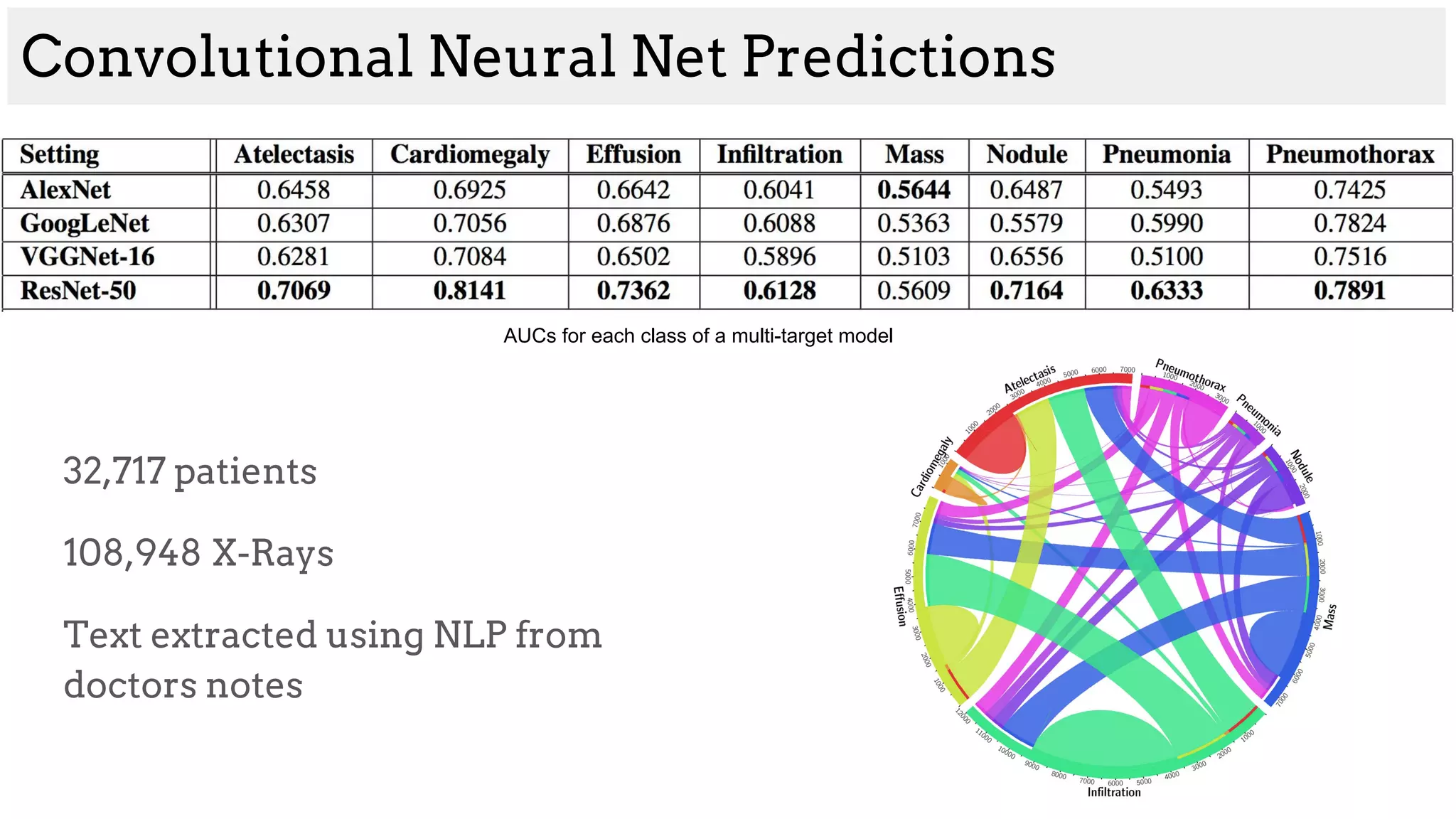
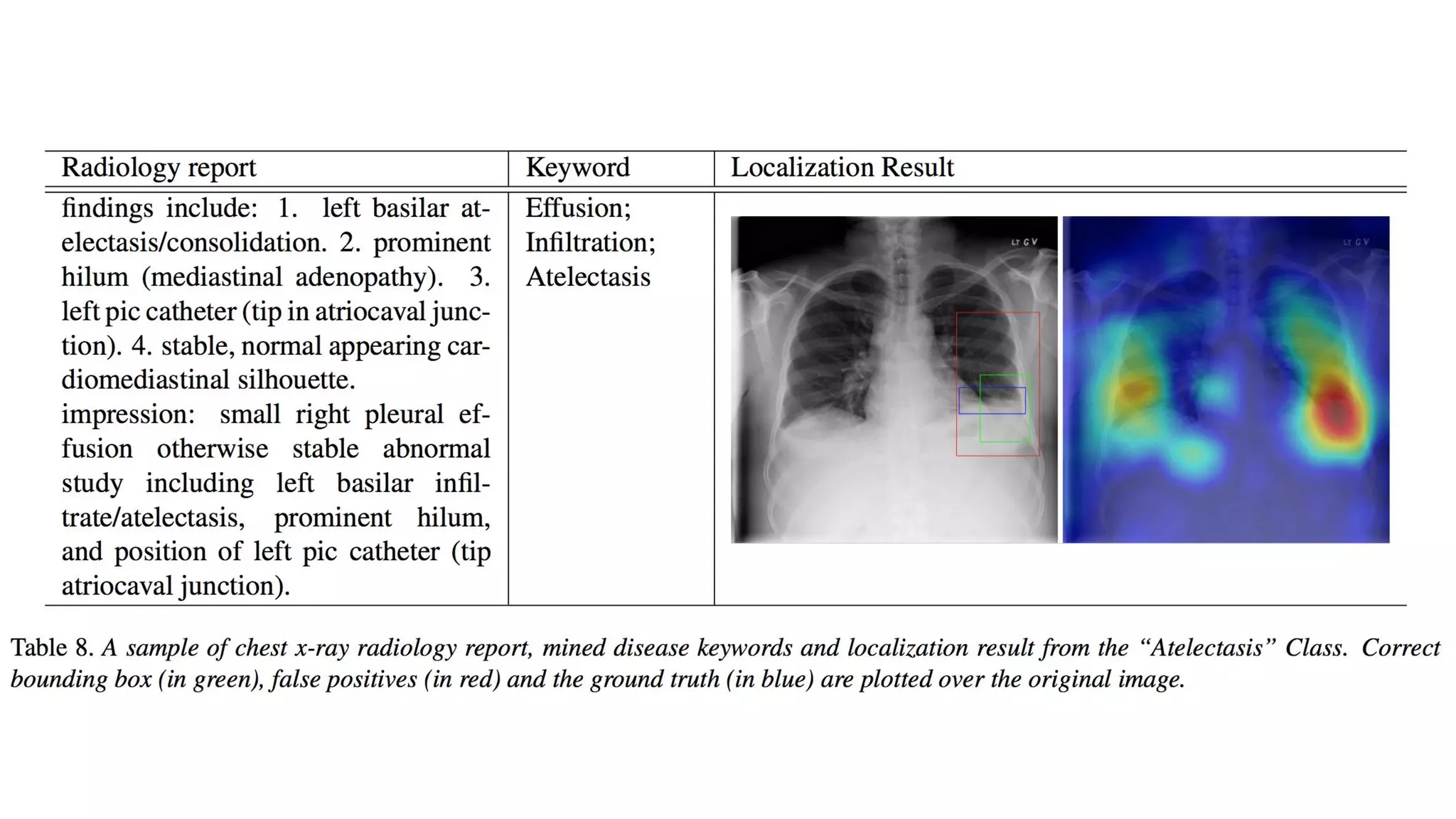
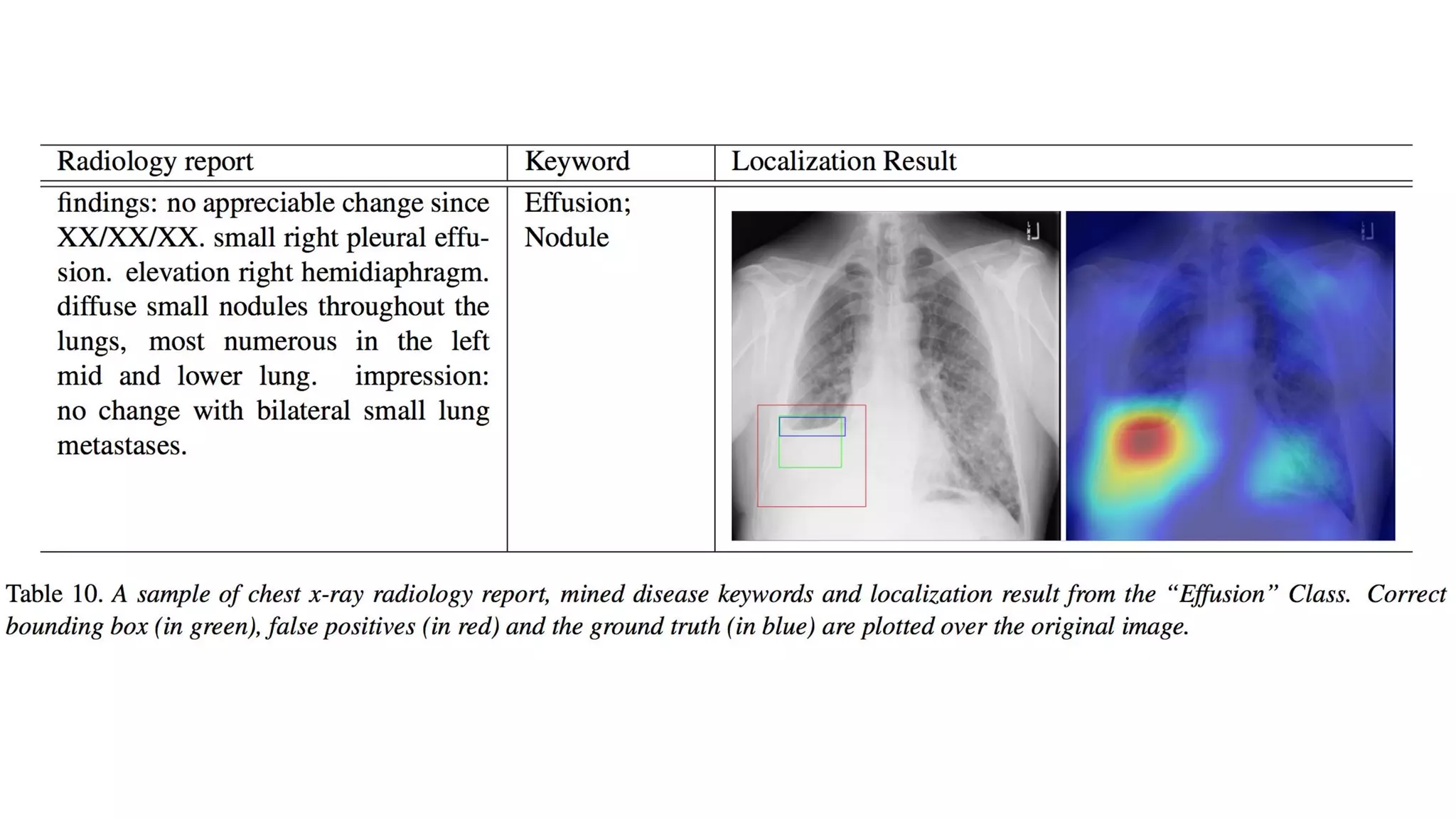
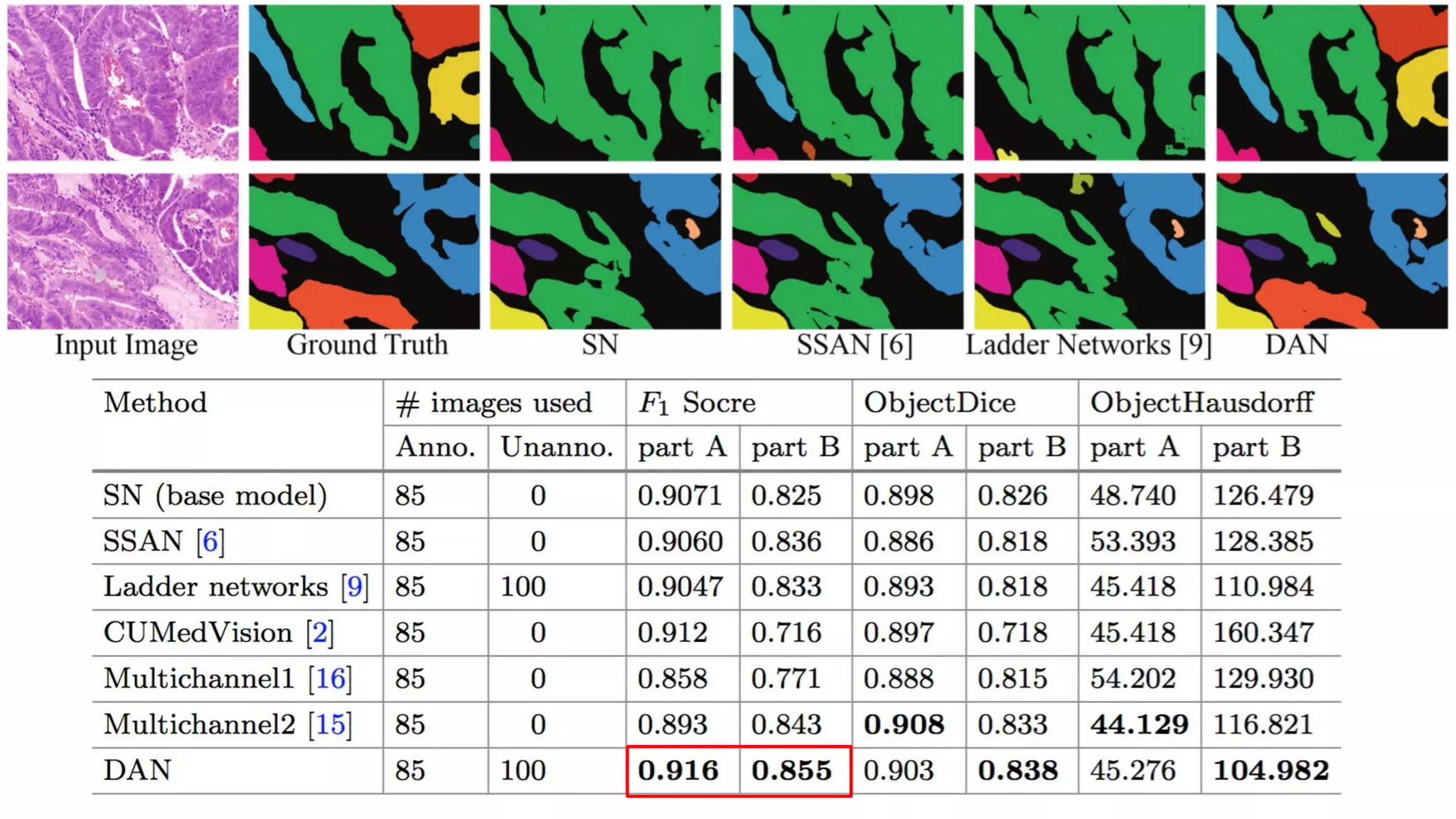
The document discusses deep learning applications in medical fields, covering topics such as image segmentation, tumor detection, and genomics. It highlights specific projects, including automated pathology using deep learning models, and methods for cell counting and gene expression prediction. Additionally, it illustrates how these technologies reduce workload and improve diagnostic accuracy in various medical contexts.

