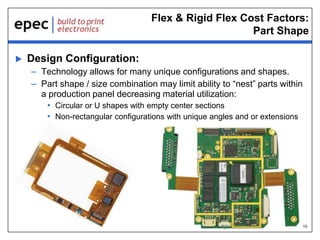
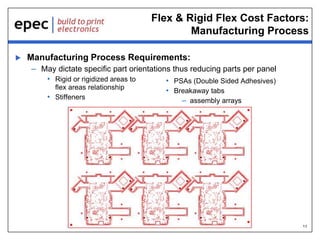
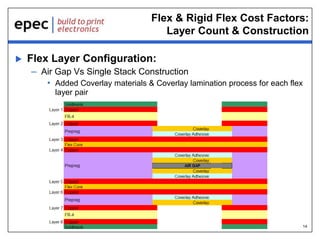
The document discusses the applications and cost drivers of flex and rigid flex PCBs, highlighting their wide use across various industries such as medical, automotive, and military. Key benefits include reduced size and weight, improved reliability, and enhanced functionality compared to alternative solutions. Additionally, it outlines factors affecting cost, including part size, shape, manufacturing processes, and technology requirements.