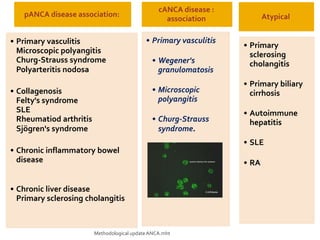
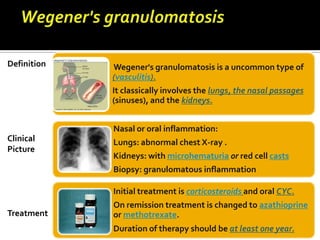
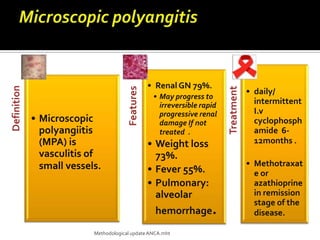
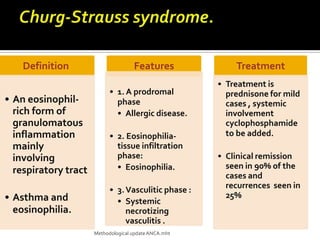
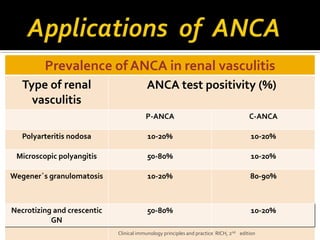
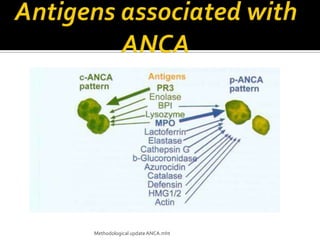
This document discusses antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA). It notes that ANCA are autoantibodies related to inflammatory disorders and were first associated with Wegener's granulomatosis in 1985. The two main ANCA antigens are proteinase 3 and myeloperoxidase. ANCA testing can aid in diagnosing and monitoring ANCA-associated vasculitis conditions. However, increasing ANCA titers do not reliably predict disease relapses.







![ Theory of molecular mimicry. Theory of defective apoptosis.
Superantigens have the ANCA may be developed
power to stimulate a strong either via ineffective
immune response . THEY apoptosis or ineffective
have regions that resemble removal of apoptotic cell
self-antigens – this is the fragments, leading to the
theory of molecular mimicry. exposure of the immune
system to molecules
classical example in post normally sequestered inside
group A streptococcal the cells. This theory solves
rheumatic heart disease, the paradox of how it could
where there is similarity be possible for antibodies to
between M proteins of be raised against the
Streptococcus pyogenes to intracellular antigenic
cardiac myosin and laminin. targets of ANCA.[4]
Methodological update ANCA.mht](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anca-121108113140-phpapp02/85/ANCA-10-320.jpg)