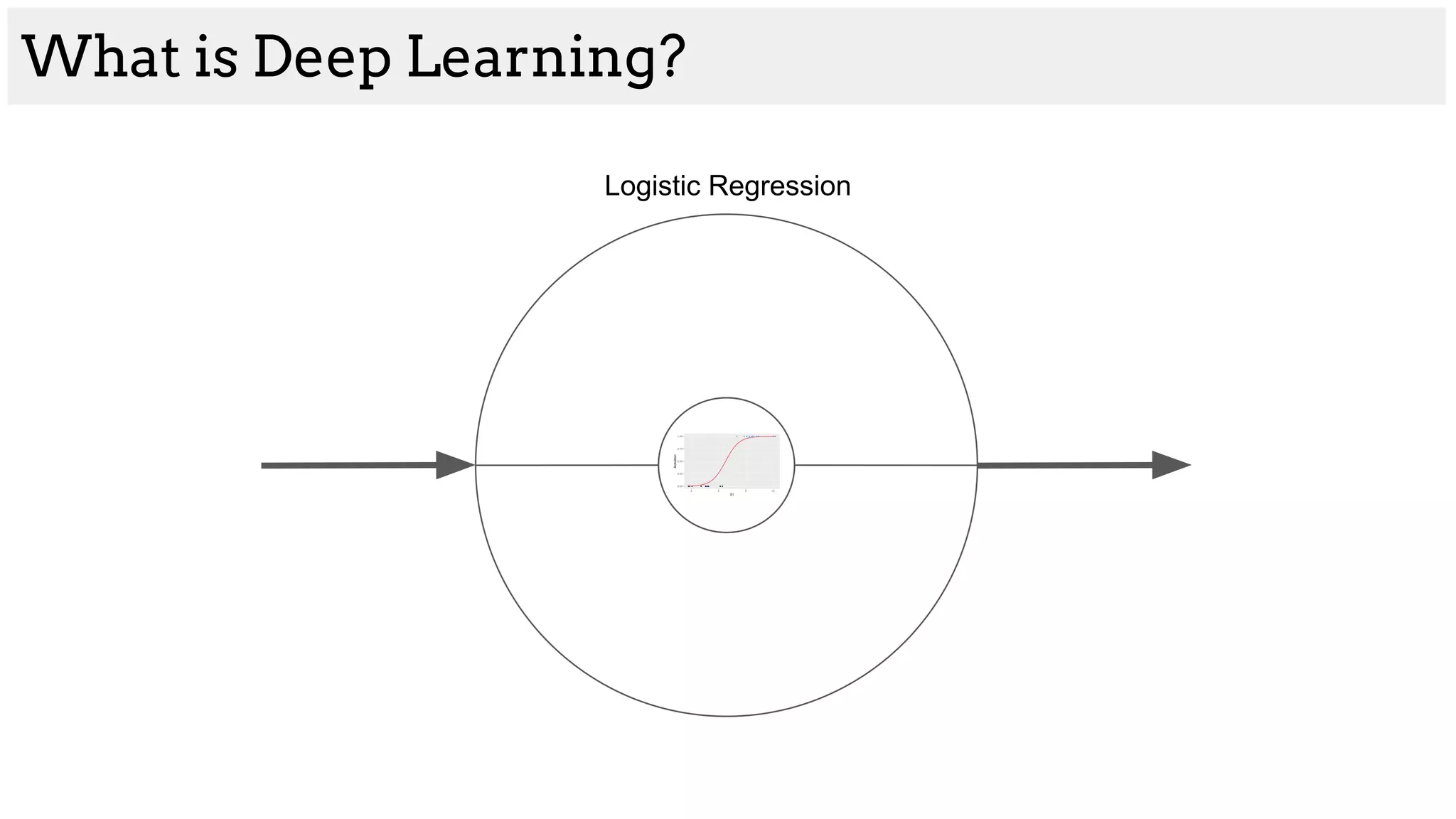
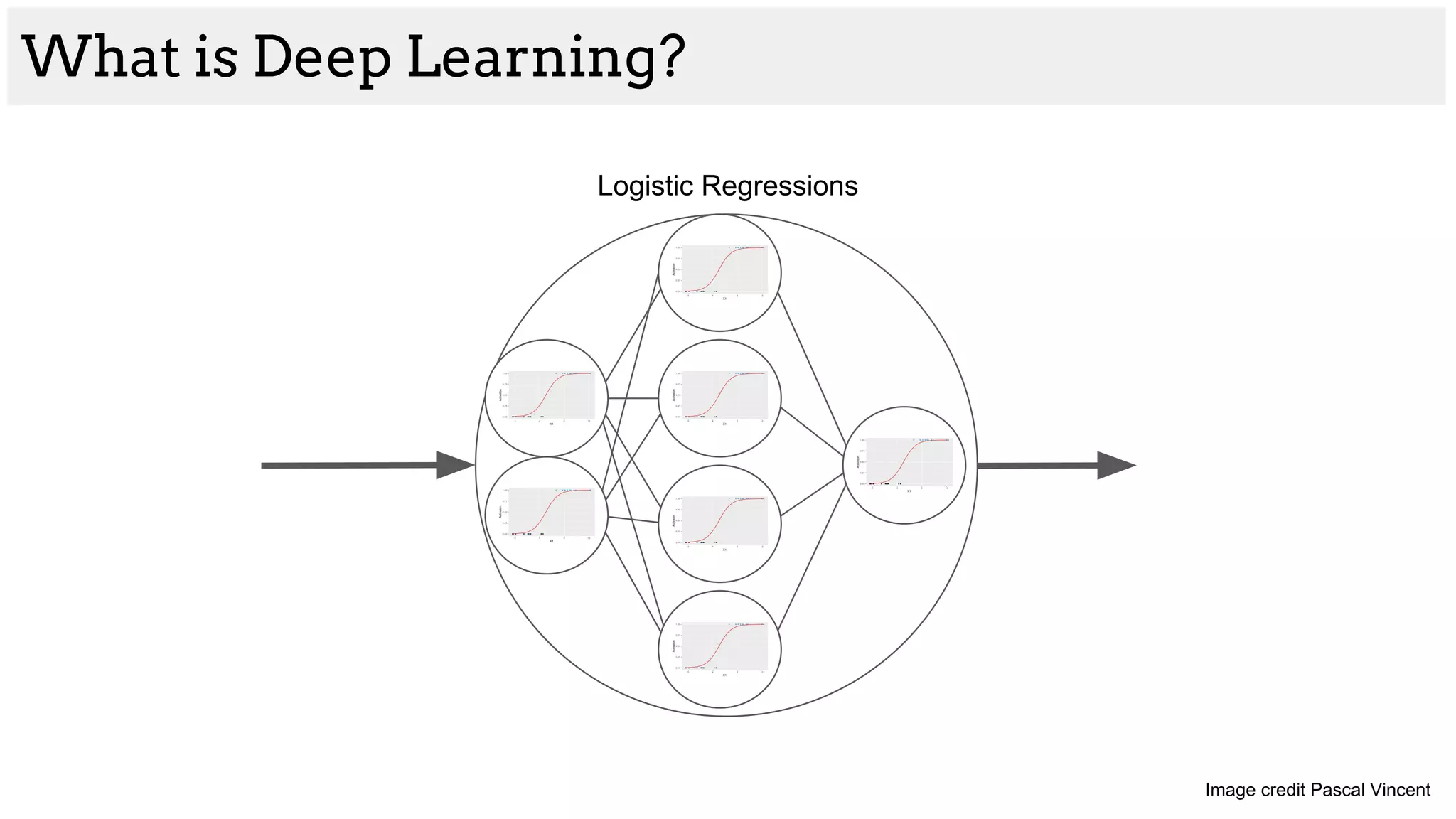
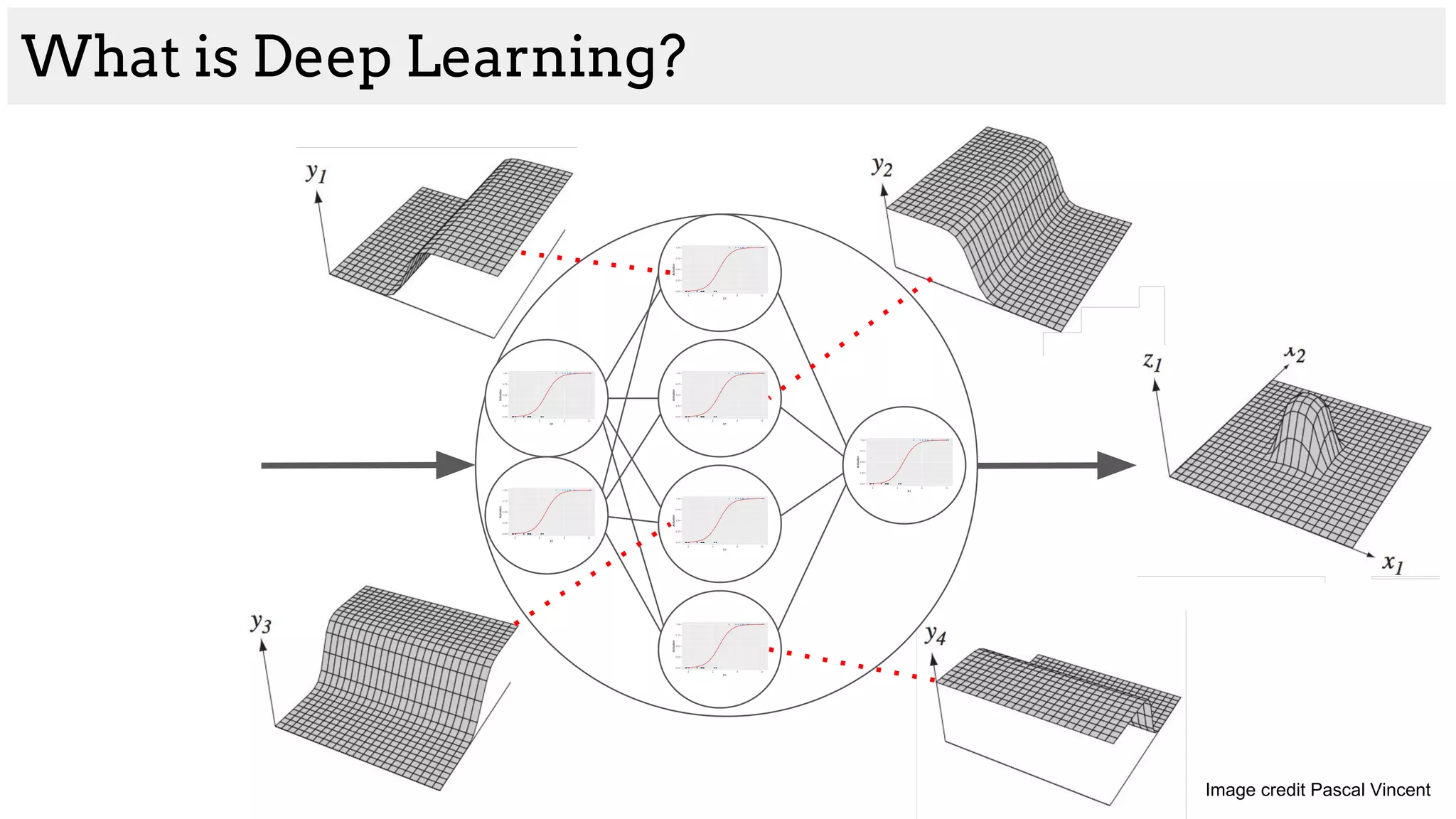
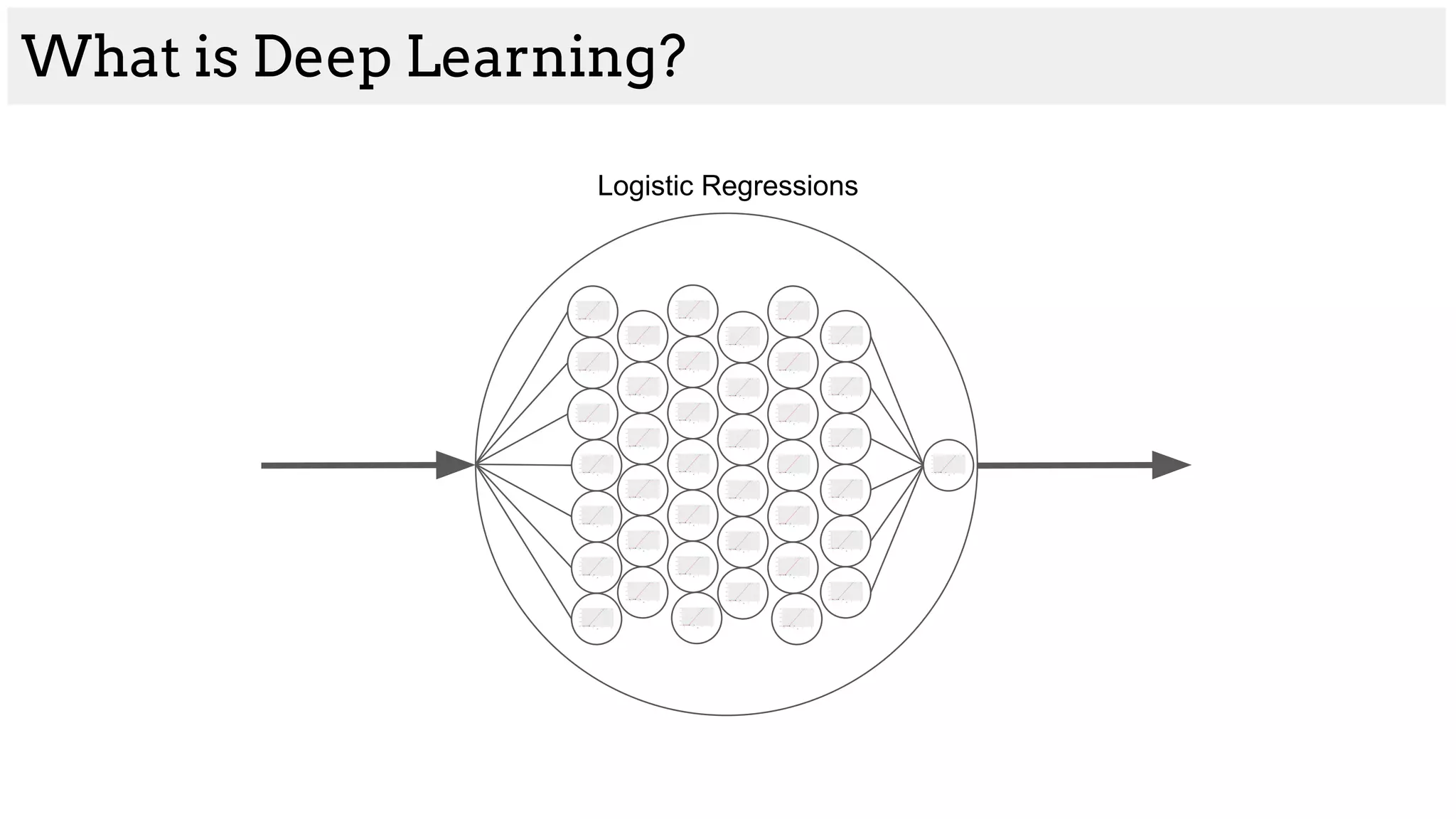
![What is Deep Learning?
