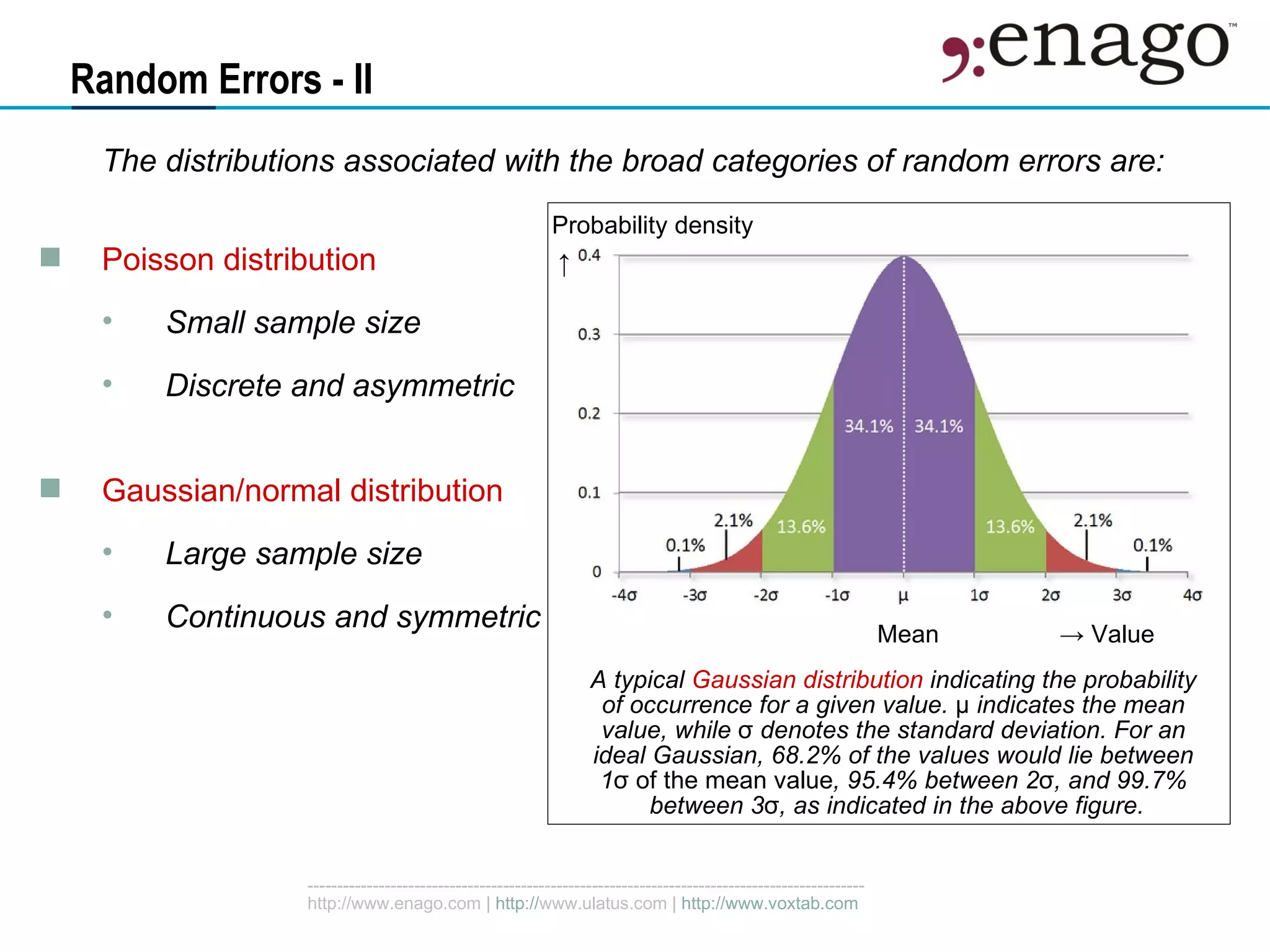
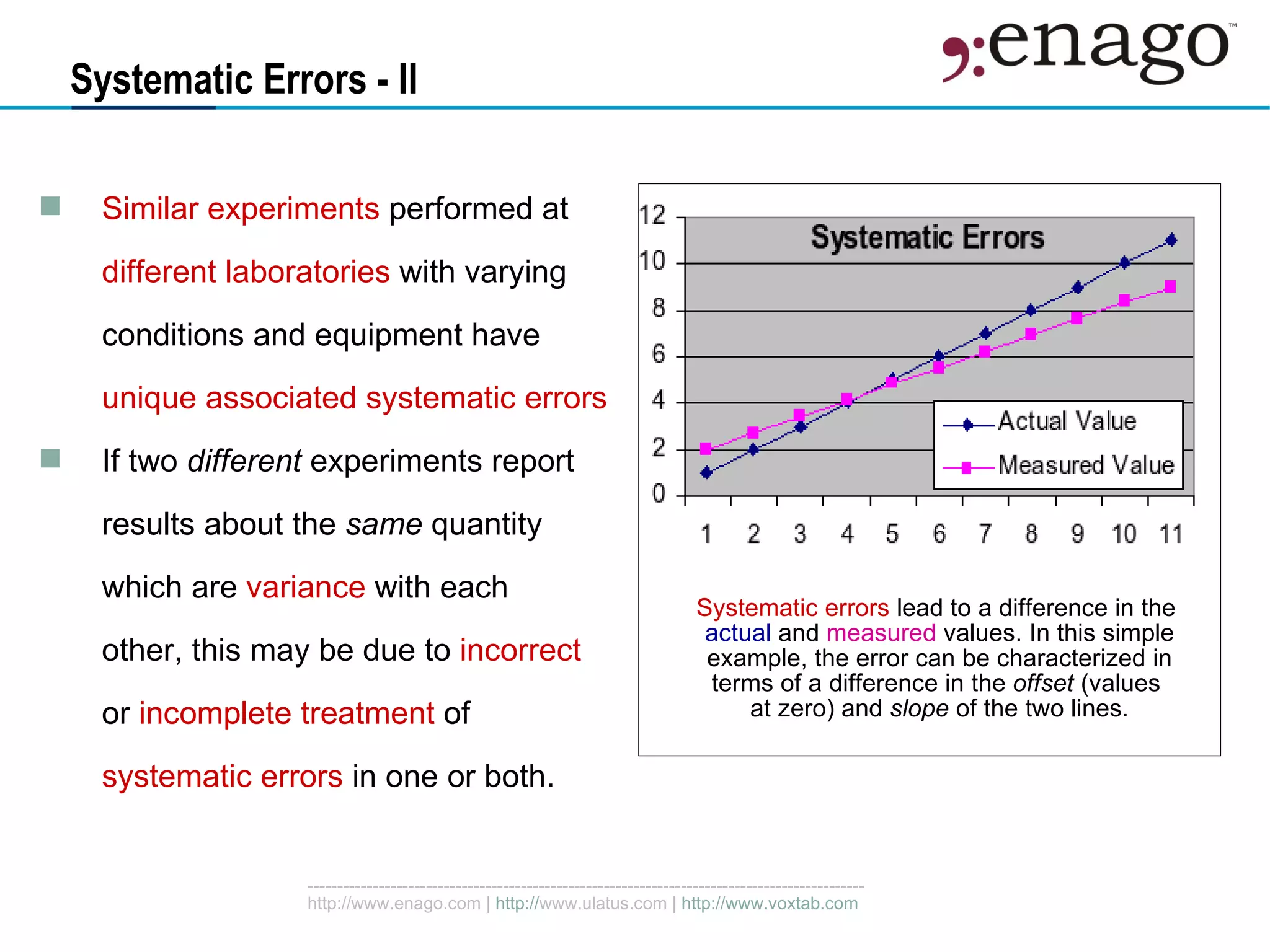
This document discusses sources of error in numerical results, including random errors and systematic errors. Random errors are due to statistical fluctuations and can be characterized by probability distributions like Gaussian. Systematic errors bias results in a predetermined way and are reduced by examining measurement methods. Propagation of errors must account for all sources of random and systematic error to obtain accurate results with appropriate error ranges.