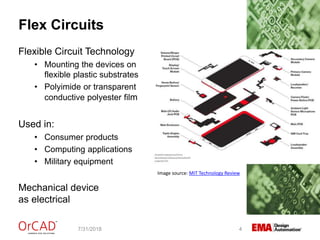
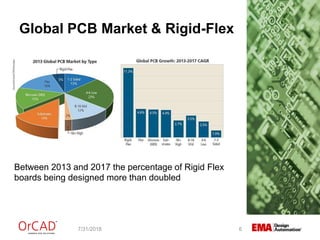
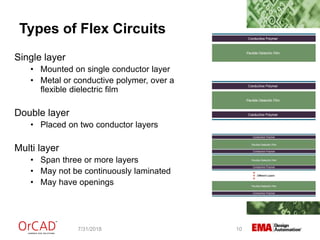
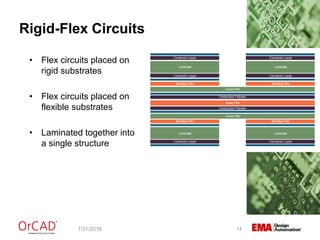
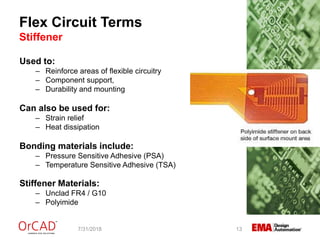
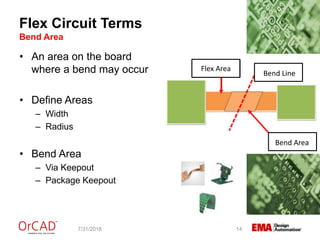
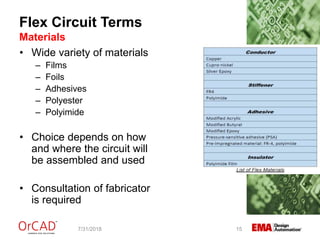
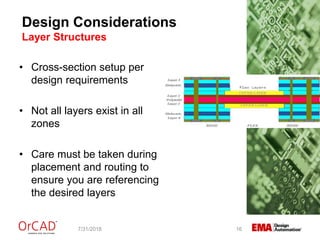
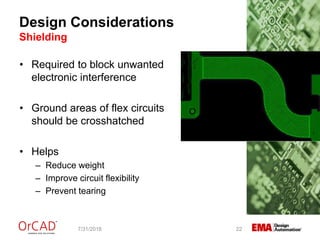
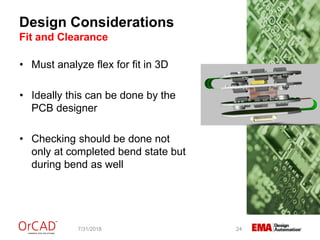
The document outlines a webinar on flexible and rigid-flex circuit technology presented by Janine Flagg from EMA Design Automation, covering design solutions, materials, and manufacturing considerations for flex circuits. It discusses the advantages and challenges of using flexible circuits in various applications, and emphasizes the importance of design considerations such as routing, placement, and communication with manufacturers. The session aims to maximize the benefits of flex in PCB designs for successful implementation.