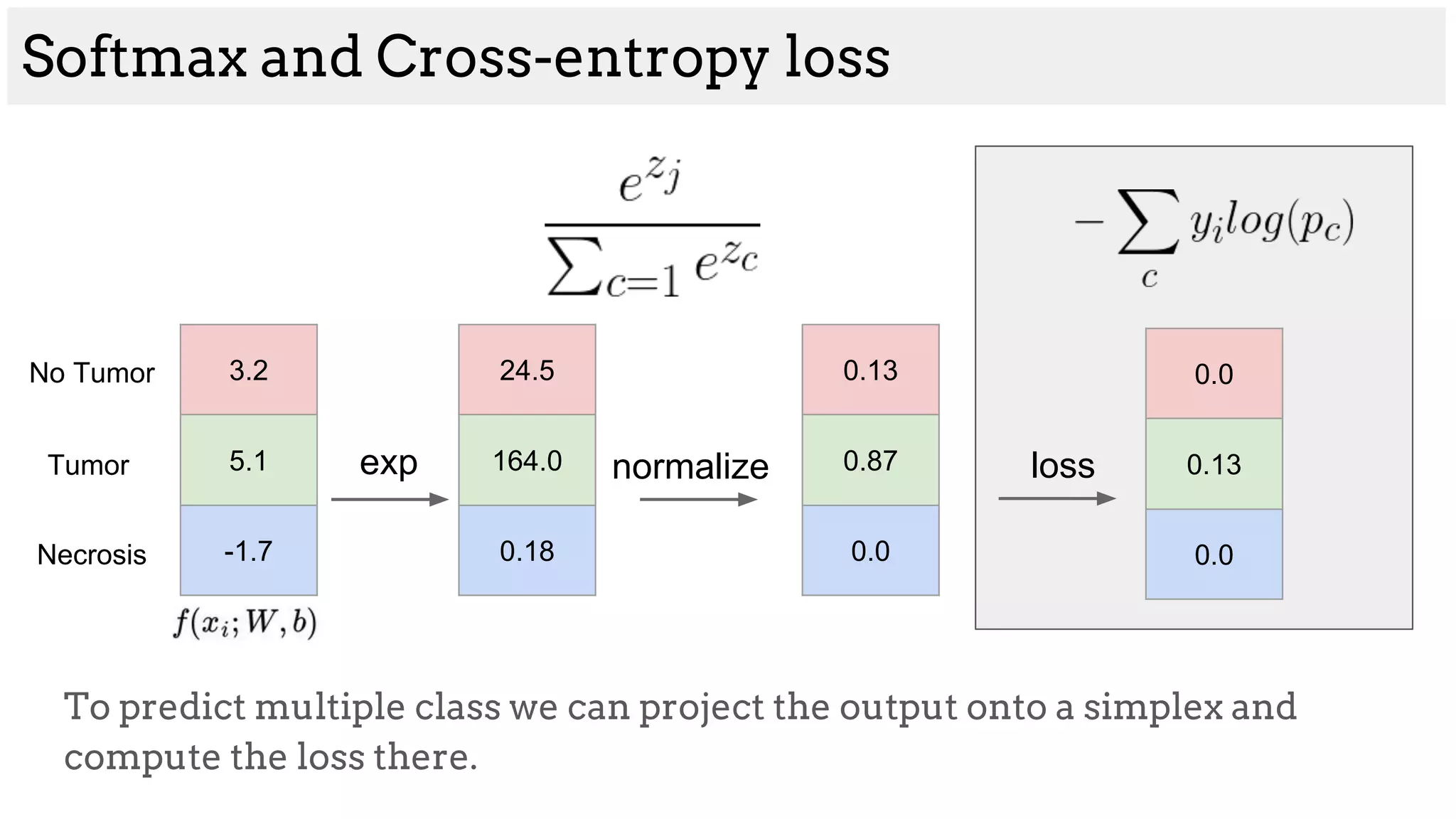
Logistic Regression
[200, 45, -4, 80] [1, 1, 0, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-2-2048.jpg)


![DownsampleUpsample
Segmentation with Deep Learning
Image by Qikui Zhu
[Ronneberger et al., U-Net: Convolutional Networks for
Biomedical Image Segmentation 2015]
[Honari et al., Recombinator Networks: Learning
Coarse-to-Fine Feature Aggregation 2015]
Images by Vincent Dumoulin (UdeM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-14-2048.jpg)

