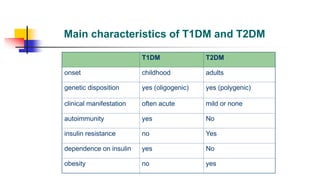
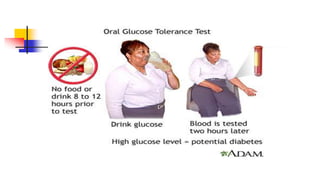
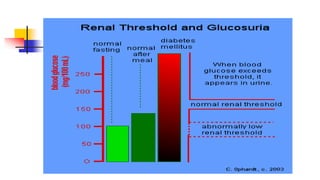
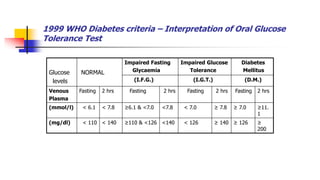
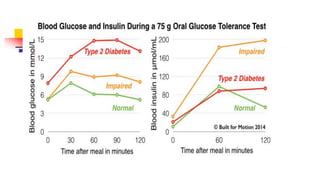
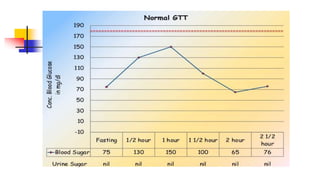
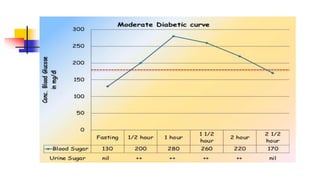
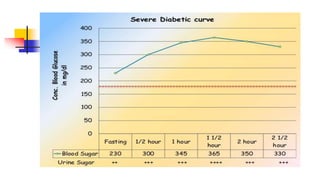
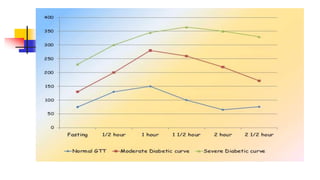
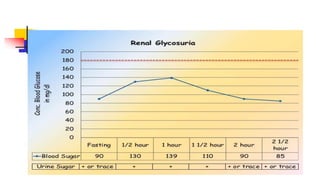
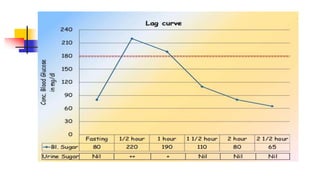
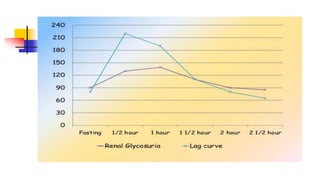
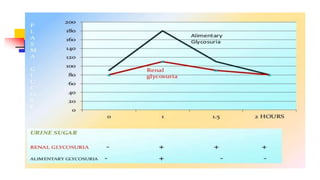
A glucose tolerance test (GTT) checks how the body metabolizes blood sugar levels over time. There are two main types: an oral GTT where glucose is ingested, and an intravenous GTT where glucose is injected. It is commonly used to screen for prediabetes and diabetes, especially in obese, pregnant, or high-risk individuals. The test involves fasting overnight, then drinking a glucose solution and having blood drawn over 3 hours to analyze the body's insulin response and how quickly glucose is cleared from the blood. Results are interpreted according to WHO criteria, with different glucose level thresholds indicating normal, prediabetes, or diabetes status.