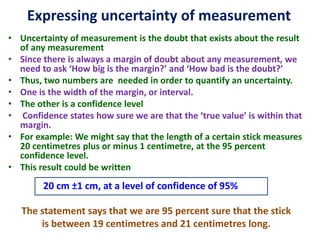
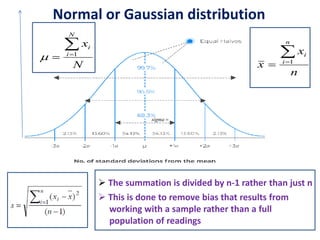
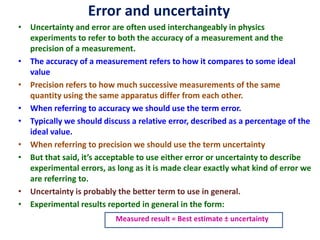
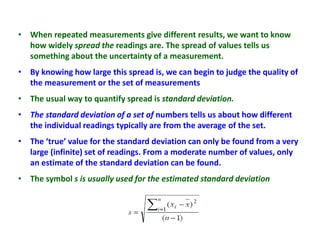
Error is the difference between the measured and true value, while uncertainty quantifies the doubt about a measurement. Uncertainty comes from sources like repeatability, reproducibility, stability, bias, and reference standards. We report uncertainty with measurements using a confidence level to convey the range we believe the true value lies within. Common ways to express uncertainty are ±1 cm at 95% confidence or best estimate ± uncertainty.