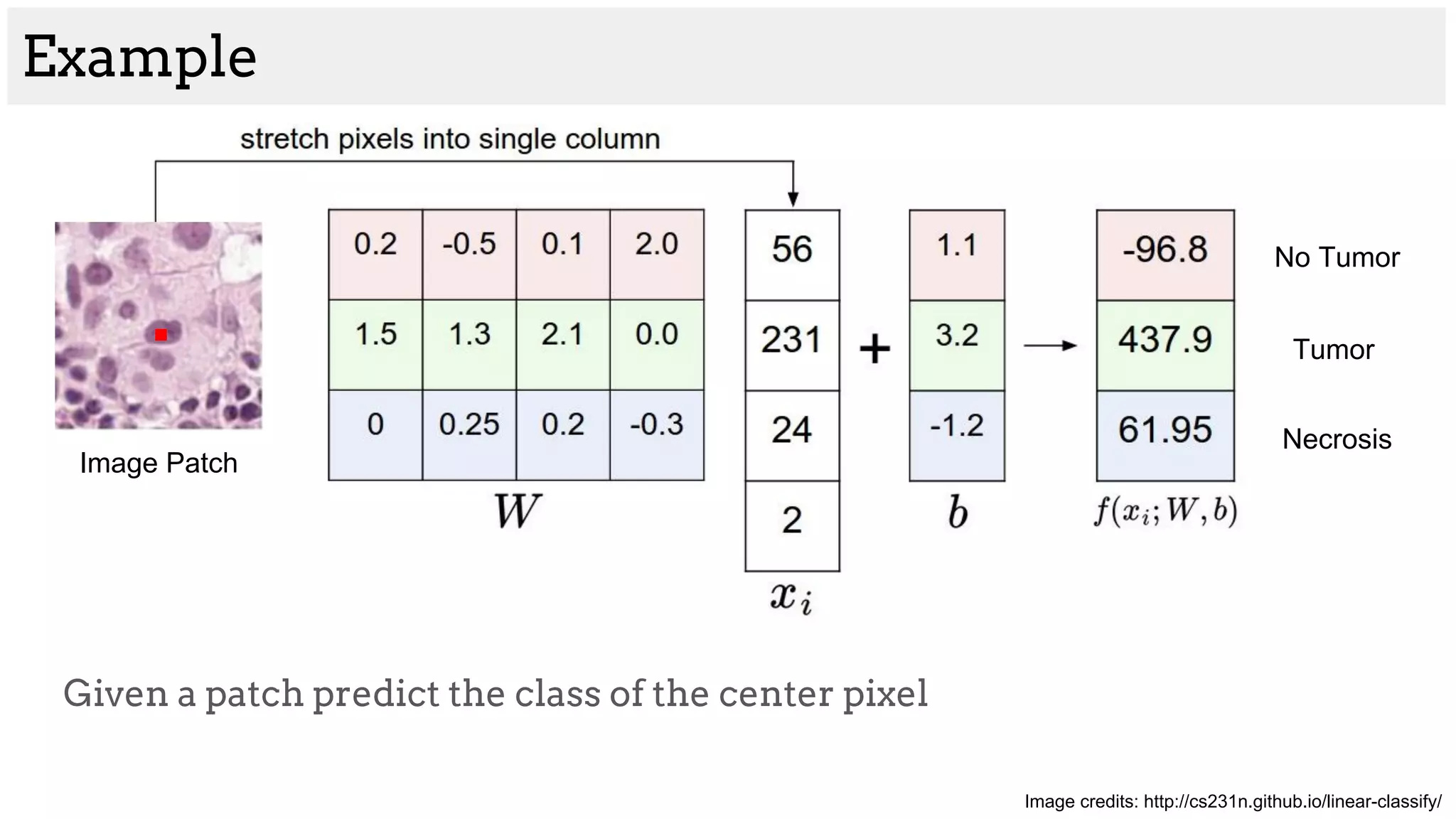
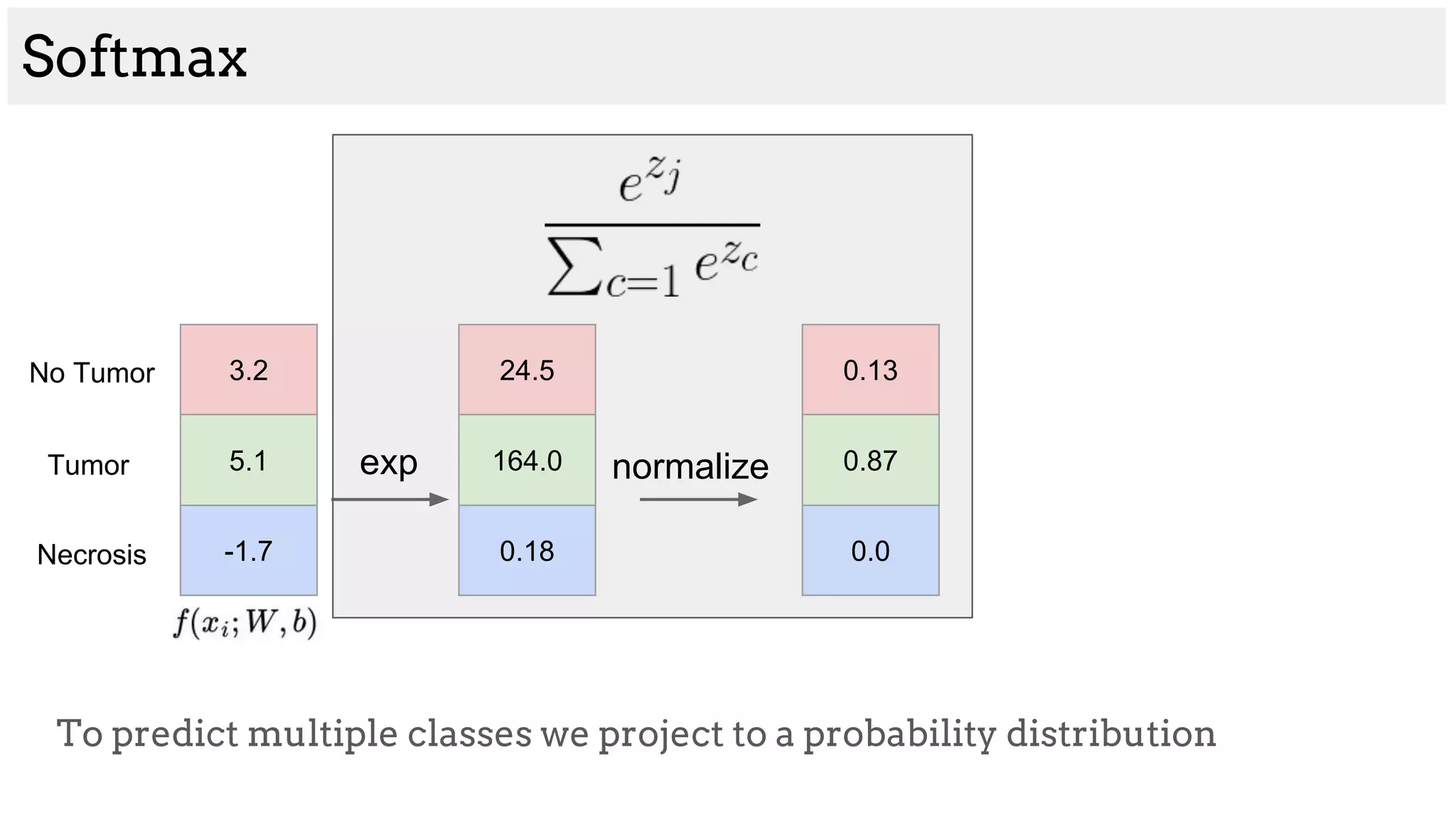
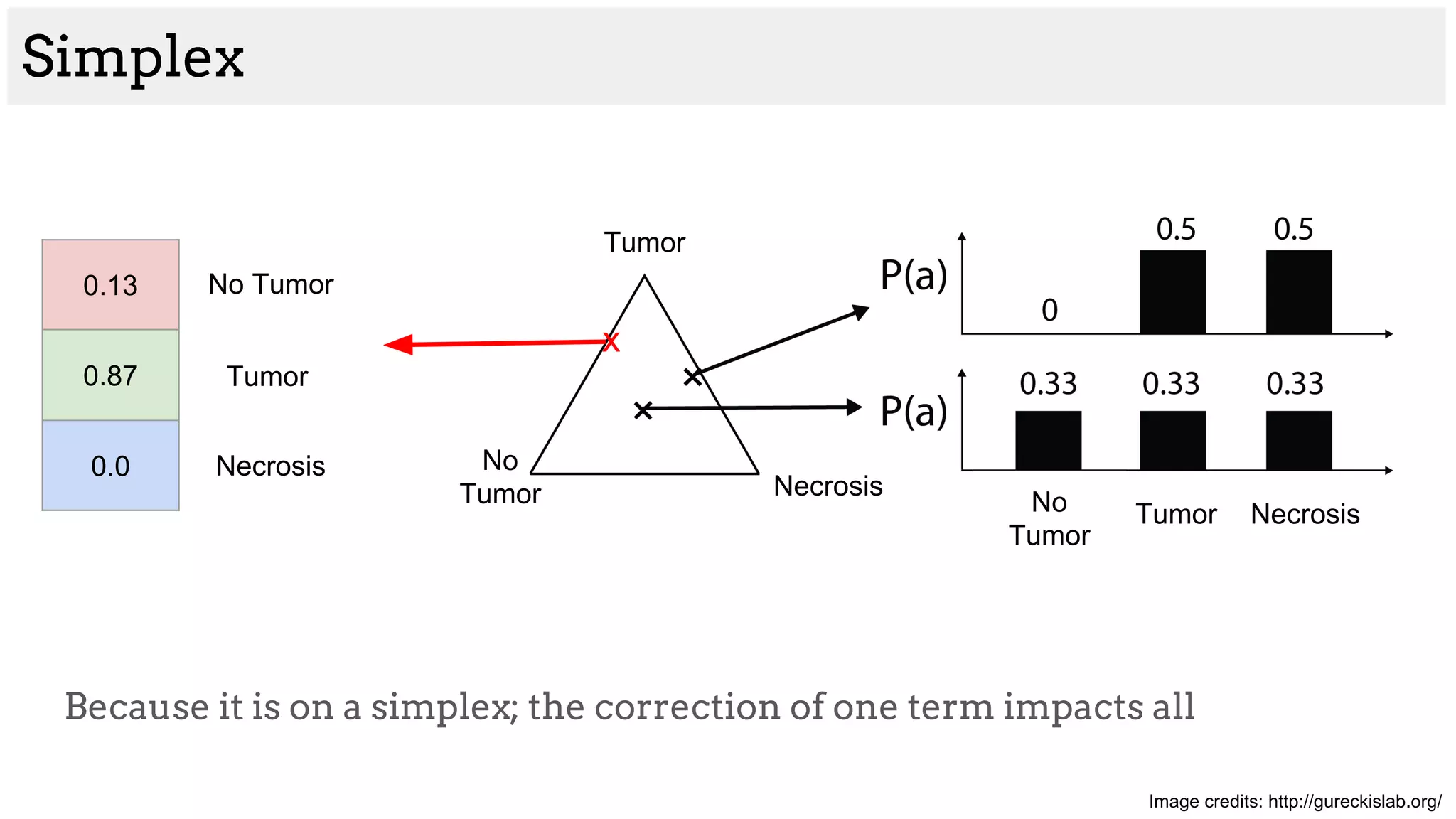
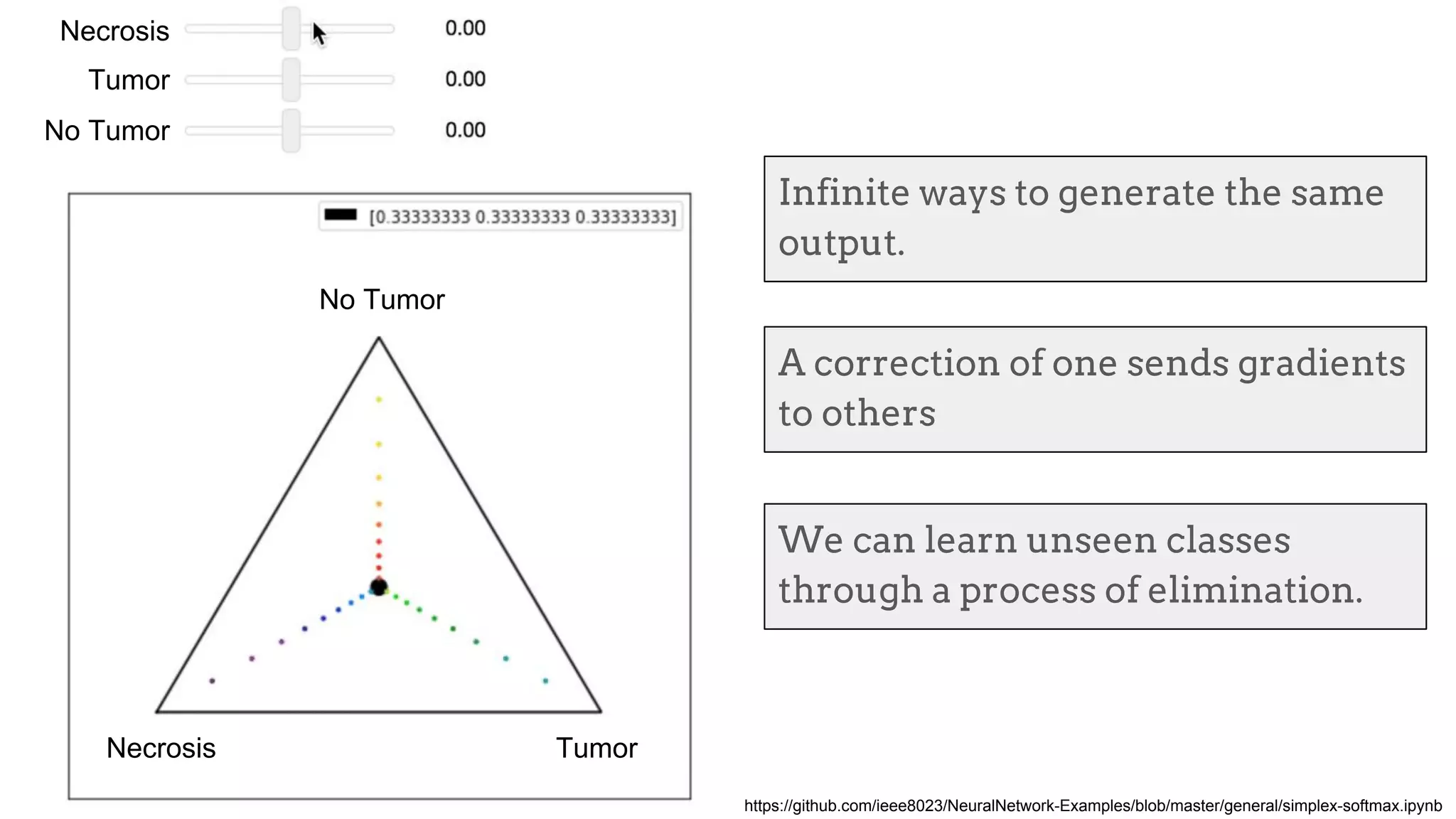

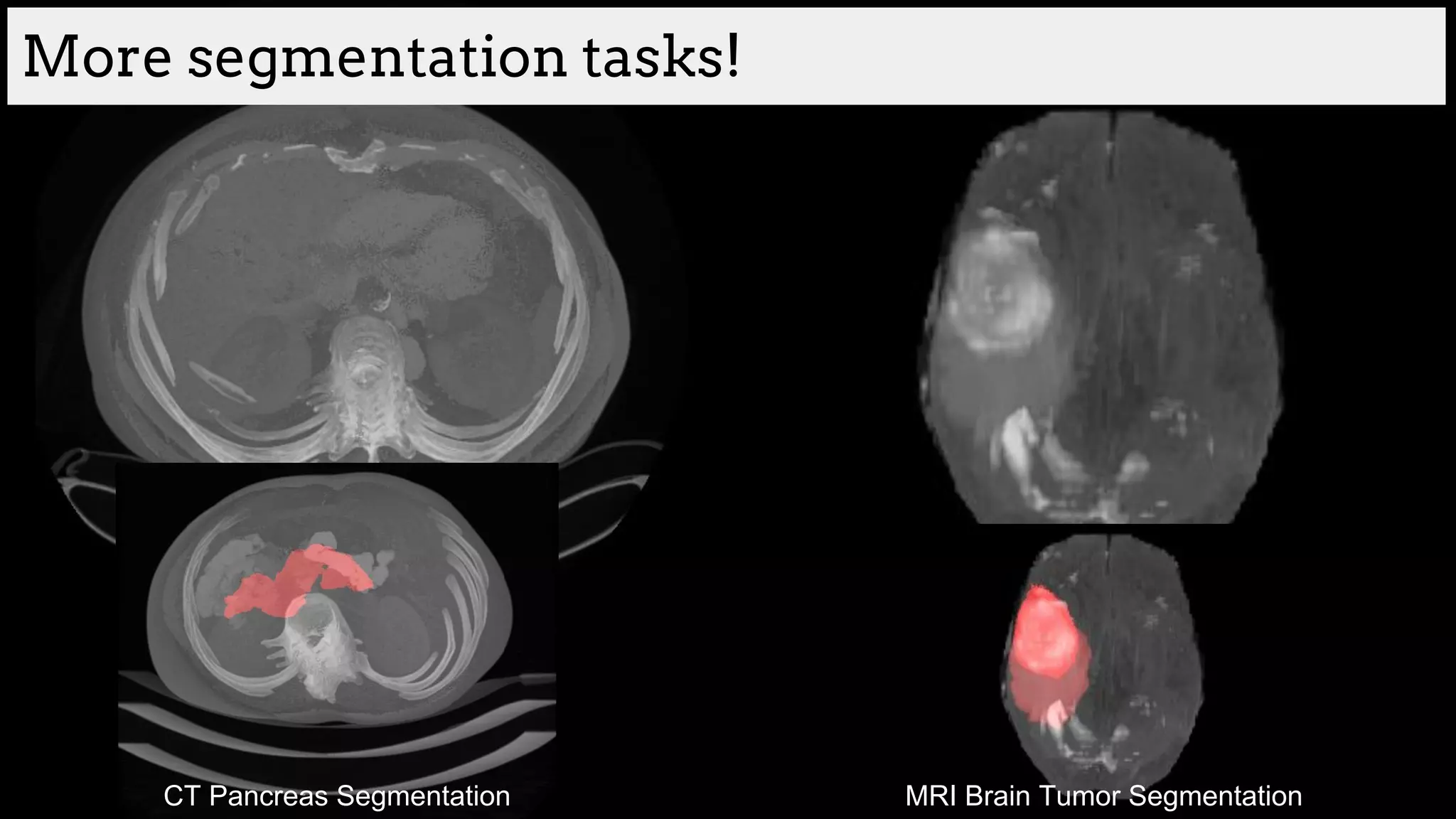
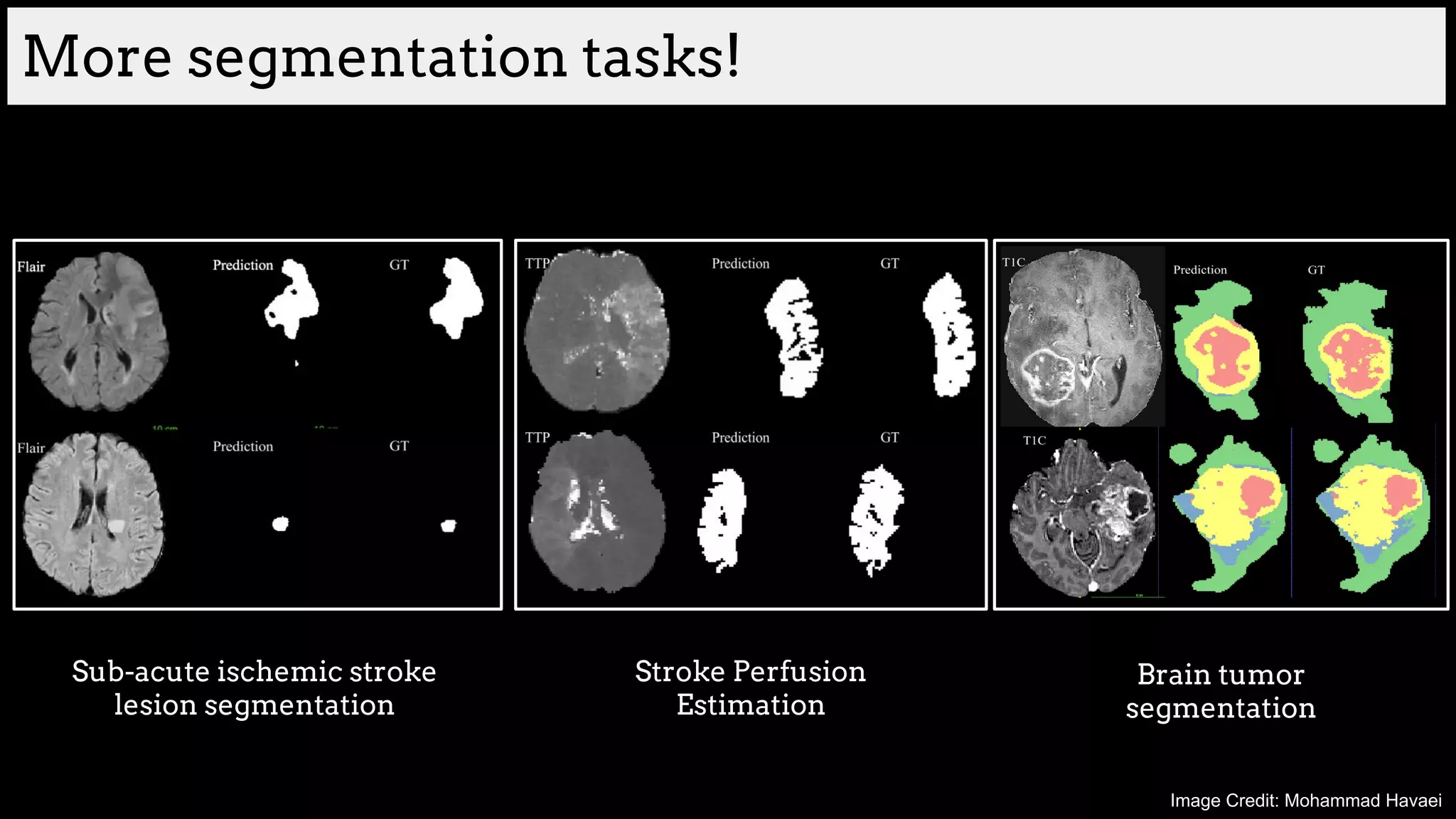
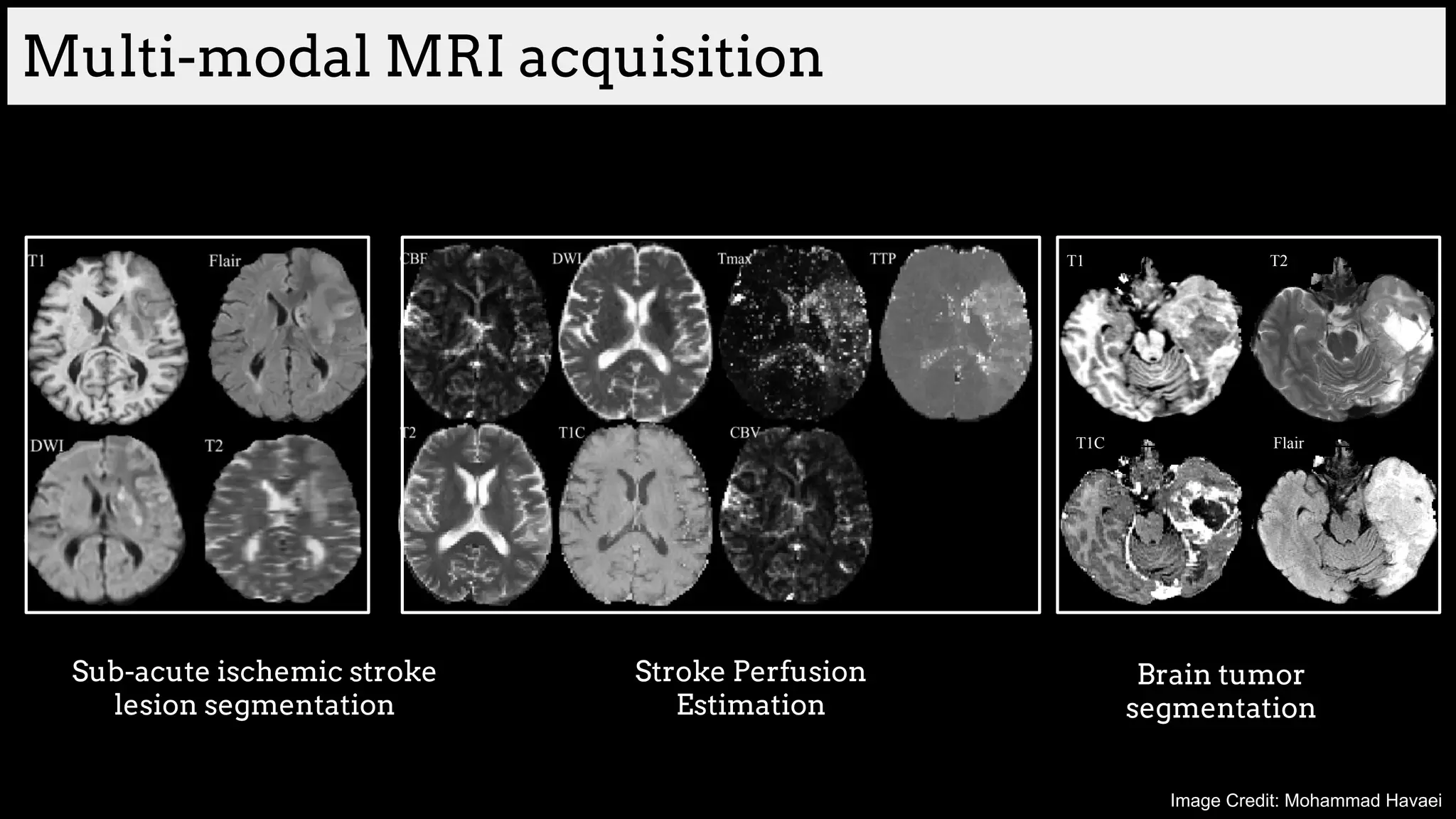
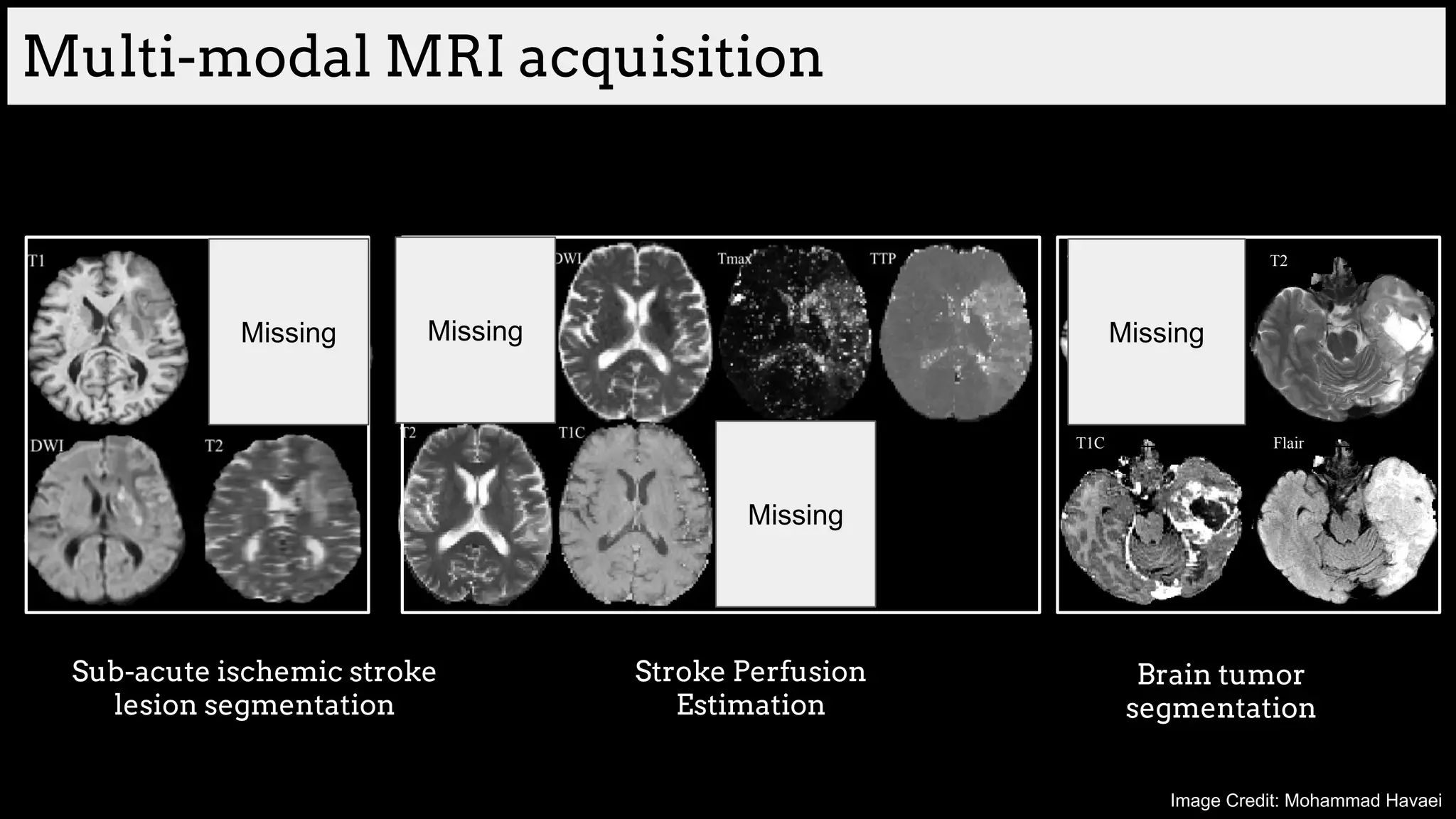
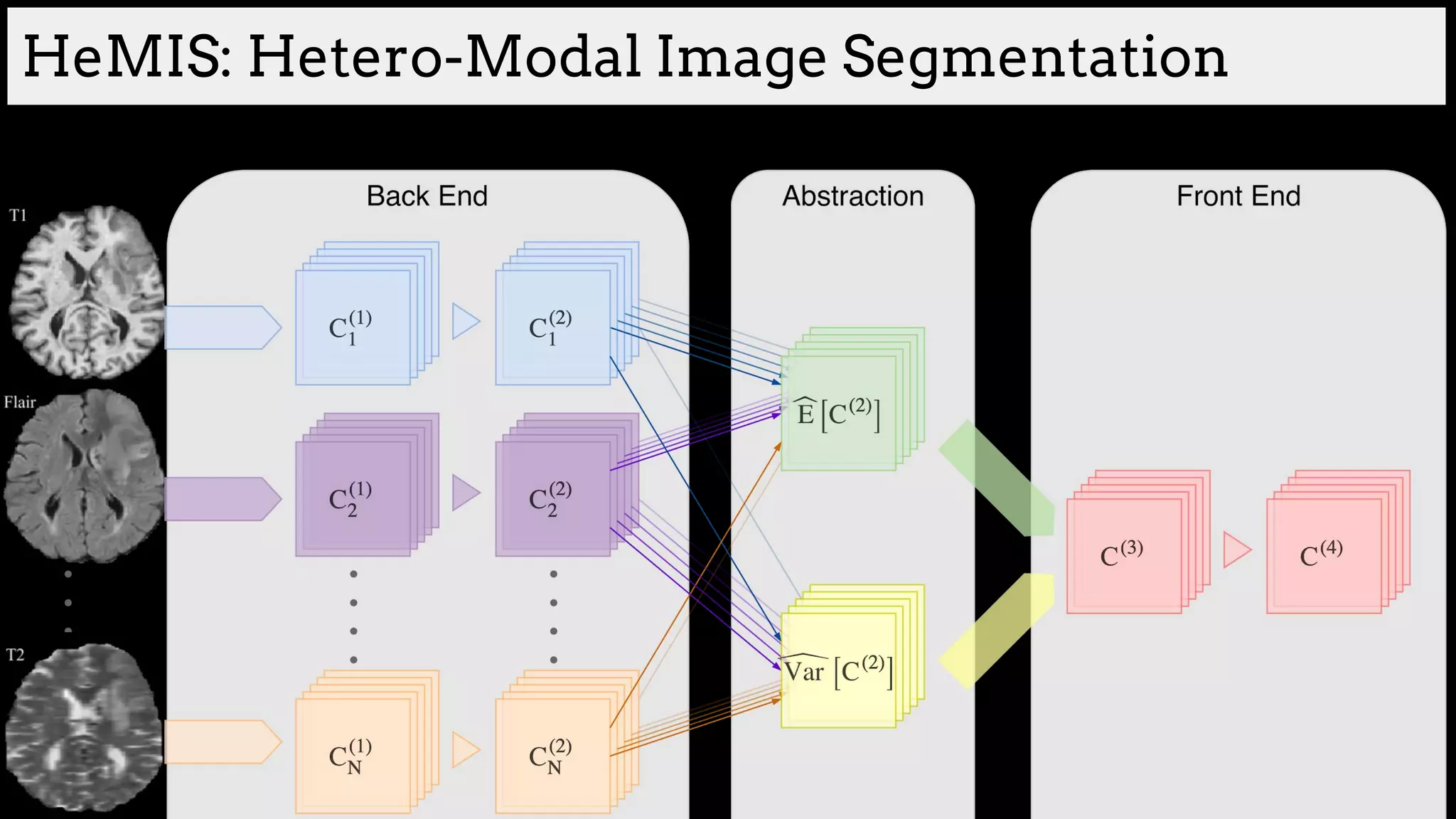
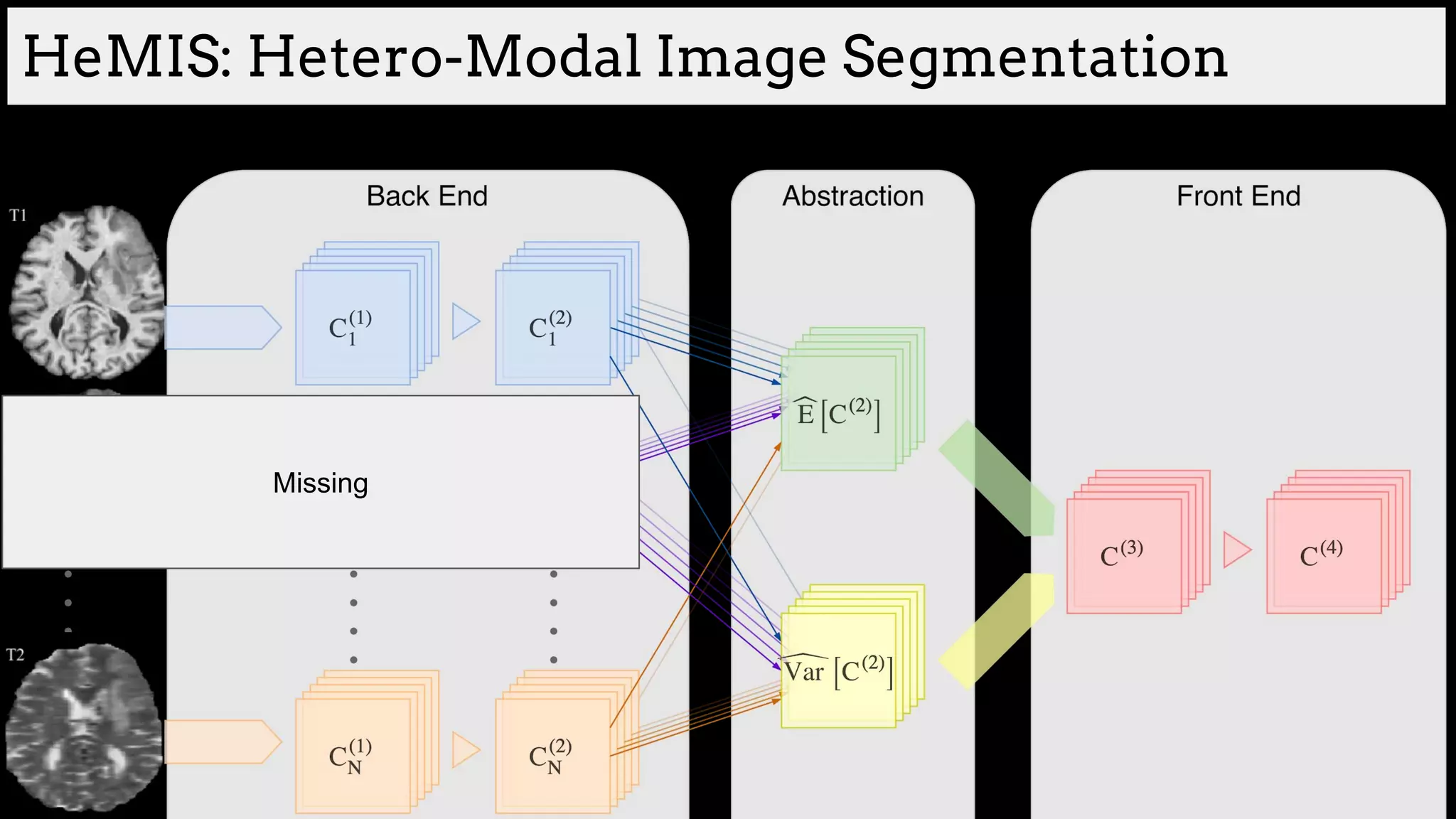

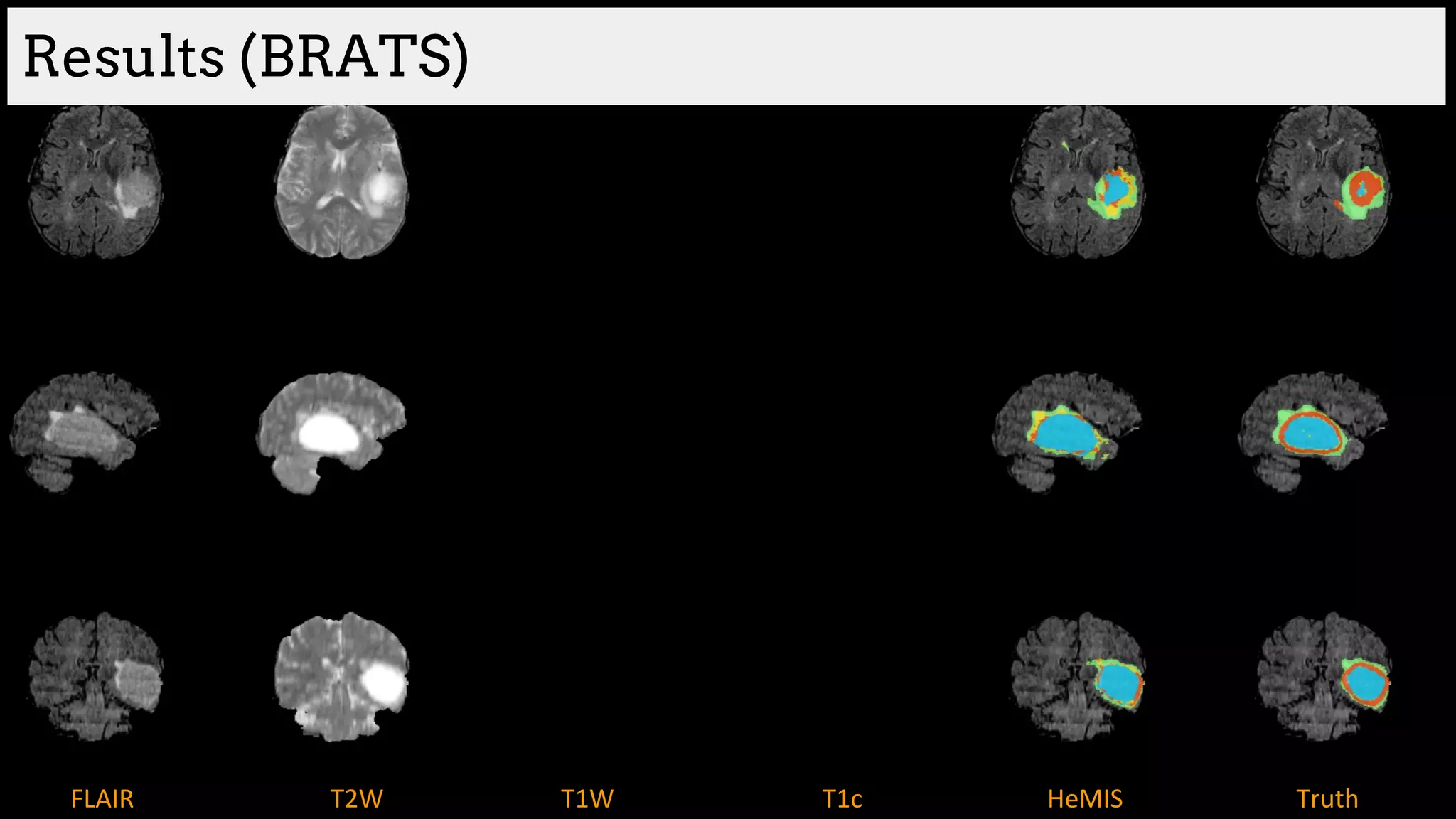
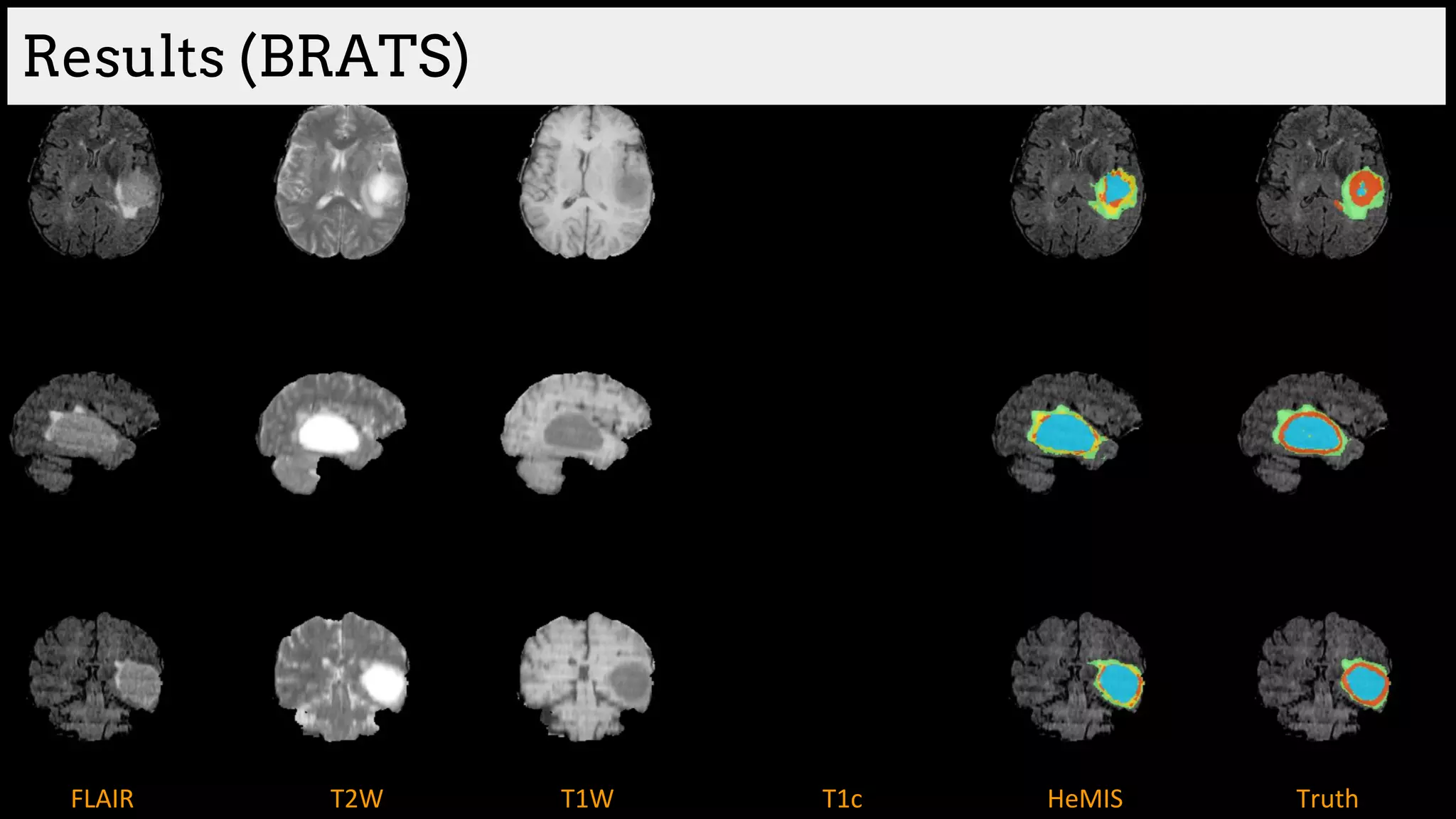
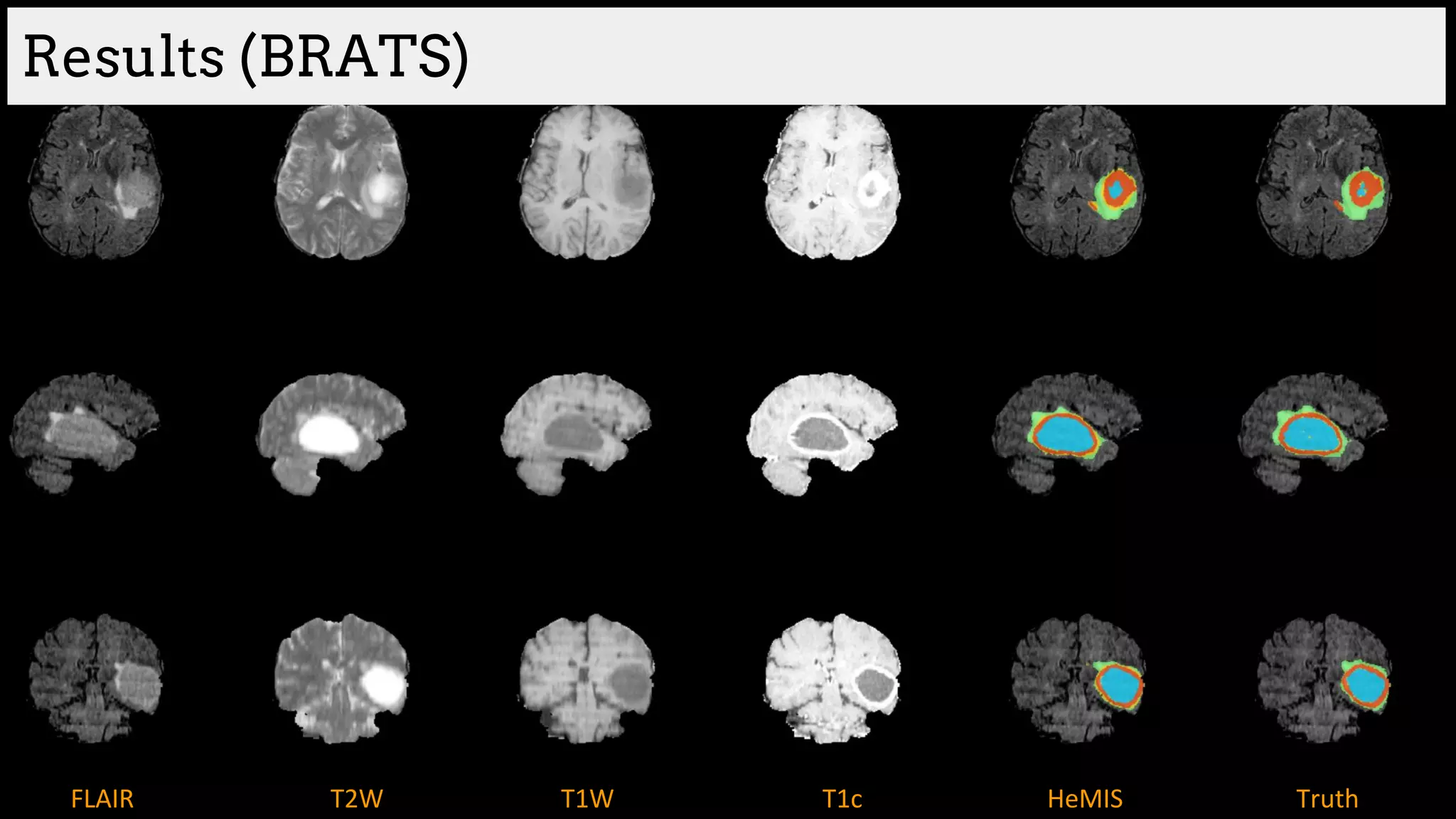
![Brain tumor segmentation (BRATS2013 dataset)
T1 T2
T1C Flair
GT
Edema
Necrosis
Non-enhanced
Enhanced
Training data:
220 subjects with high grade and
54 subjects with low grade tumors
Dice Similarity
[Havaei et al. HeMIS: Hetero-Modal Image Segmentation, MICCAI 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-34-2048.jpg)


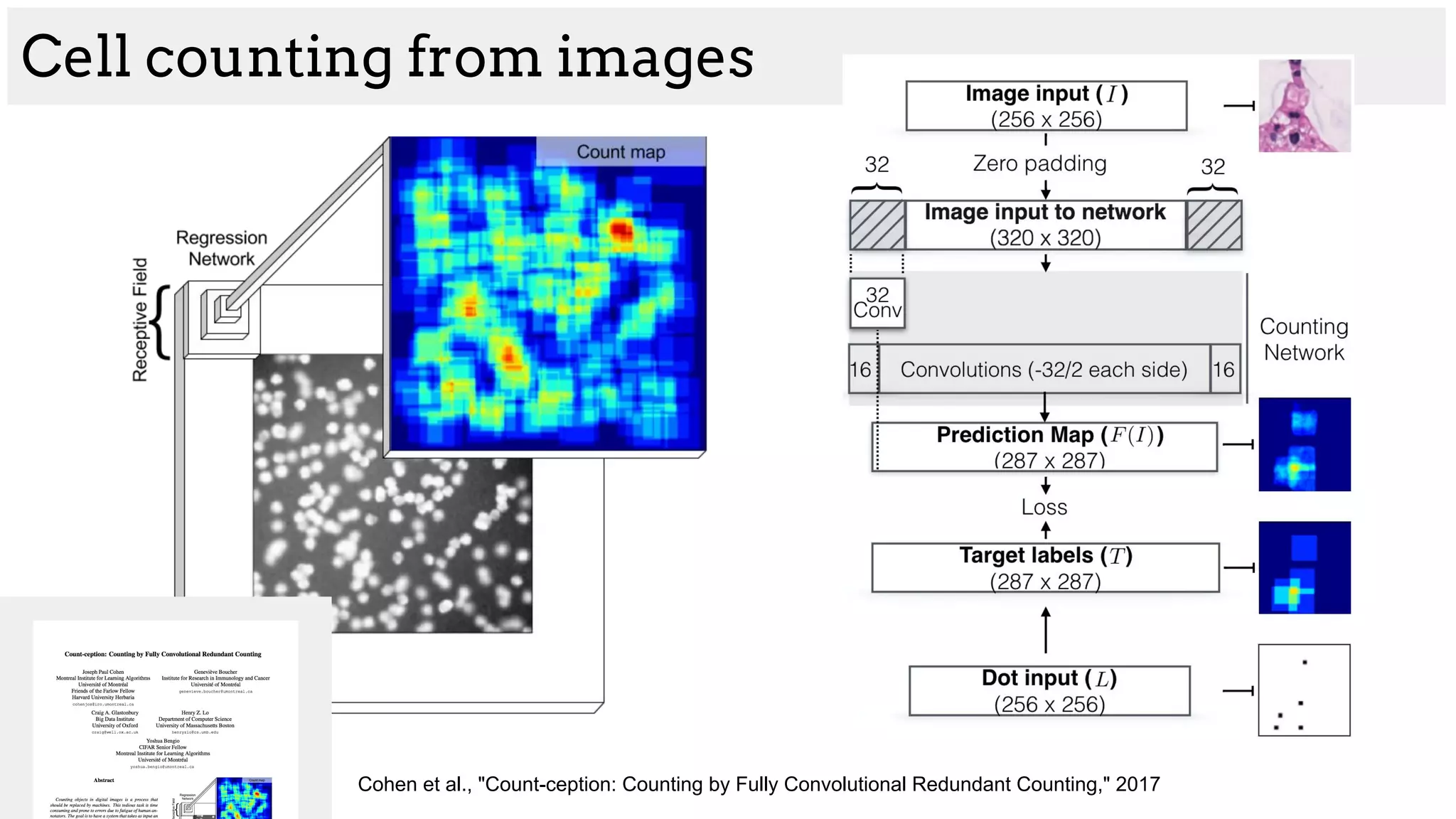
![[Cohen et al. 2017]
Complicated cell structure
Cell counting from images](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-41-2048.jpg)
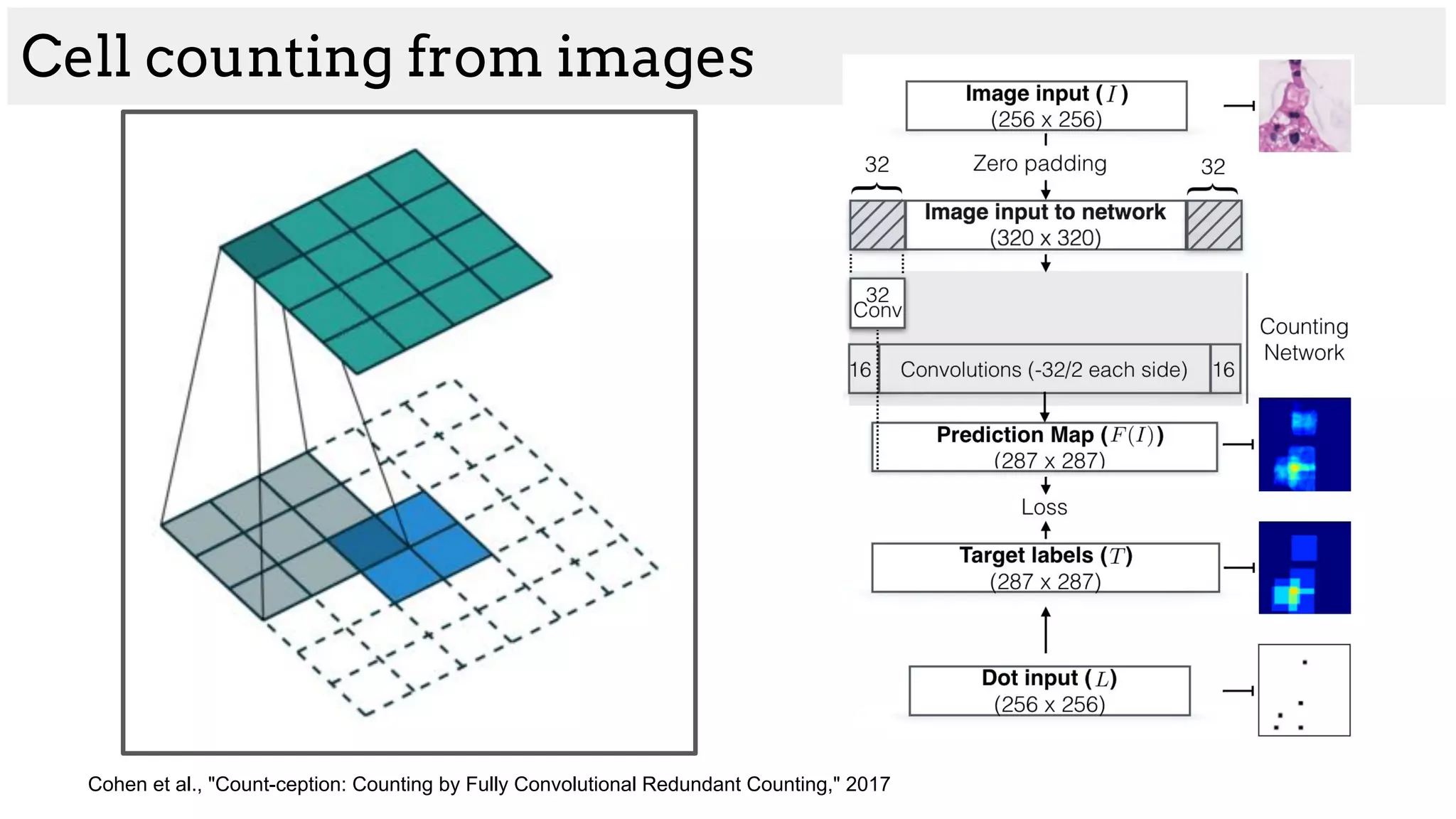
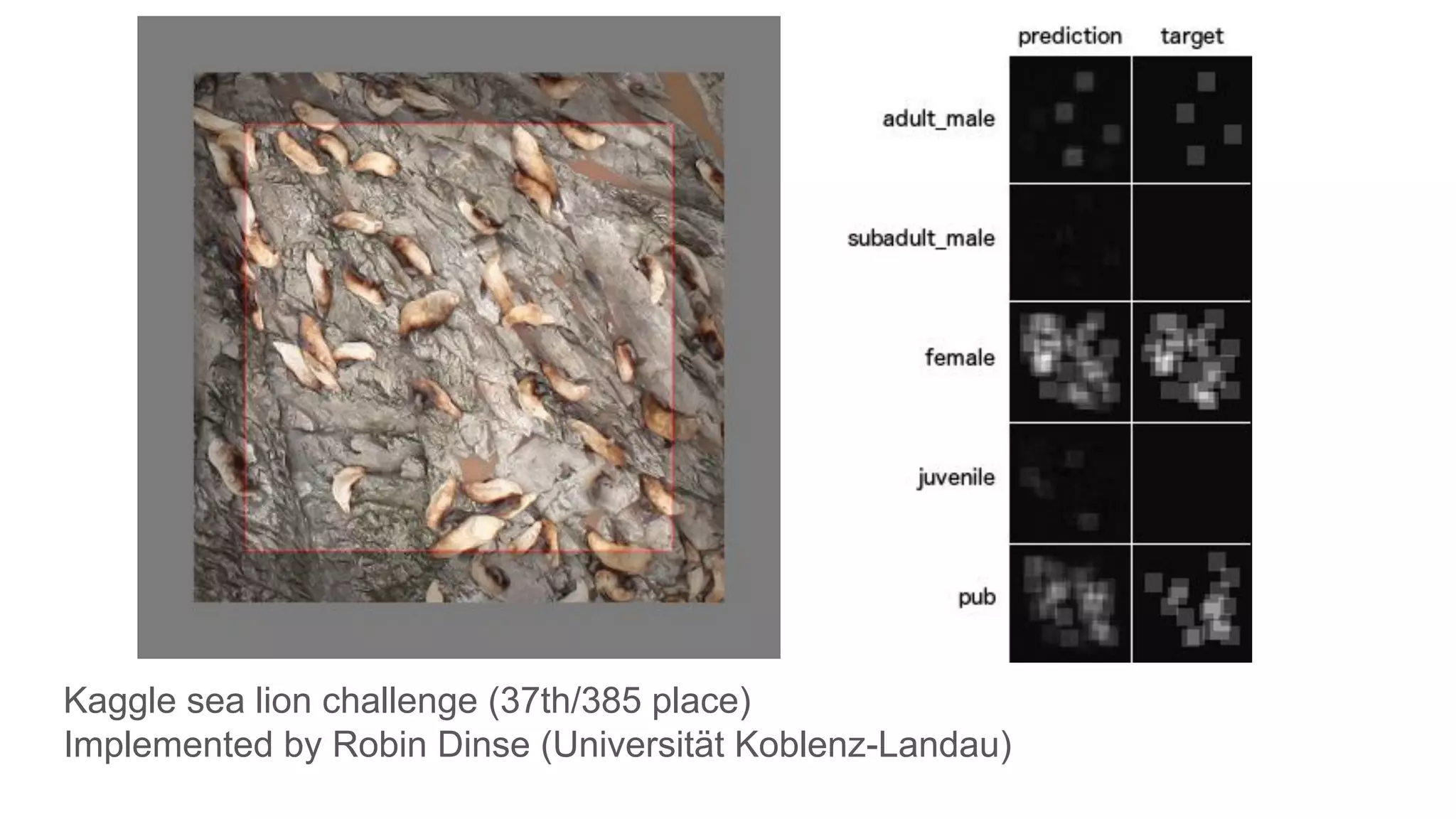
![[Cohen et al. 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-44-2048.jpg)
![[Cohen et al. 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-45-2048.jpg)

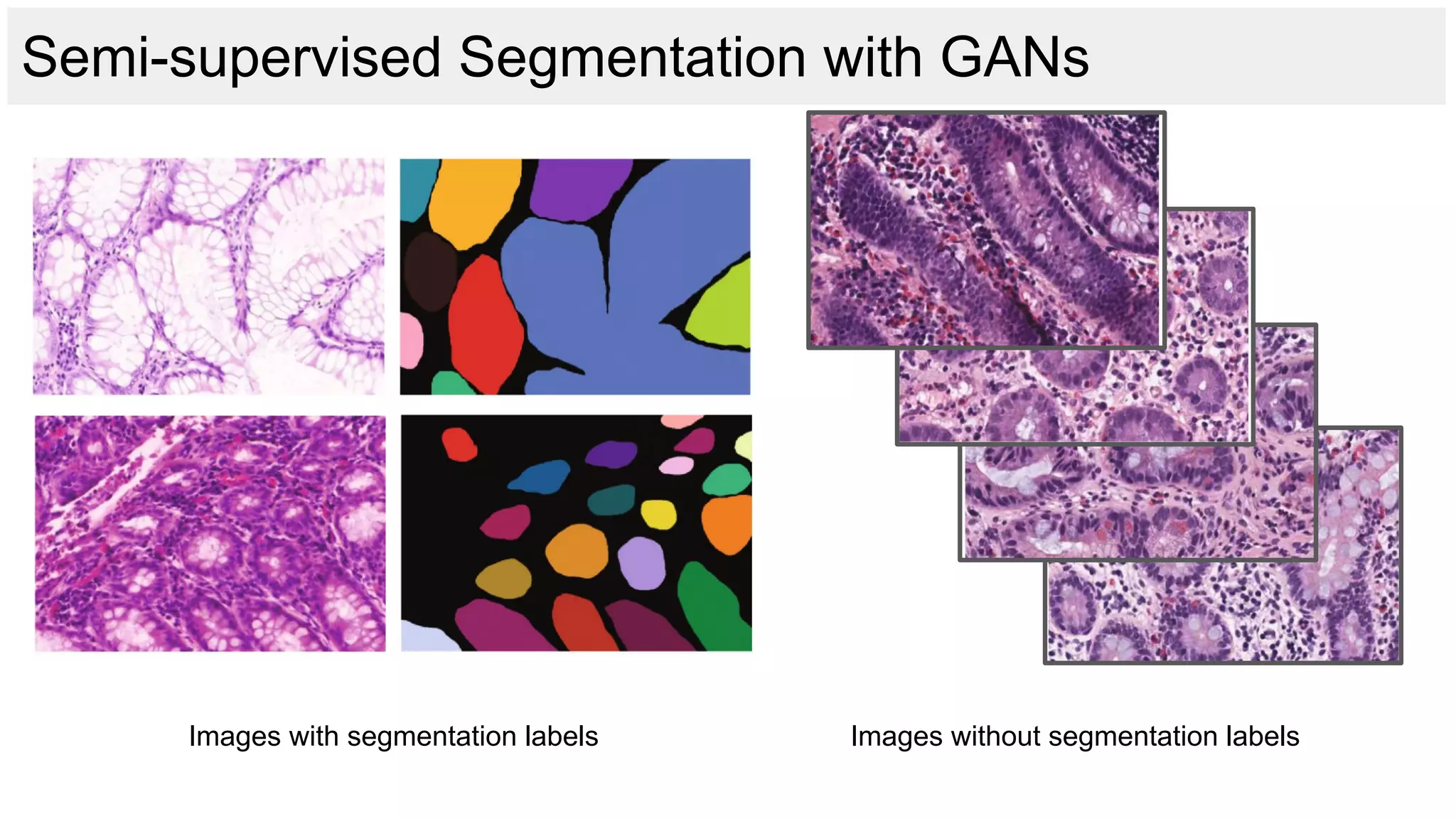
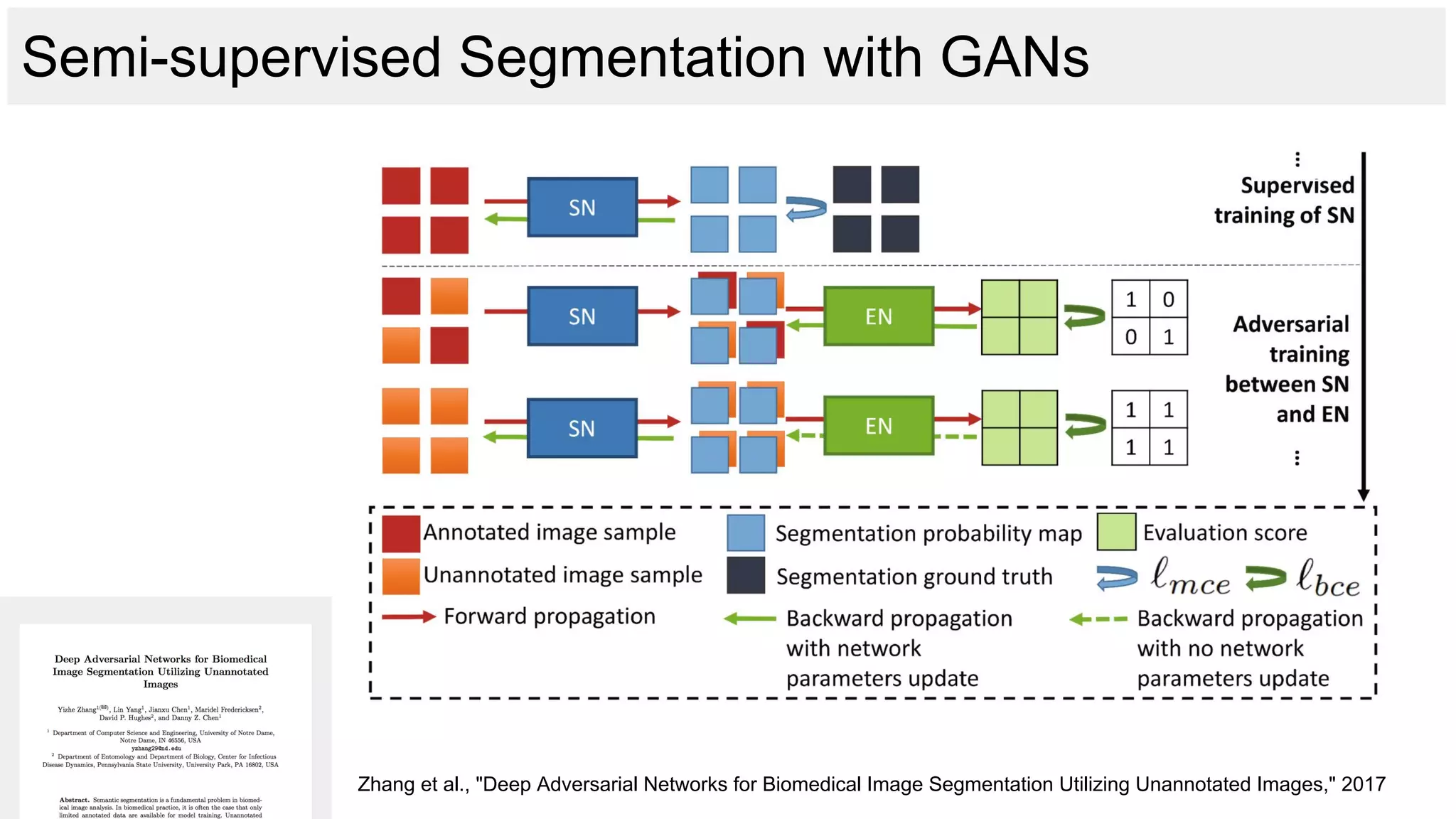

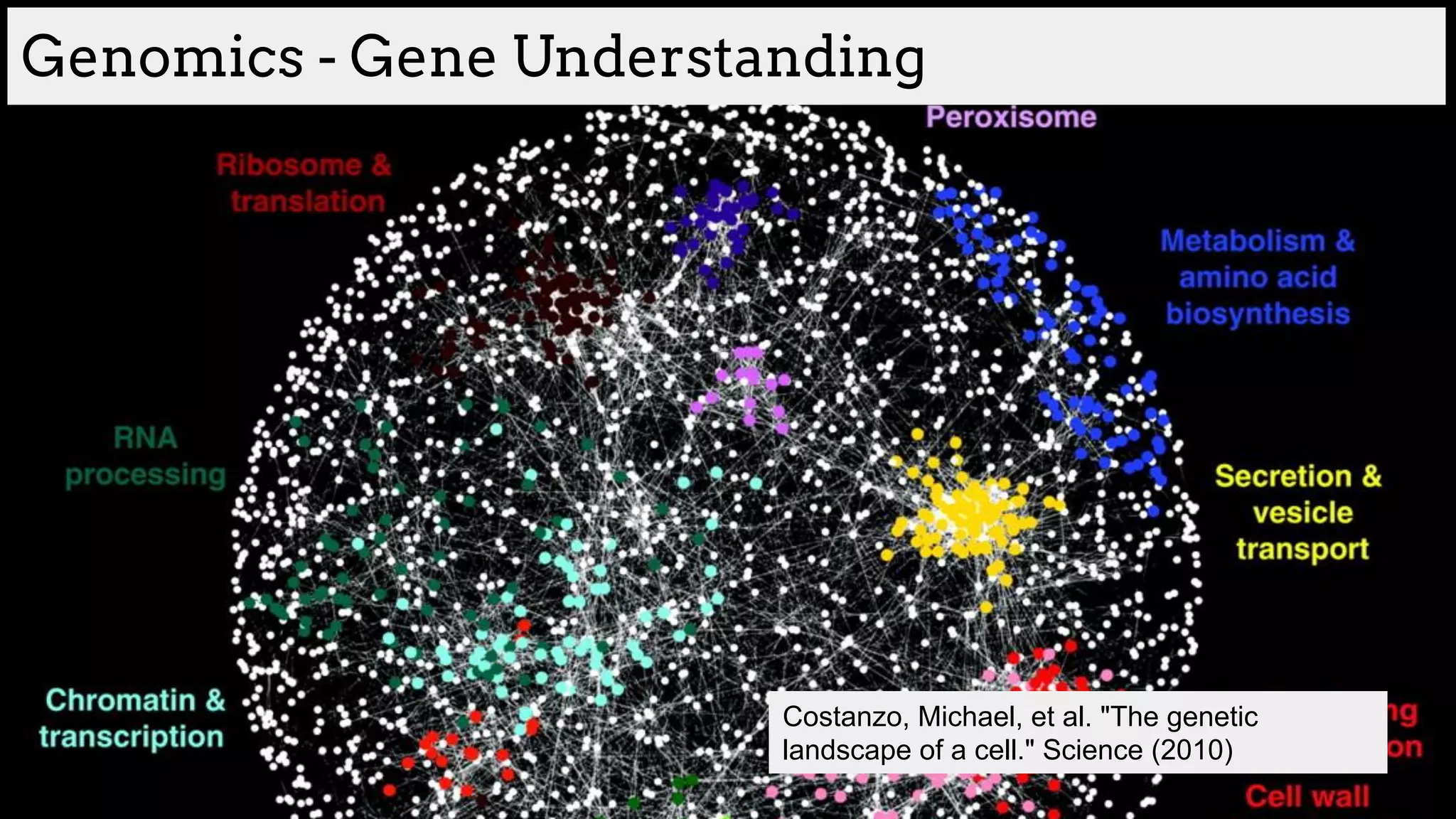
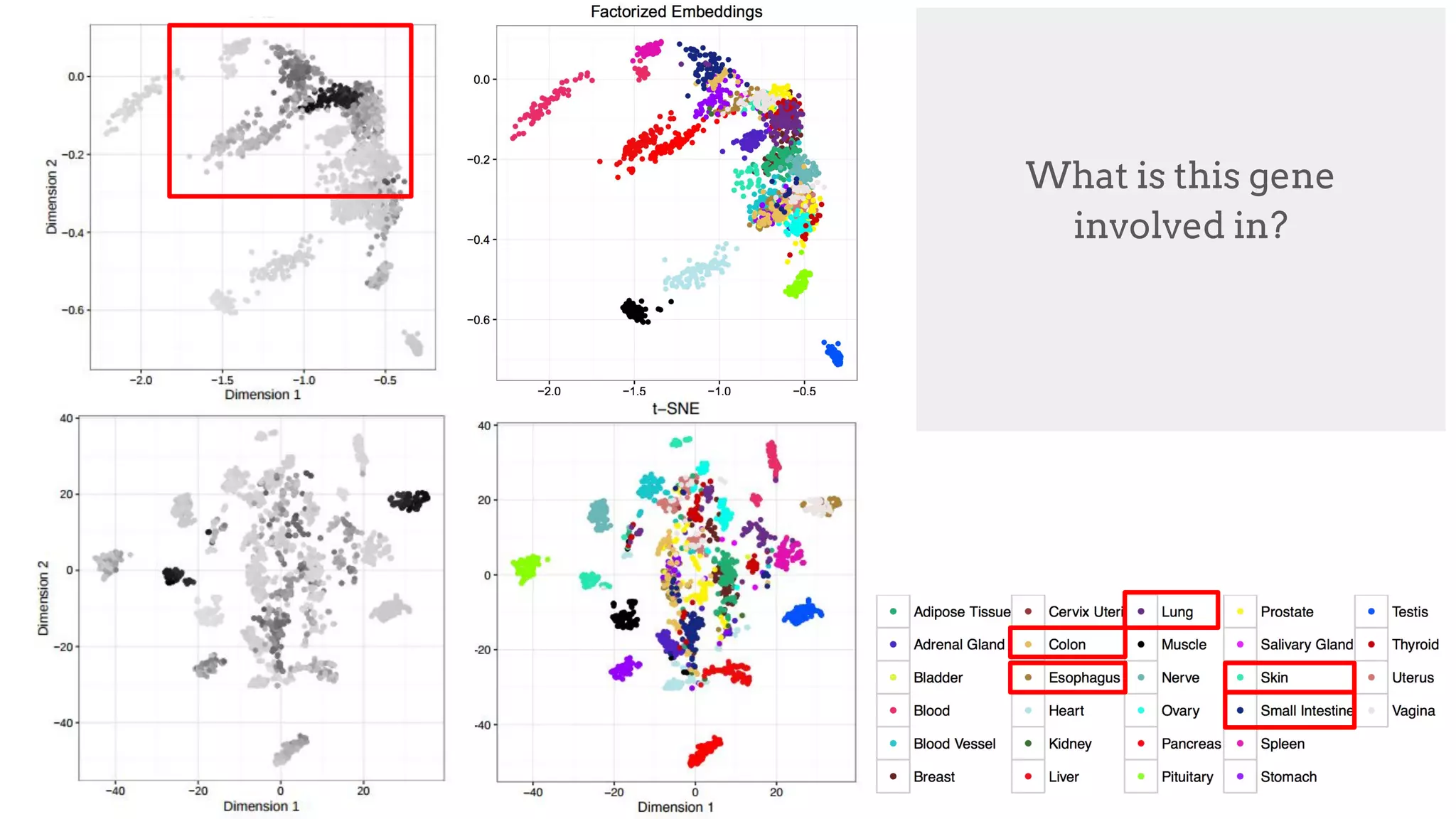
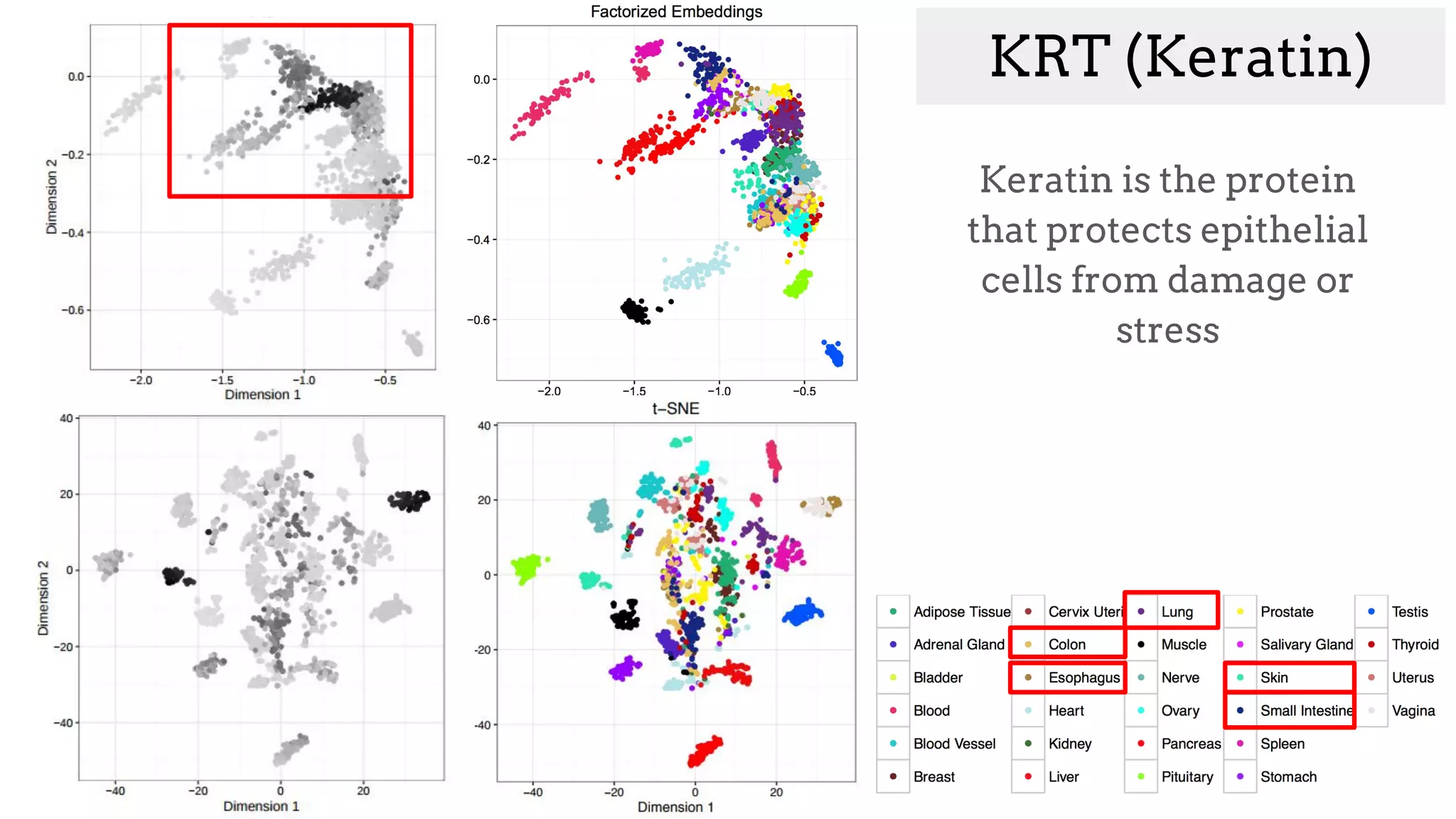
![Gene understanding
How can we represent different tissue types?
[Trofimov et al. ICML WCB 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-53-2048.jpg)
![Factorized Embeddings
Gene expression is predicted given
(Tissue, Gene) pair
Genes condition Tissue Prediction
Tissues condition Gene Prediction
Embedding locations are updated
based on function
[Trofimov et al. ICML WCB 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-54-2048.jpg)
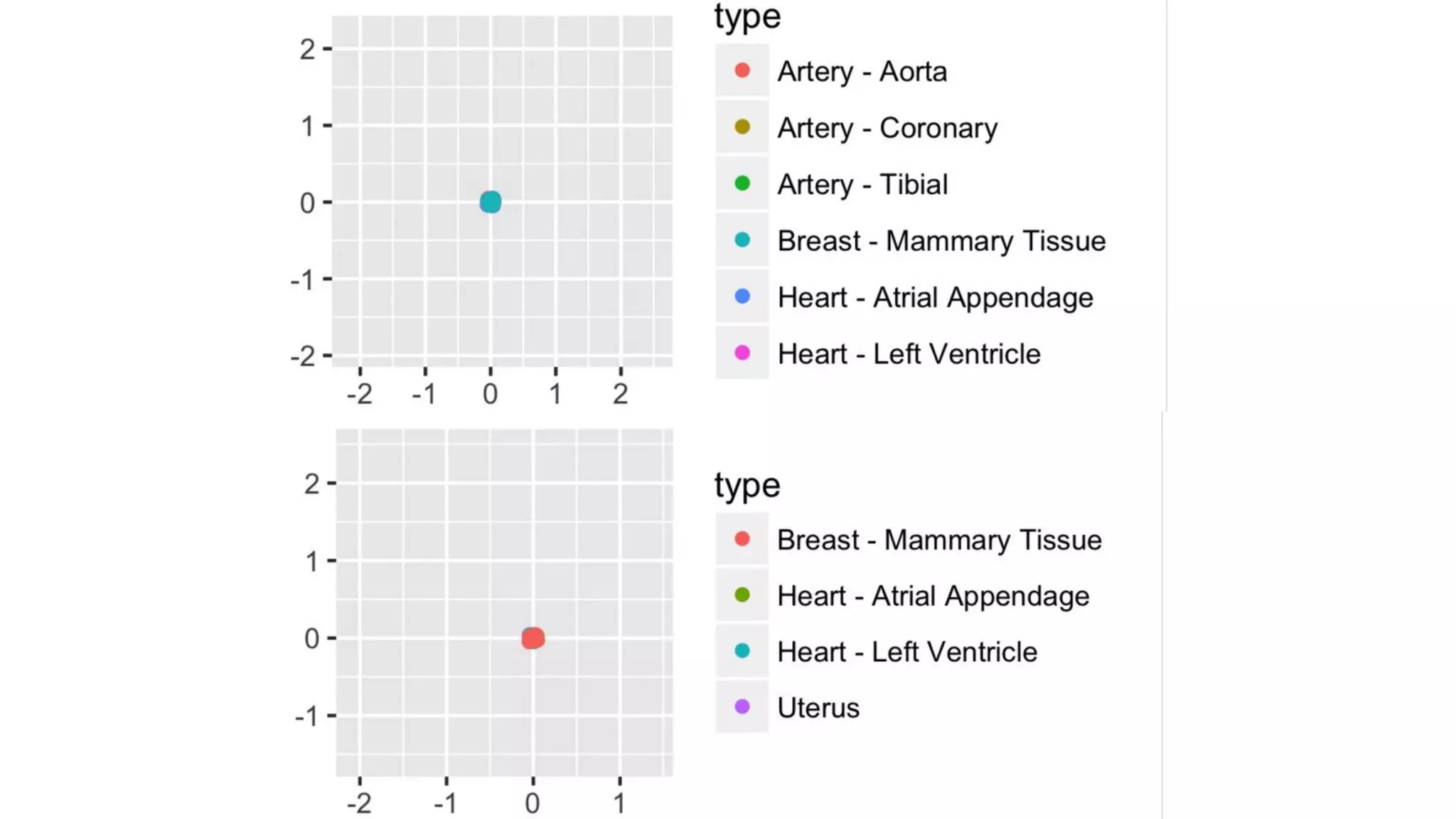
![MYH6
"Muscle contraction"
[uniprot.org]
We can visualize an
expression level for every
tissue embedding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-56-2048.jpg)
![MYH6
"Muscle contraction"
[uniprot.org]
What is this gene
involved in?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-57-2048.jpg)
![MYH6
"Muscle contraction"
[uniprot.org]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asurveyofdeeplearningapproachestomedicalapplications212018-181220165353/75/A-survey-of-deep-learning-approaches-to-medical-applications-58-2048.jpg)